Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Mar 26, 2025; 17(3): 102088
Published online Mar 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i3.102088
Published online Mar 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i3.102088
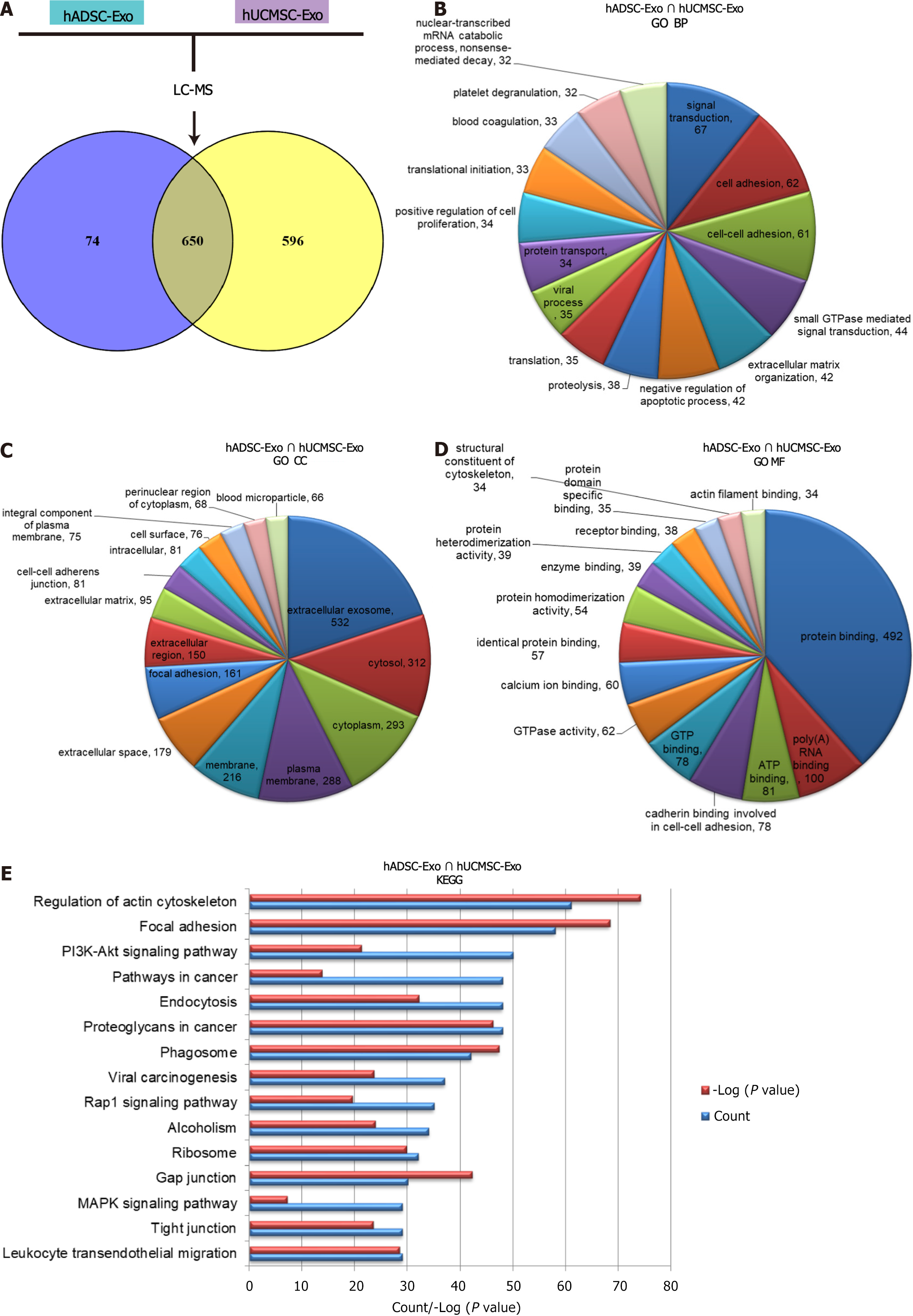
Figure 2 Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry proteome analysis data of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome and human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome.
A: Venn map showing the intersection proteins of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome (hADSC-Exo) and human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome (hUCMSC-Exo); B-D: Gene Ontology analysis of hADSC-Exo and hUCMSC-Exo liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry common proteins. A chart indicates biological process (B), cellular components (C) and molecular function (D); E: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway of hADSC-Exo and hUCMSC-Exo common proteins. hADSC-Exo: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome; hUCMSC-Exo: Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosome; LC-MS: Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry; GO: Gene Ontology; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; BP: Biological process; CC: Cellular component; MF: Molecular function.
- Citation: Fu Y, Han YT, Xie JL, Liu RQ, Zhao B, Zhang XL, Zhang J, Zhang J. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes enhance the development of hair follicle to ameliorate androgenetic alopecia. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(3): 102088
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i3/102088.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i3.102088