Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2025; 17(7): 101929
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.101929
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.101929
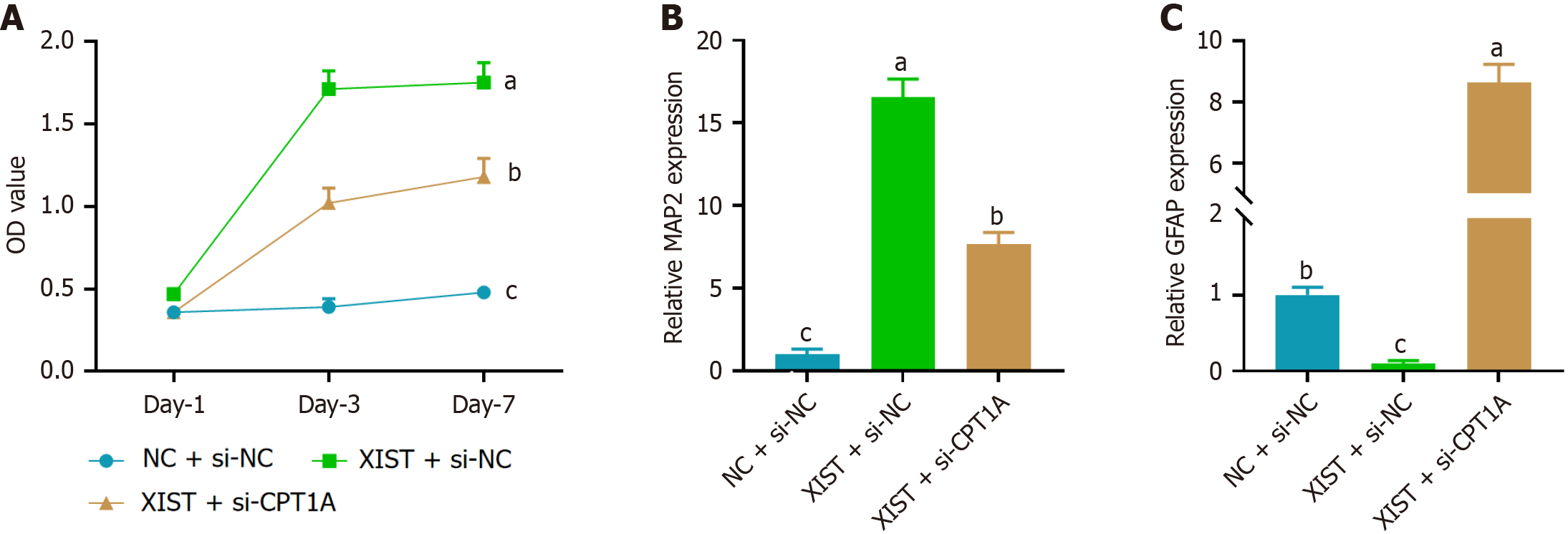
Figure 5 Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A knockdown reversed the effects of X inactive-specific transcript overexpression on neural differentiation in neural stem cells.
A: CCK-8 assay showed that X inactive-specific transcript (XIST) overexpression promoted neural stem cell proliferation, while carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A (CPT1A) knockdown (si-CPT1A) reversed this effect; B: Relative expression of the neuronal marker microtubule-associated protein 2 at day 7, showing that XIST overexpression significantly upregulated microtubule-associated protein 2 expression, an effect reversed by CPT1A knockdown; C: Relative expression of the astrocytic marker glial fibrillary acidic protein at day 7, showing that XIST overexpression downregulated glial fibrillary acidic protein expression, with CPT1A knockdown reversing this effect. Data are presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. XIST: X inactive-specific transcript; NC: Negative control; CPT1A: Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A; MAP2: Microtubule-associated protein 2; GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein.
- Citation: Zeng SX, Ye JT, Huang SH, Liu RX. X inactive-specific transcript regulates mitochondrial function and neuronal differentiation of stem cells via IGF2BP2/CPT1A axis in models of spinal cord injury. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(7): 101929
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i7/101929.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.101929