Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Mar 26, 2021; 13(3): 221-235
Published online Mar 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i3.221
Published online Mar 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i3.221
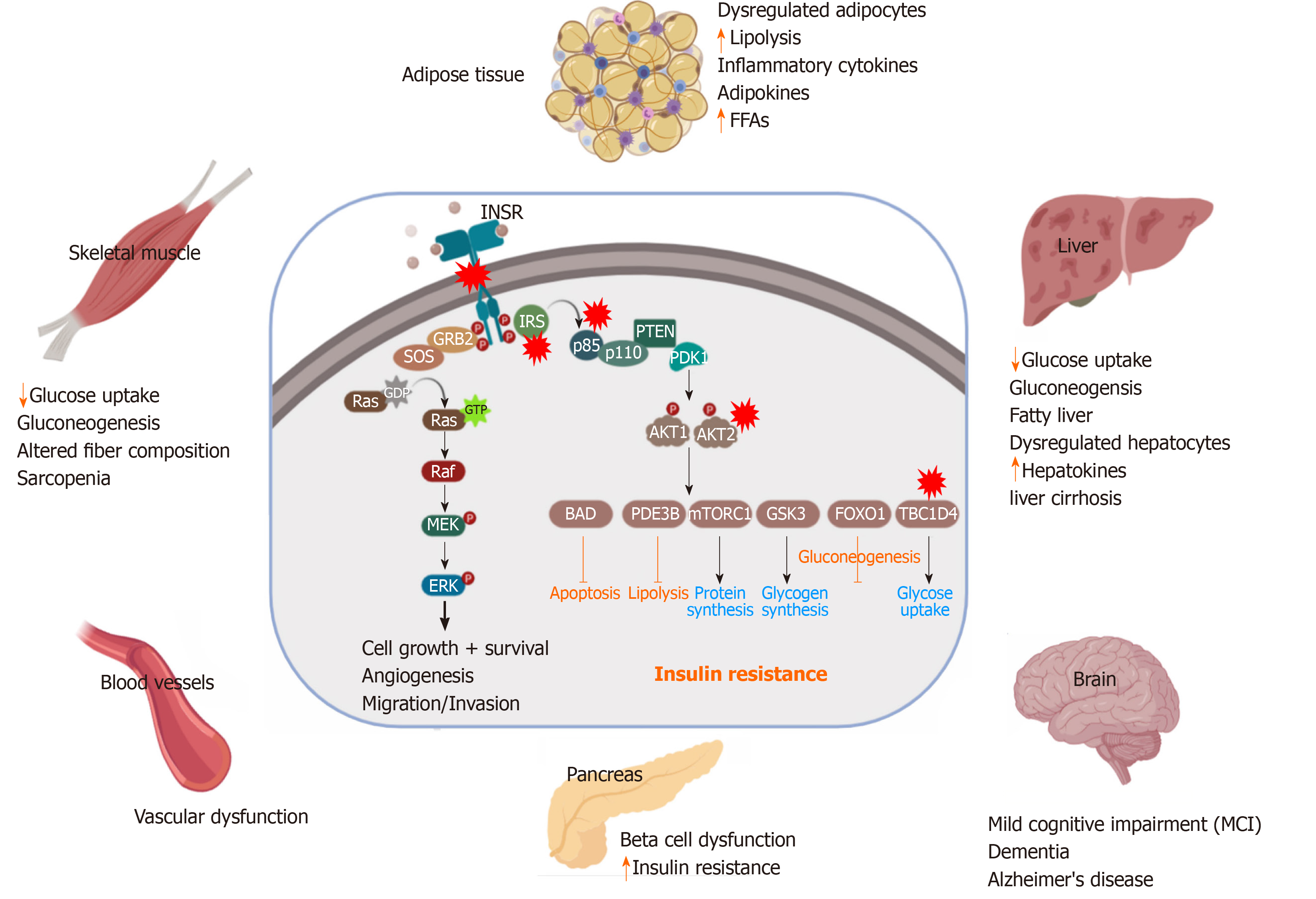
Figure 2 Pathological effect and consequence of insulin resistance.
Genetic alterations and mutations in the insulin signaling pathway can lead to insulin resistance (IR) in the insulin-target tissues. The red stars indicate the reported genetically defective molecules, such as insulin receptor, insulin receptor substrates, p85, AKT and TBC1D4. In response to IR, the insulin target tissues (adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, liver, pancreas, brain and blood vessels) show activation of the catabolic processes and accumulation of toxic metabolic byproducts and the inflammatory cytokines, leading to pancreatic β-cell dysfunction and other metabolic disorders. INSR: Insulin receptor; IRS: Insulin receptor substrate; PDK1: Phosphatidylinositide dependent protein kinase 1; GSK3: Glycogen synthase kinase 3; FoxO: Forkhead box O; mTORC: mTOR complex; GTP: Guanosine triphosphate; FFAs: Free fatty acids.
- Citation: Elsayed AK, Vimalraj S, Nandakumar M, Abdelalim EM. Insulin resistance in diabetes: The promise of using induced pluripotent stem cell technology. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(3): 221-235
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i3/221.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i3.221