Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2021; 13(9): 1293-1306
Published online Sep 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i9.1293
Published online Sep 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i9.1293
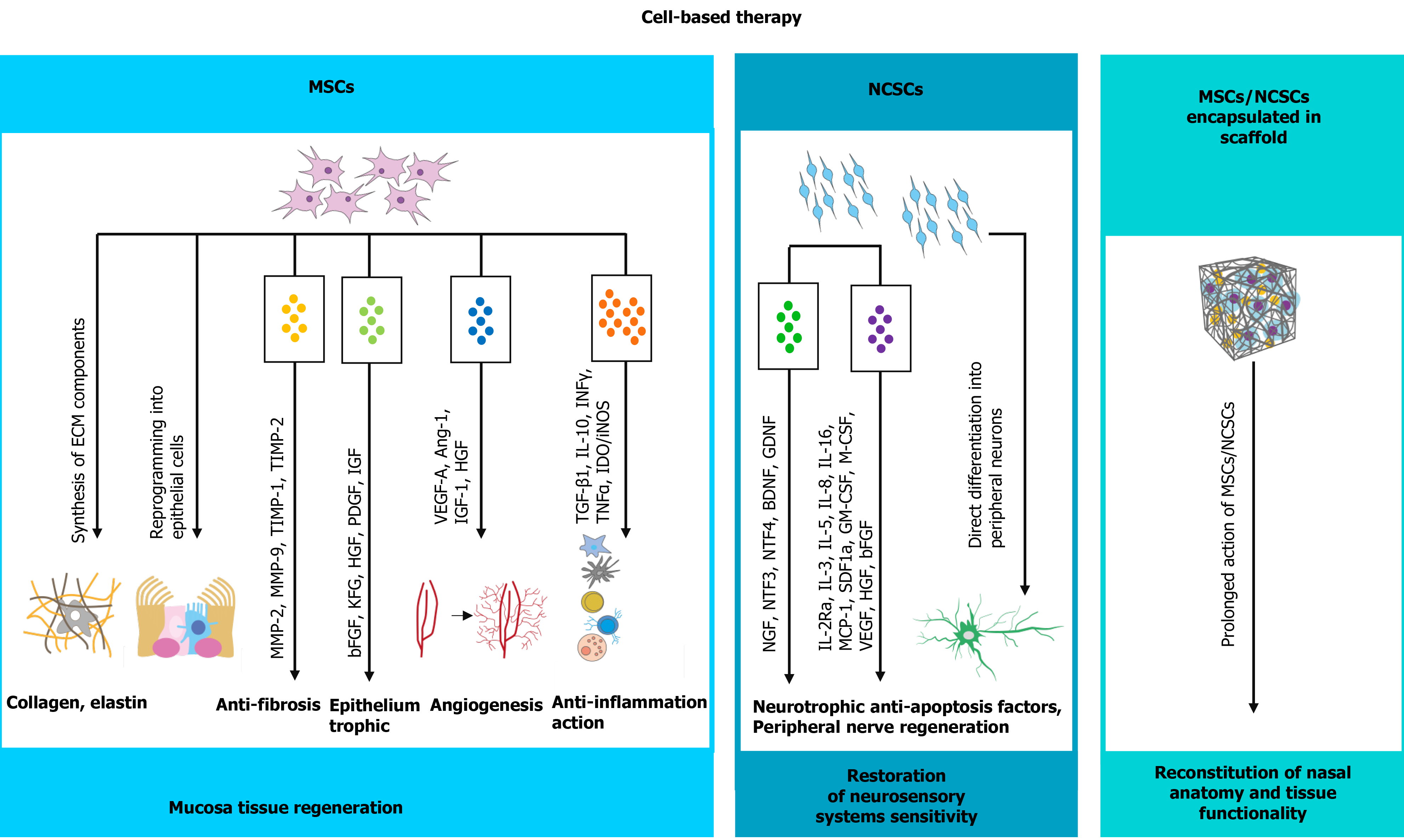
Figure 3 Realization of stem cells therapeutic potential in management of empty nose syndrome (possible mechanisms).
The therapeutic effect of stem cell transplantation could be realized by two main ways. The first one is direct differentiation of transplanted stem cells under the impact of specific environmental factors, such as hypoxia and inflammation. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have the ability to transdifferentiate in mucosa epithelial cells, while neural crest-derived stem cells (NCSCs) can form peripheral neurons. However, very small amount, around 1-3%, of transplanted stem cells can differentiate. The 95% of stem cells therapeutic potential are implemented in indirect way via secreting plethora of paracrine factors and extracellular vesicles. MSCs-derived secretory factors promote neovascularization, immunomodulatory anti-inflammatory effect, anti-apoptotic and anti-fibrotic effect, and reduce oxidative stress that create favorable environment for mucosa regeneration. NCSCs, in particular, have strong neuroprotective properties, thus local NCSCs injection in empty nose syndrome patients could also stimulate nerve recovery by trophic support or direct reintegration in damaged tissue. MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; NCSCs: Neural crest-derived stem cells.
- Citation: Gordiienko IM, Gubar OS, Sulik R, Kunakh T, Zlatskiy I, Zlatska A. Empty nose syndrome pathogenesis and cell-based biotechnology products as a new option for treatment. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(9): 1293-1306
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i9/1293.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i9.1293