Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2025; 17(6): 106272
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106272
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106272
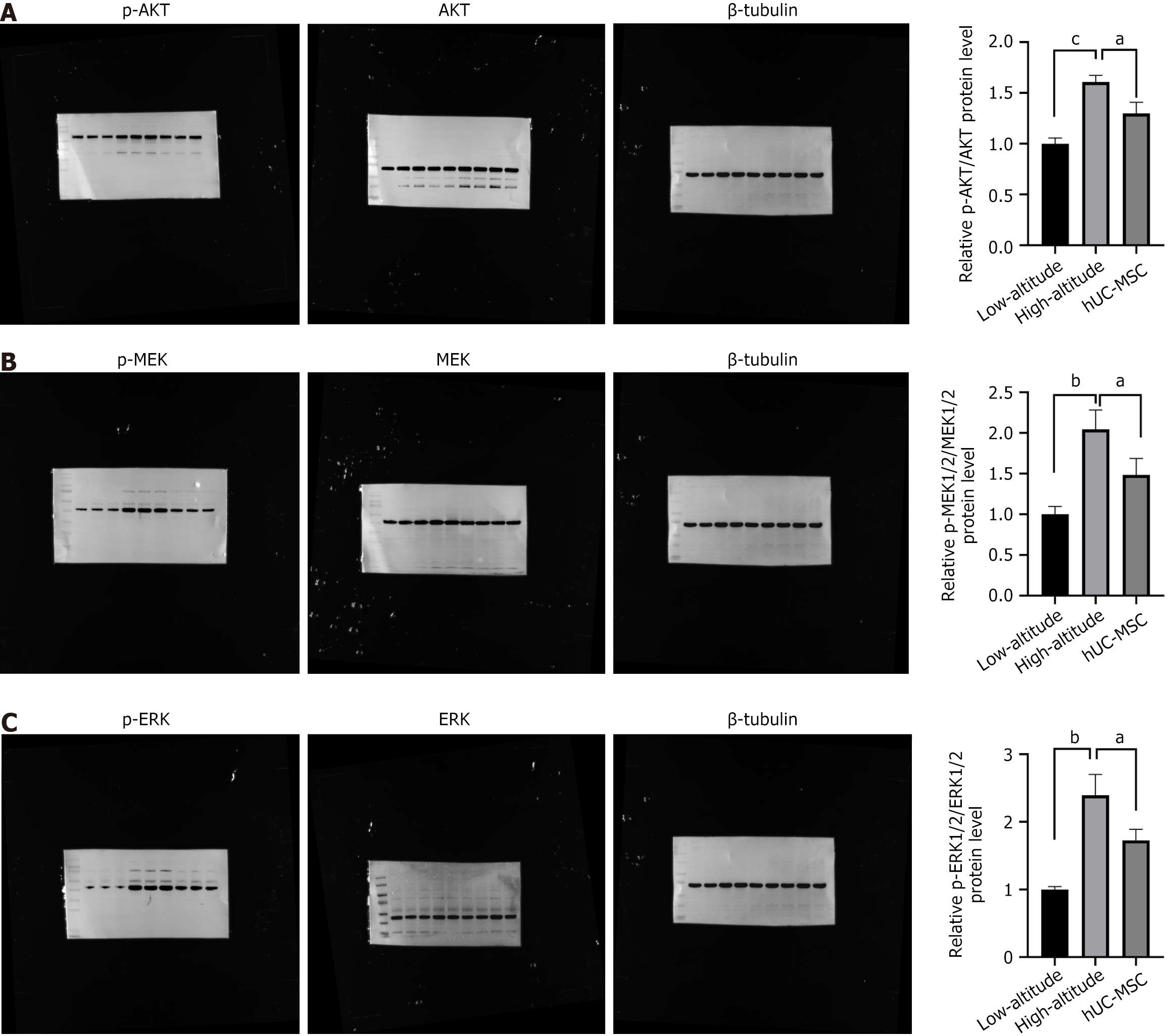
Figure 5 Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce the release of platelet α-granules in rats exposed to acute high-altitude hypoxia via the protein kinase B/mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular-signal regulated kinase pathway.
A: Expression of p-protein kinase B in the different groups; B: Expression of p-mitogen-activated protein kinase in the different groups; C: Expression of p-extracellular-signal regulated kinase in the different groups. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. AKT: Protein kinase B; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK: Extracellular-signal regulated kinase; hUC-MSC: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell.
- Citation: Zhang B, Gao BD, Su Y, Mi WJ, Zeng TX, Ma FF, Ha XQ. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce platelet α-granule release in rats via the AKT/MEK/ERK pathway during acute exposure to high-altitude hypoxia. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(6): 106272
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i6/106272.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106272