Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Mar 26, 2020; 12(3): 203-221
Published online Mar 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i3.203
Published online Mar 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i3.203
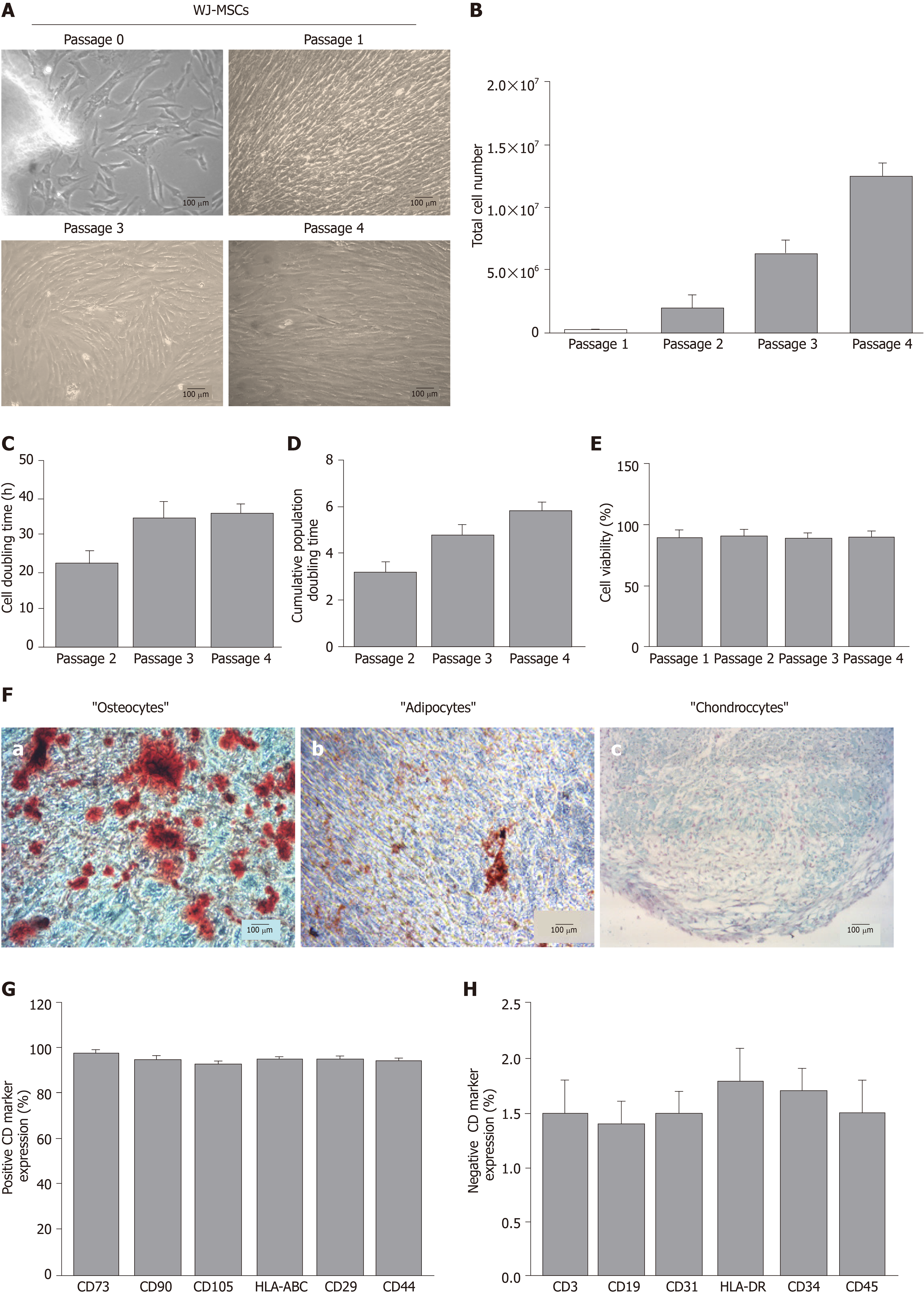
Figure 1 Evaluation of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from the Wharton’s Jelly.
A: Morphological features of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from the Wharton’s Jelly tissue (WJ-MSCs) from P0 to P4 (A-a to A-d); B-F: Determination of total cell number (B), cell doubling time (C), cumulative PD (D) and cell viability (E) of WJ-MSCs from P0 to P4. Evaluation of tri-lineage differentiation capability of WJ-MSCs into “osteocytes” (F-a), “adipocytes” (F-b) and “chondrocytes” (F-c) as indicated by Alizarin Red-S, Oil-Red-O and Alcian blue, respectively. G, H: Positive (G) and negative (H) expression of CD markers in WJ-MSCs based on flow cytometric analysis. Images A-a to A-d and F-a to F-c were obtained with original magnification 10× and 100 μm scale bars. WJ-MSCs: Mesenchymal stromal cells derived from the Wharton’s Jelly tissue.
- Citation: Mallis P, Papapanagiotou A, Katsimpoulas M, Kostakis A, Siasos G, Kassi E, Stavropoulos-Giokas C, Michalopoulos E. Efficient differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells from Wharton’s Jelly mesenchymal stromal cells using human platelet lysate: A potential cell source for small blood vessel engineering. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(3): 203-221
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i3/203.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i3.203