Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2019; 11(12): 1045-1064
Published online Dec 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i12.1045
Published online Dec 26, 2019. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i12.1045
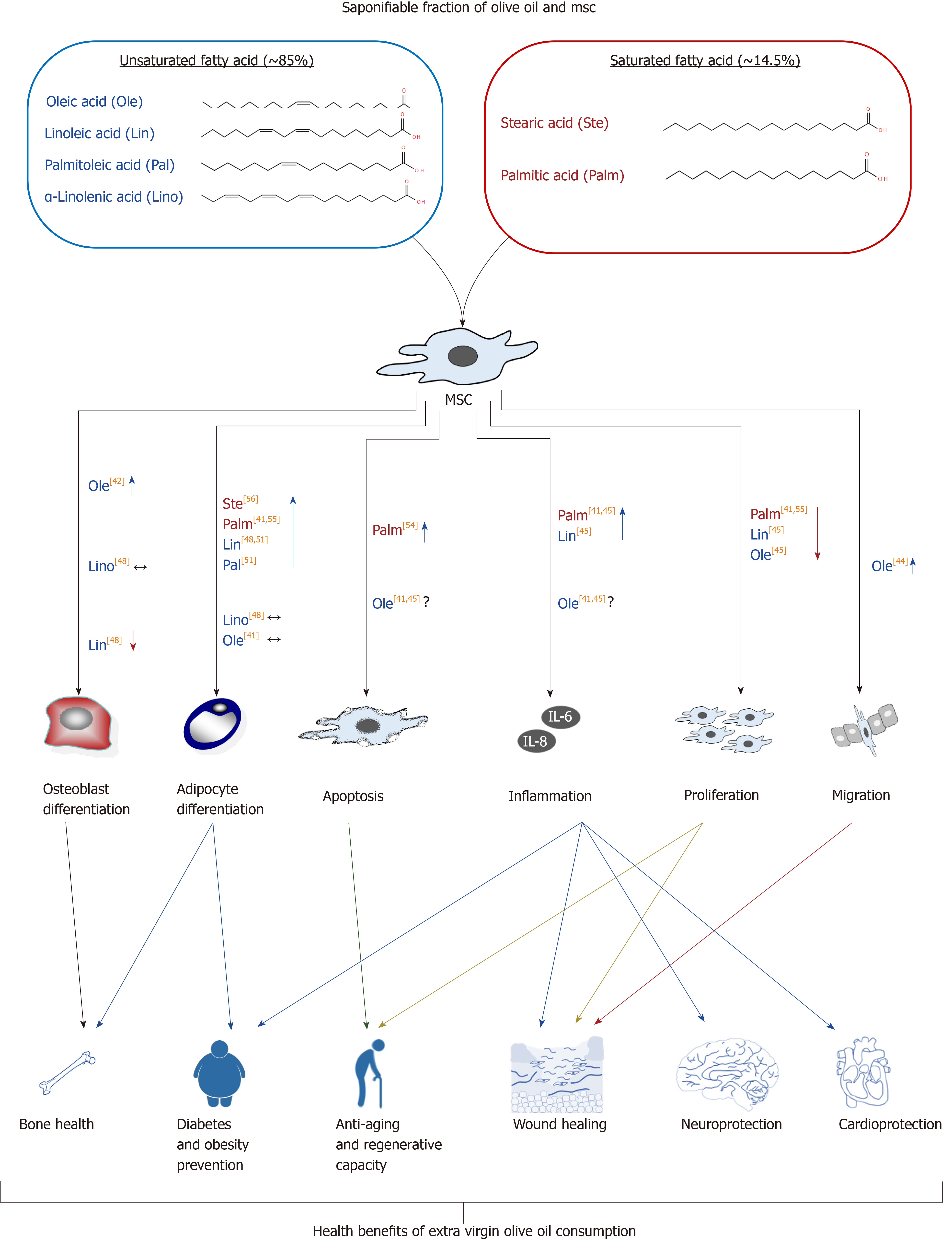
Figure 2 Effects of saponifiable fraction of olive oil on mesenchymal stem cells.
Unsaturated fatty acid residues present in olive oil have effects on several biological activities of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), including differentiation, proliferation, inflammation, migration, and apoptosis, among others. Such effects can be related to different aspects of human health, being modulated by olive oil consumption. They include better bone health, less incidence of diabetes and obesity, and better regenerative, neurological and cardiovascular capacities, among others. Several residues of fatty acids studied (other than oleic acid) may increase adipogenesis and inflammation, inhibiting MSC proliferation. Fortunately, oleic acid accounts for the highest percentage (55% to 83%) of total fatty acid residues of olive oil. Therefore, its positive effects prevail after olive oil intake. Among others, they include increase of osteoblastogenesis and MSC migration, not affecting adipogenesis, apoptosis or inflammatory status. Symbols: ↑ and ↓ represent increase or reduction of effect, respectively, due to involved fatty acid residues; The ↔ indicates that the studies carried out so far have not found significant effects on the evaluated parameter; The ? indicates contradictory data. The numbers in square brackets indicate the bibliographical references. MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells.
- Citation: Casado-Díaz A, Dorado G, Quesada-Gómez JM. Influence of olive oil and its components on mesenchymal stem cell biology. World J Stem Cells 2019; 11(12): 1045-1064
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v11/i12/1045.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v11.i12.1045