Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2025; 17(7): 101929
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.101929
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.101929
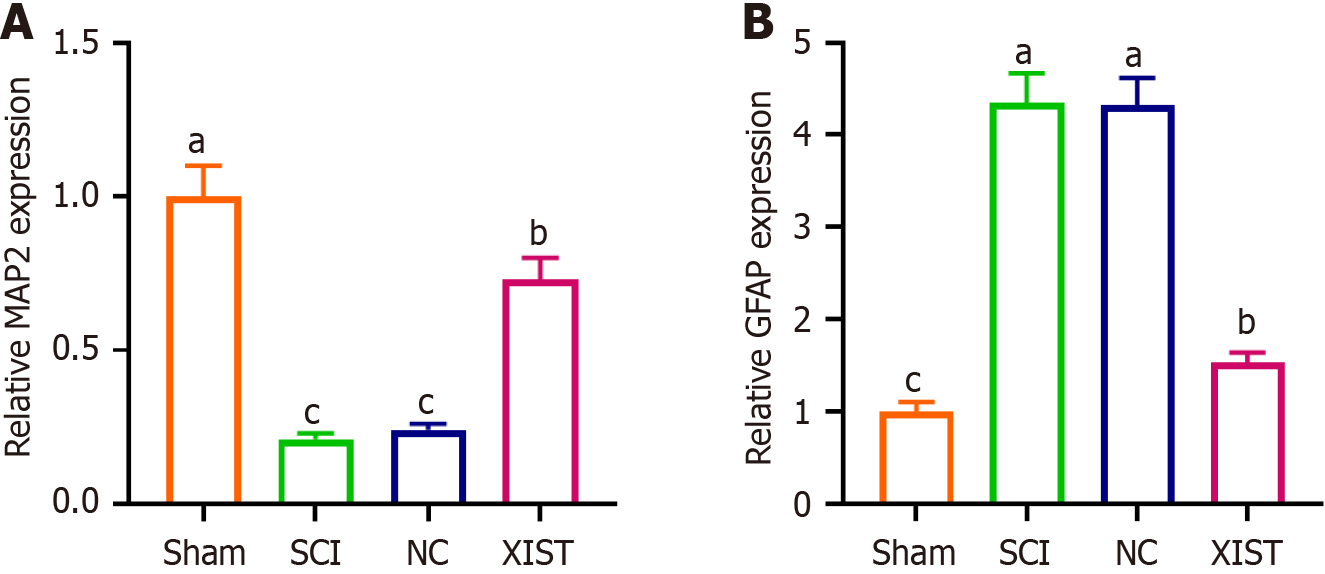
Figure 7 X inactive-specific transcript reverses the effects of spinal cord injury on microtubule-associated protein 2 and glial fibrillary acidic protein expression.
A: Real-time quantitative PCR analysis of microtubule-associated protein 2 expression, showing a significant reduction in the spinal cord injury group and reversal by X inactive-specific transcript treatment; B: Real-time quantitative PCR analysis of glial fibrillary acidic protein expression, showing a significant increase in the spinal cord injury group and reversal by X inactive-specific transcript treatment. Data are presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 indicates sham vs spinal cord injury, bP < 0.05 indicates spinal cord injury vs X inactive-specific transcript, cP < 0.05 indicates negative control vs X inactive-specific transcript. XIST: X inactive-specific transcript; NC: Negative control; SCI: Spinal cord injury; MAP2: Microtubule-associated protein 2; GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein.
- Citation: Zeng SX, Ye JT, Huang SH, Liu RX. X inactive-specific transcript regulates mitochondrial function and neuronal differentiation of stem cells via IGF2BP2/CPT1A axis in models of spinal cord injury. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(7): 101929
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i7/101929.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.101929