Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2020; 12(12): 1553-1575
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1553
Published online Dec 26, 2020. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1553
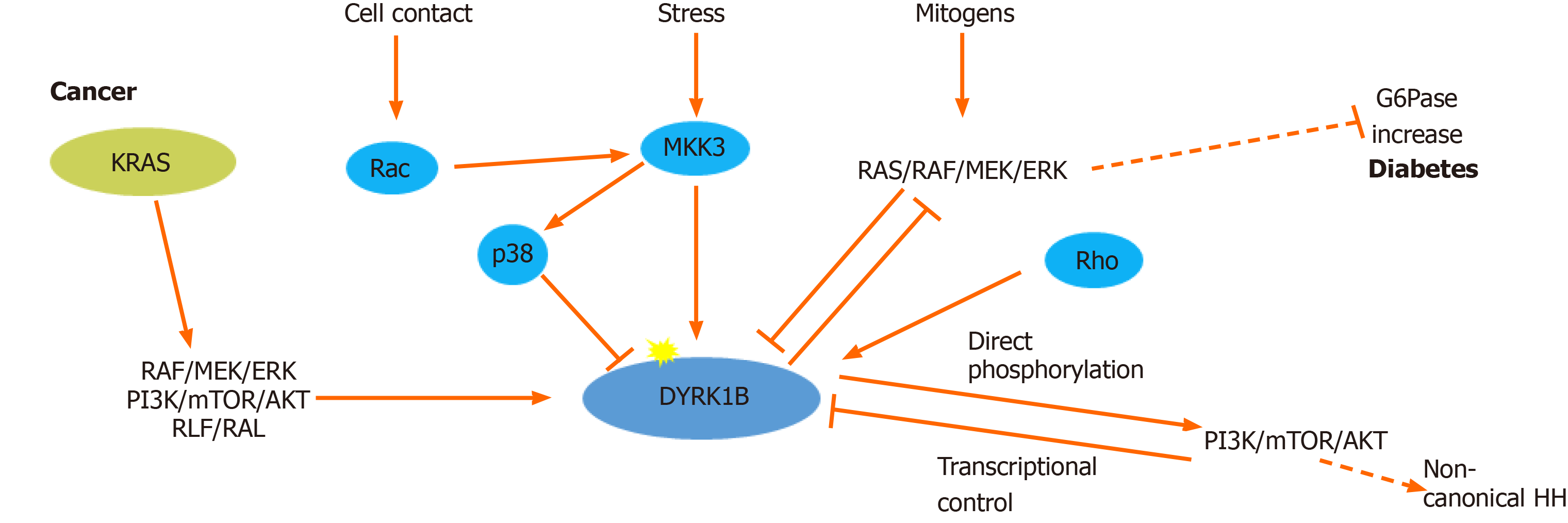
Figure 1 Regulation of dual-specificity tyrosine-regulated kinase 1B expression and activity.
Dual-specificity tyrosine-regulated kinase 1B (DYRK1B) expression and activity is regulated at transcriptional, translational and post-translational level. Rho GTPases (RhoA, Cdc42 and Rac1) promote transcriptional up-regulation of DYRK1B, while serum mitogens down-regulate DYRK1B through RAS/RAF/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) signaling pathway. Under stress conditions, MKK3 activates DYRK1B and p38, while DYRK1B is physically sequestered and inhibited by p38. In cancer, DYRK1B is involved in a complex crosstalk with hedgehog (HH). Oncogenic mutant RAS (KRAS) initiates the non-canonical HH pathway through the activation of DYRK1B, via an unknown mechanism, employing several RAS effectors, such as: RAF/MEK/ERK, PI3K/AKT and RLF/RAL. DYRK1B enhances non-canonical HH signaling by promoting PI3K/mTOR/AKT signaling. Conversely, activated AKT directly inhibits expression of DYRK1B. In metabolic syndrome, which is accompanied by diabetes, DYRK1B is implicated in glucose homeostasis, promoting the expression of the key gluconeogenic enzyme glucose-6-phosphatase (G6pase), through inhibition of the RAS–RAF–MEK pathway. Dashed lines represent indirect mechanisms and yellow stars represent phosphorylations. ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinases.
- Citation: Kokkorakis N, Gaitanou M. Minibrain-related kinase/dual-specificity tyrosine-regulated kinase 1B implication in stem/cancer stem cells biology. World J Stem Cells 2020; 12(12): 1553-1575
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v12/i12/1553.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1553