Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2025; 17(5): 106150
Published online May 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i5.106150
Published online May 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i5.106150
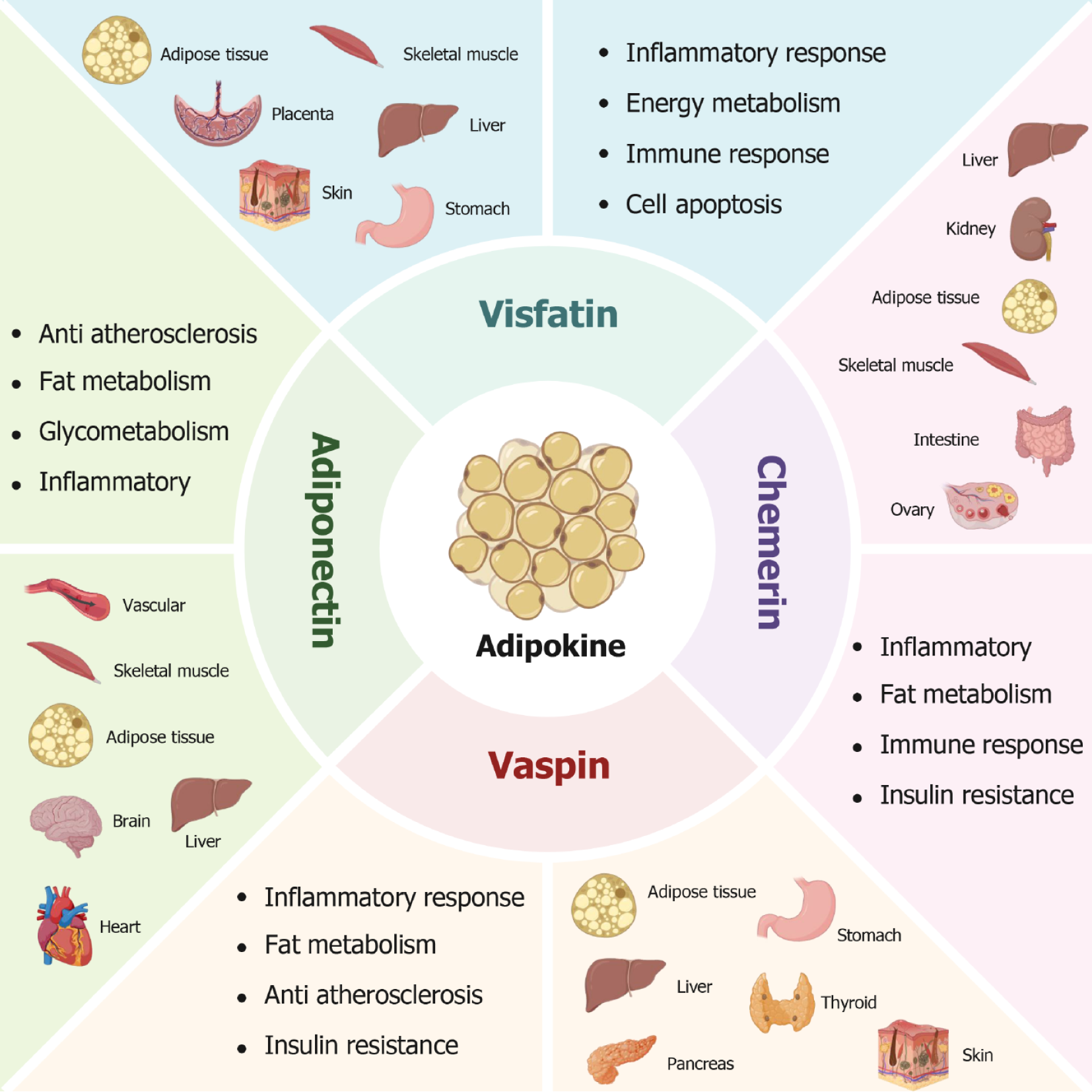
Figure 1 The distribution and biological roles of four adipokines (visfatin, chemerin, vaspin, and adiponectin) in human tissues and organs.
Visfatin primarily comes from visceral adipose tissue, but it is also expressed in placenta, skin, liver, stomach and hypothalamus, and plays an important role in regulating energy metabolism, inflammatory reaction, apoptosis and immune response. Chemerin is mainly secreted by adipocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells and endothelial cells, showing multiple biological effects, such as regulating adipocyte differentiation, participating in immune response, and promoting cholesterol uptake by macrophages. Vaspin is composed of fat, liver, stomach, skin and other organs, which can participate in regulating inflammatory reaction, insulin resistance and adipocyte differentiation and other physiological processes, thus playing an important role in maintaining metabolic homeostasis of the body. Adiponectin is mainly secreted by blood vessels, fat, brain, skeletal muscle and so on to the whole body, which plays a role in lipid metabolism, inflammatory reaction and so on.
- Citation: Wen RM, Wang HX. Effect of adipokines on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell function. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(5): 106150
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i5/106150.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i5.106150