Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2020; 12(7): 633-658
Published online Jul 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i7.633
Published online Jul 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i7.633
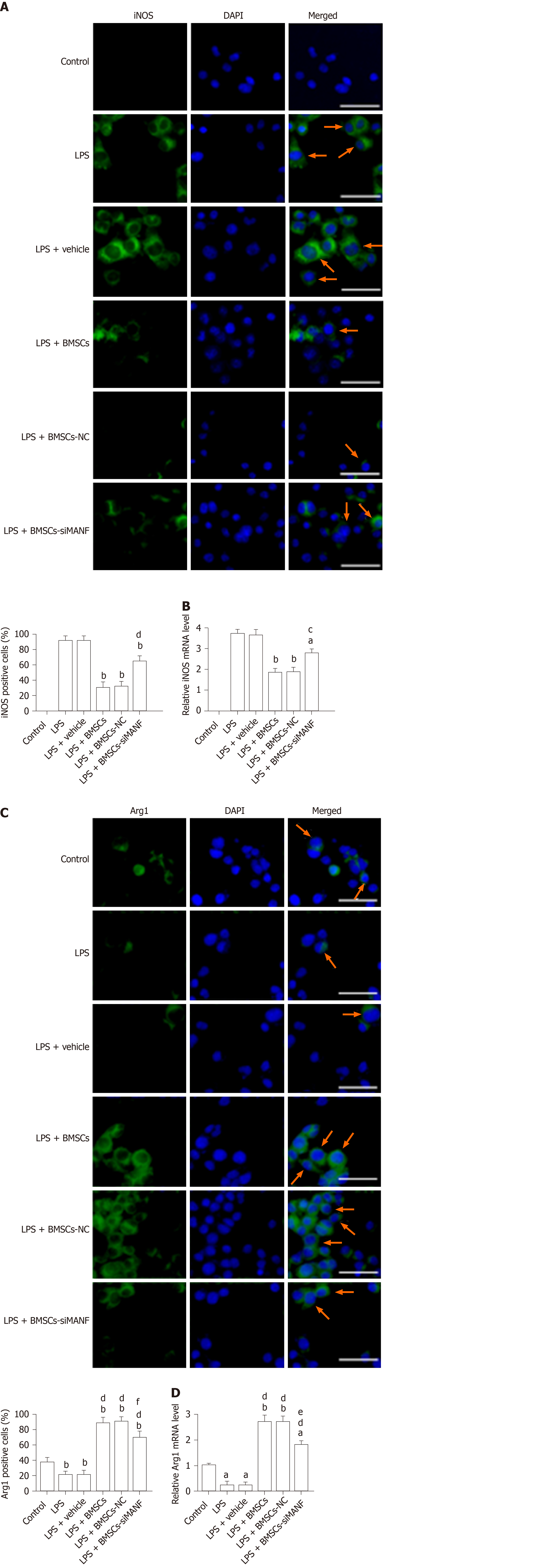
Figure 7 In vitro analysis of M1 and M2 polarization markers following exposure to lipopolysaccharide and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.
A and B: Immunocytochemistry (A) and qRT-PCR analysis (B) of iNOS expression in microglia. Representative images of immunofluorescence staining for iNOS (green), with DAPI (blue) as a nuclear counterstain, are shown. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs LPS and LPS + vehicle groups; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs LPS + BMSCs and LPS+BMSCs-NC groups. Scale bar = 50 μm. Arrows point to the iNOS+ cells; C and D: Immunocytochemistry (C) and qRT-PCR analysis (D) of Arg1 expression in LPS-stimulated microglia in the presence or absence of BMSCs. Representative images of immunofluorescence staining for Arg1 (green), with DAPI (blue) as a nuclear counterstain, are shown. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, vs Control group; dP < 0.001 vs LPS and LPS + vehicle groups; eP < 0.05, fP < 0.01 vs LPS + BMSCs and LPS+BMSCs-NC groups. Scale bar = 50 μm. Arrows point to the Arg1+ cells. The values are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 6). LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; BMSCs: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; BMSCs-NC: Negative control-transfected BMSCs; BMSCs-siMANF: MANF siRNA-transfected BMSCs; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; Arg-1: Arginase-1; DAPI: 4'6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
- Citation: Yang F, Li WB, Qu YW, Gao JX, Tang YS, Wang DJ, Pan YJ. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induce M2 microglia polarization through PDGF-AA/MANF signaling. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(7): 633-658
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i7/633.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i7.633