Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Mar 26, 2020; 12(3): 203-221
Published online Mar 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i3.203
Published online Mar 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i3.203
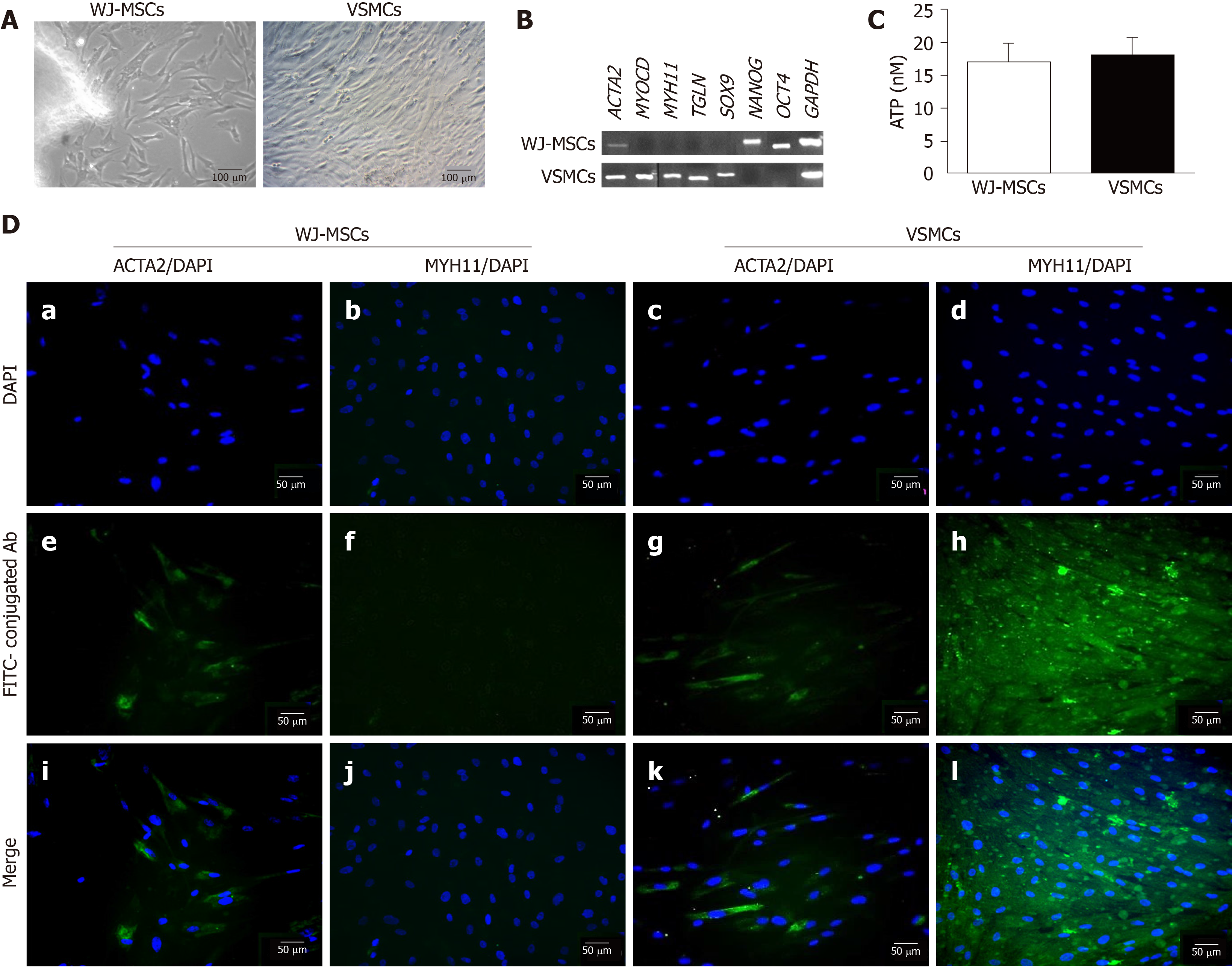
Figure 2 Differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from the Wharton’s Jelly tissue into vascular smooth muscle cells.
A: Morphological features of untreated mesenchymal stromal cells derived from the Wharton’s Jelly tissue (WJ-MSCs) and differentiated vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs); B: Polymerase chain reaction results regarding the expression of VSMC-specific genes, such as ACTA2, MYOCD, MYH11 and TGLN, and pluripotency-related genes, including NANOG and OCT4 in untreated WJ-MSCs and differentiated VSMCs. GAPDH was the desired house-keeping gene for current analysis; C: Determination of WJ-MSC and VSMC proliferation by performing the ATP assay; Indirect immunofluorescence against the early VSMC marker ACTA2 and late VSMC marker MYH11 in untreated WJ-MSCs (D-a, D-e, D-i and D-b, D-f, D-j) and differentiated VSMCs (D-c, D-g, D-k and D-d, D-h, D-l) in combination with DAPI, respectively. Images A-a and A-b were presented with 10× original magnification and 100 μm scale bars. Images D-a to D-l were presented with 20× original magnification and 50 μm scale bars. WJ-MSCs: Mesenchymal stromal cells derived from the Wharton’s Jelly tissue; VSMCs: Vascular smooth muscle cells.
- Citation: Mallis P, Papapanagiotou A, Katsimpoulas M, Kostakis A, Siasos G, Kassi E, Stavropoulos-Giokas C, Michalopoulos E. Efficient differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells from Wharton’s Jelly mesenchymal stromal cells using human platelet lysate: A potential cell source for small blood vessel engineering. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(3): 203-221
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i3/203.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i3.203