Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2025; 17(5): 103100
Published online May 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i5.103100
Published online May 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i5.103100
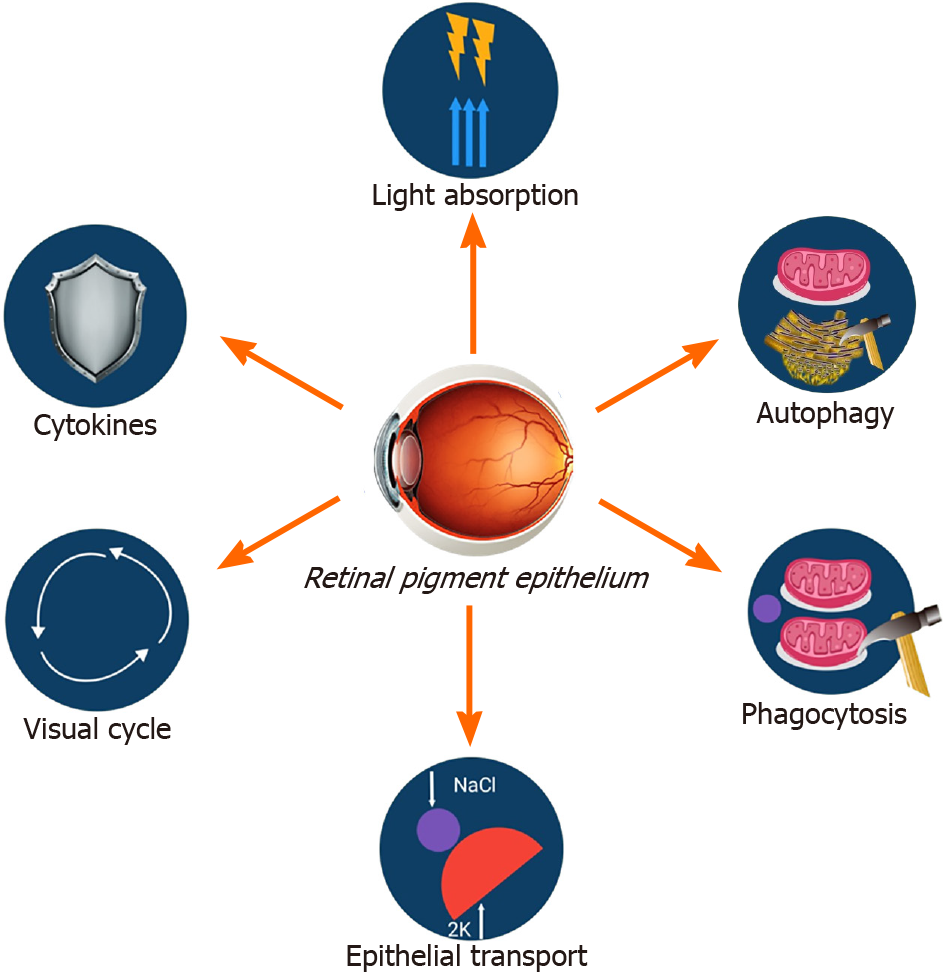
Figure 1 Different aspects involved in retinal pigment epithelium function.
The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is essential to preserve retinal health and visual function. This structure enhances light absorption via melanin granules, thereby mitigating phototoxic damage to photoreceptors. The RPE recycles visual pigments vital for phototransduction. The diagram illustrates photoreceptor outer segment phagocytosis, a process essential for retinal homeostasis and photoreceptor lifetime. Furthermore, RPE-mediated release of growth factors, including vascular endothelial growth factor and pigment epithelium-derived factor, modulates choroidal blood flow and inhibits pathological neovascularization. Specific membrane transporters allow for the movement of nutrients, ions, and waste products between the neural retina and choroid, ensuring optimal metabolic activity. The RPE preserves the outer blood-retinal barrier via tight junctions, safeguarding the retina from systemic variations and immune-mediated harm.
- Citation: Sorrentino FS, Parmeggiani F, Gardini L, Fontana L, Musa M, Gagliano C, Zeppieri M. Stem cell therapy for retinal pigment epithelium disorders. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(5): 103100
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i5/103100.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i5.103100