Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2025; 17(7): 105371
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.105371
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.105371
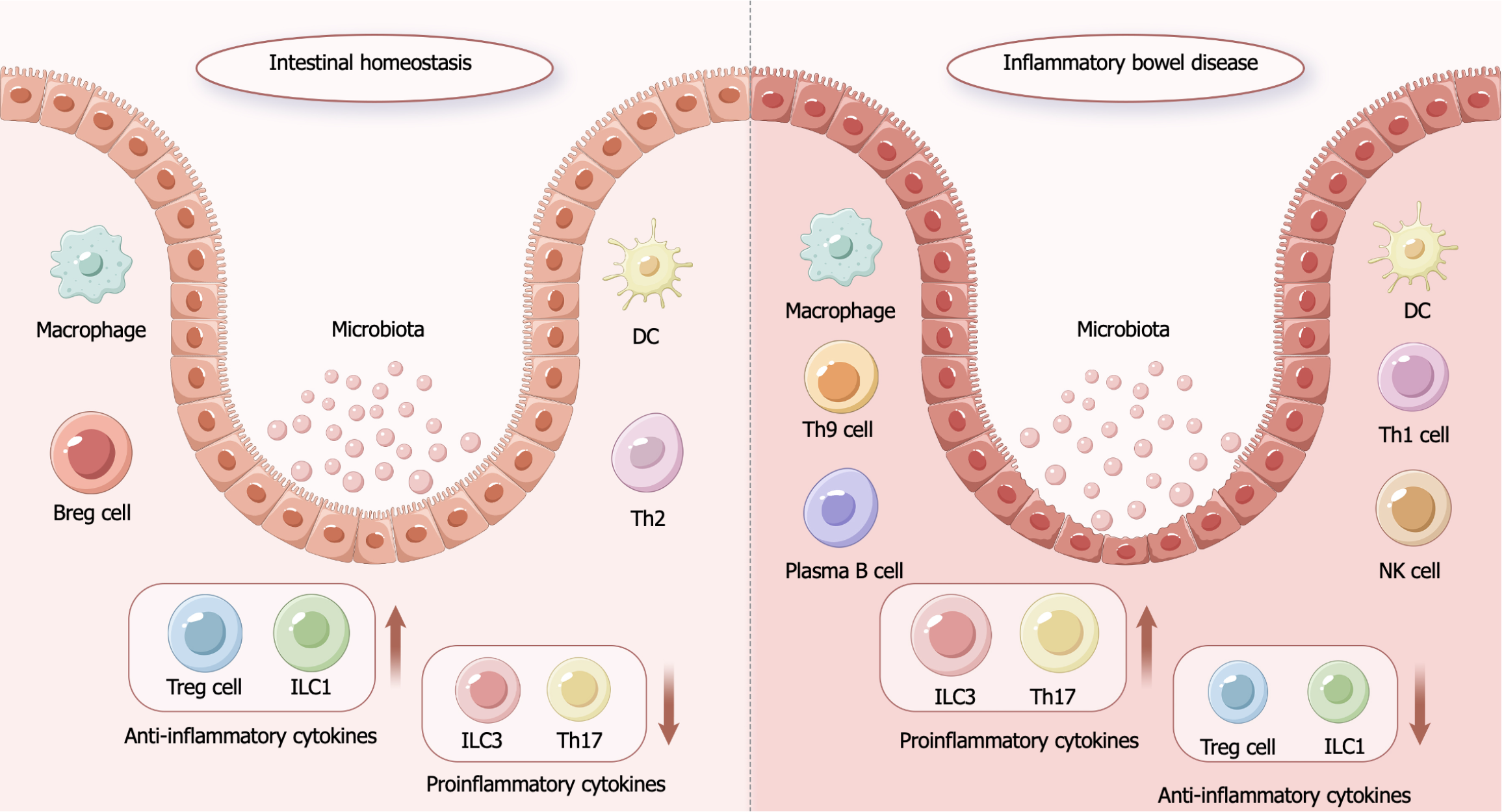
Figure 1 The pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease.
In intestinal homeostasis state, the colonic epithelium is structurally intact, microorganisms are isolated from the intestine by the intestinal barrier, the body’s immune system is in a state of balance and the intestinal microenvironment is in a state of homeostasis. In the state of inflammatory bowel disease, the colonic epithelial structure is disrupted, the intestinal barrier is not functioning, microorganisms in the intestinal tract are exposed underneath the mucous membrane, and the expression of proinflammatory-related factors increases, thereby disrupting the immune balance and the homeostasis of the intestinal microenvironment. DC: Dendritic cell; Breg: Regulatory B cell; Th2: T helper type 2 cell; Treg: Regulatory T cell; ILC1: Type-1 innate lymphoid cell; ILC3: Type-3 innate lymphoid cell; Th17: T helper type 17 cell; Th9: T helper type 9 cell; Th1: T helper type 1 cell; NK: Natural killer.
- Citation: Ma WG, Si YX, Zhang YL, Gao WF, Dong YG, Li YQ, Xu ZF, Xi Q, Li ZZ. Combining acupuncture and mesenchymal stem cell therapy offers promise as a treatment for inflammatory bowel disease. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(7): 105371
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i7/105371.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.105371