Copyright
©©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Stem Cells. Jan 26, 2022; 14(1): 104-116
Published online Jan 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i1.104
Published online Jan 26, 2022. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i1.104
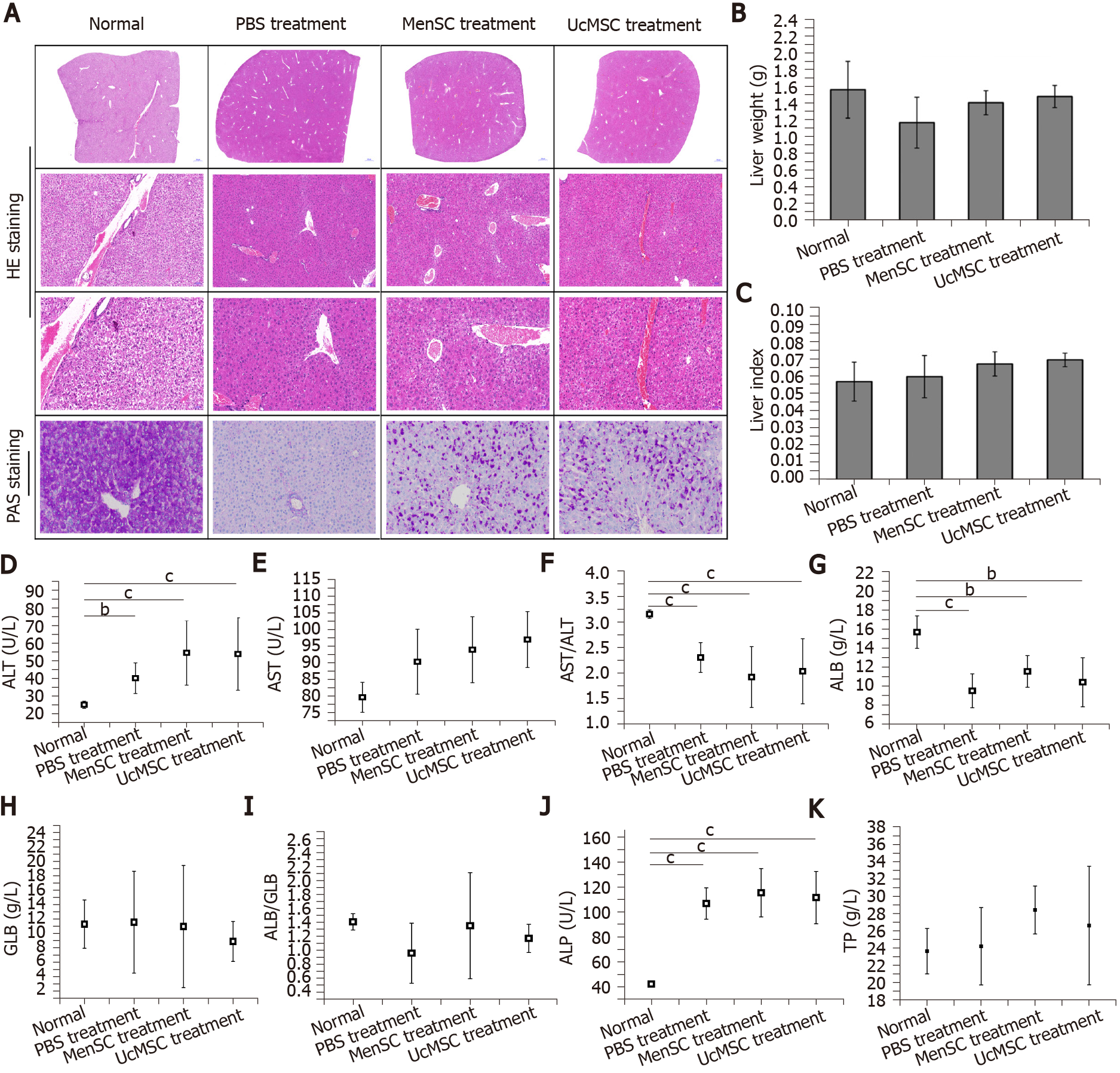
Figure 3 Morphological and functional improvements in the livers of streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes mice after mesenchymal stem cell transplantation.
A: Morphological changes in the livers of mice were examined by hematoxylin and eosin staining (the images in the top row provide a full view of the livers, and the images in the middle row are locally magnified), and the capacity for glycogen synthesis and storage in the livers was determined by Periodic Acid-Schiff staining; B and C: Mesenchymal stem cell treatment had no obvious effect on the liver weights or liver indexes in streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes mice; D-K: The activities of alanine transaminase and aspartic acid transaminase in the mouse serum were examined, and the concentrations of albumin, globulin, total protein, and alkaline phosphatase in the serum were measured. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; UcMSC: Umbilical cord-derived MSC; MenSC: Menstrual blood-derived endometrial stem cells; UA: Uric acid; CRE: Creatinine; HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; PAS: Periodic Acid-Schiff; ALT: Alanine transaminase; AST: Aspartic acid transaminase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; ALB: Albumin; GLB: Globulin; TP: Total protein.
- Citation: Sun YL, Shang LR, Liu RH, Li XY, Zhang SH, Ren YK, Fu K, Cheng HB, Yahaya BH, Liu YL, Lin JT. Therapeutic effects of menstrual blood-derived endometrial stem cells on mouse models of streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes. World J Stem Cells 2022; 14(1): 104-116
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v14/i1/104.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v14.i1.104