Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2023; 15(10): 960-978
Published online Oct 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i10.960
Published online Oct 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i10.960
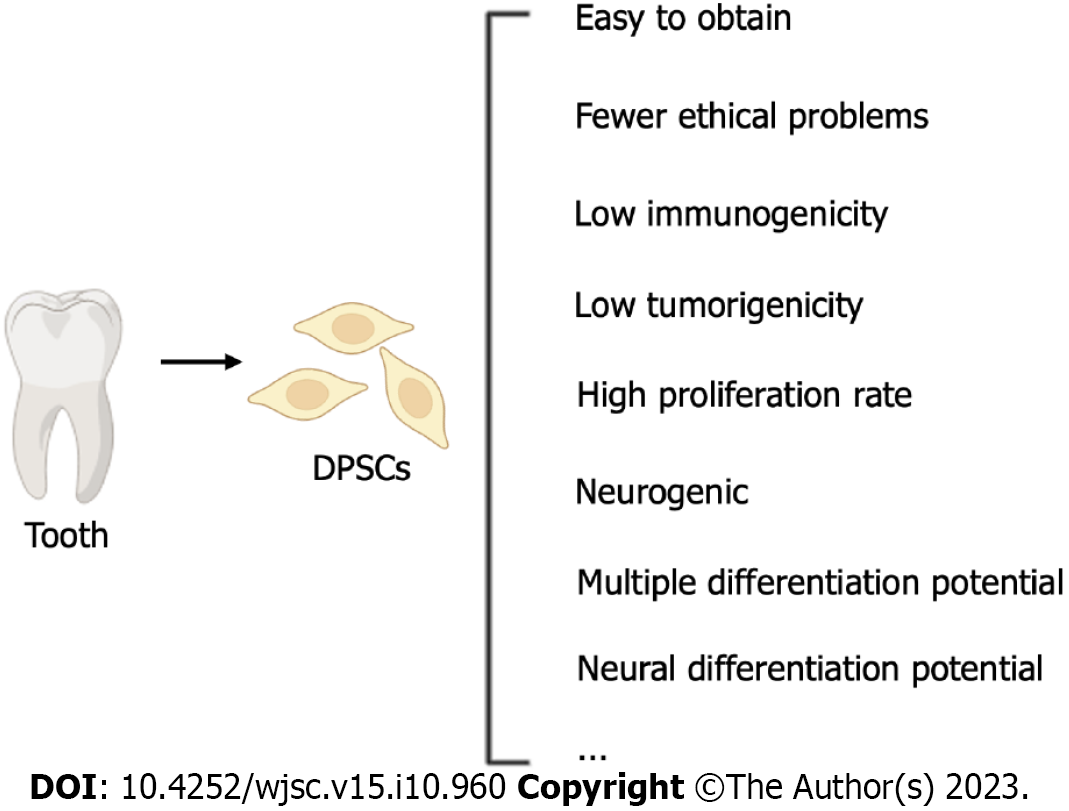
Figure 1 Advantages of dental pulp stem cells as alternative stem cells for nerve regeneration.
The figure was created with BioRender.com. DPSCs: Dental pulp stem cells.
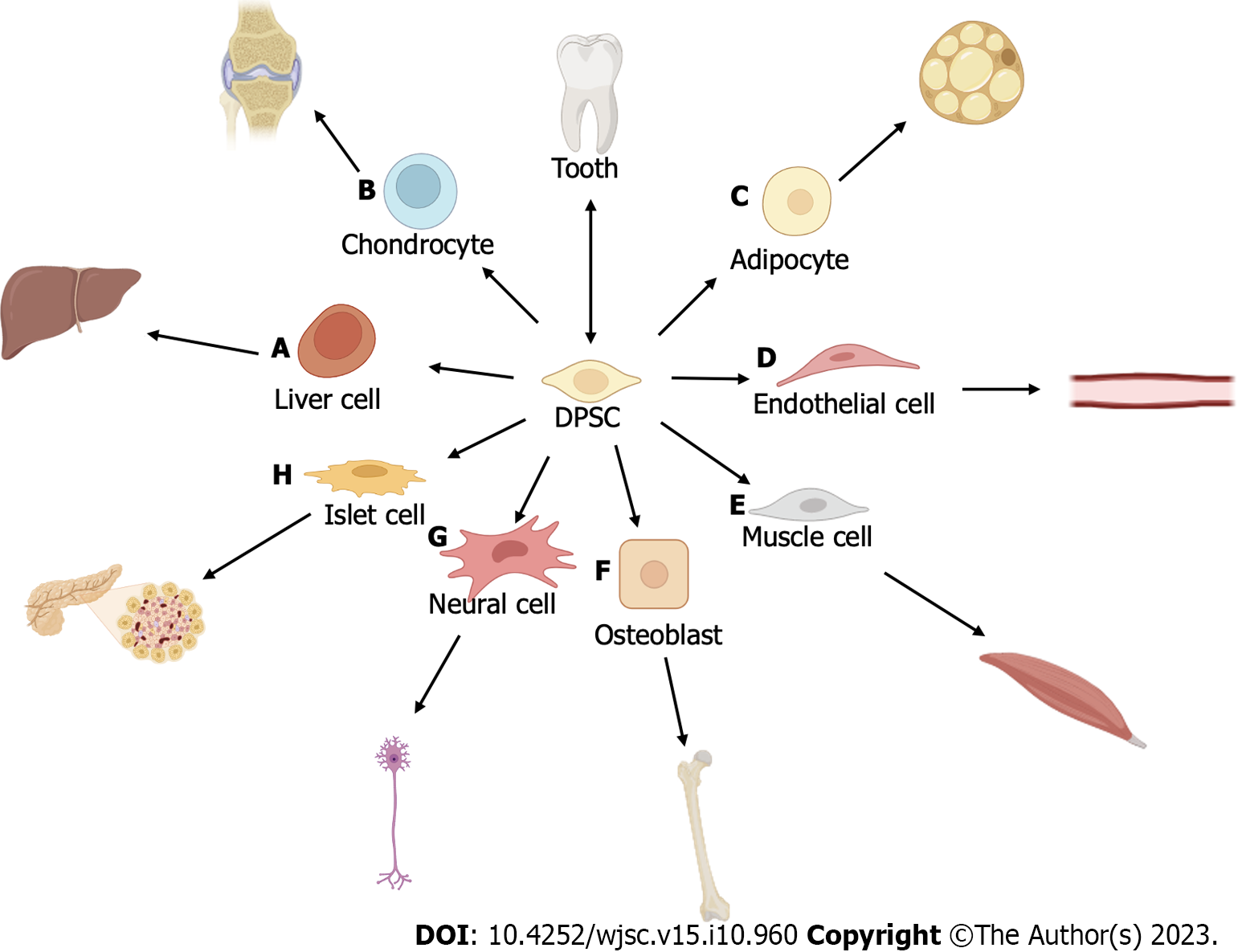
Figure 2 Ability of dental pulp stem cells to differentiate into other types of cells.
Dental pulp stem cells derived from dental pulp exhibit both self-proliferation ability and the capability to differentiate into multiple lineages in vitro. A: Liver stem cell; B: Chondrocyte; C: Adipocyte; D: Endothelial cell; E: Muscle cell; F: Osteoblast; G: Neural cell; H: Islet cell. The figure was created with BioRender.com. DPSC: Dental pulp stem cell.
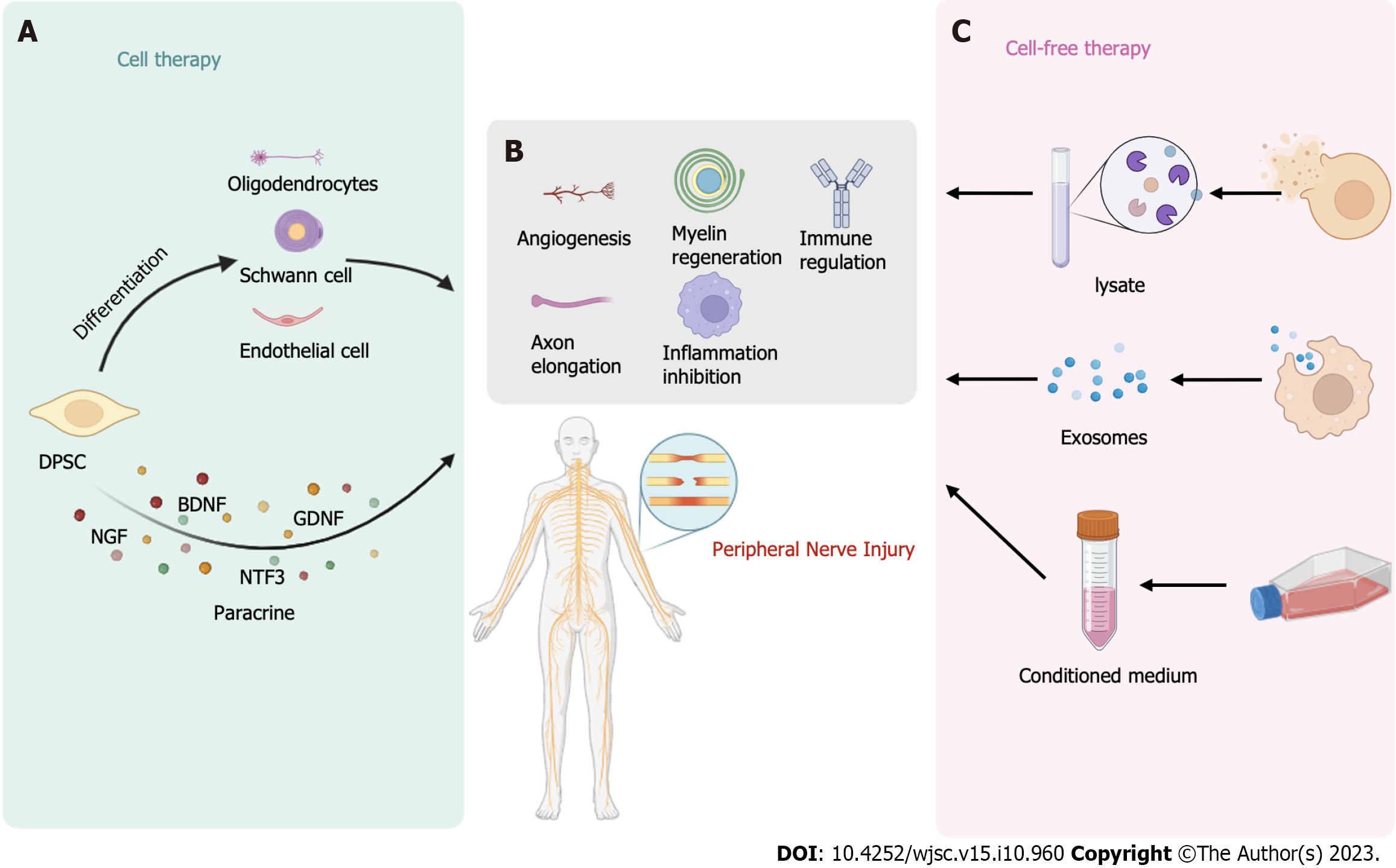
Figure 3 Treatment of peripheral nerve injury by cell/acellular therapies involving dental pulp stem cells.
A: Dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) can directly differentiate into nerve cells or endothelial cells and can also protect nerves and promote nerve regeneration through paracrine neurotrophic factors; B: DPSCs can treat peripheral nerve injury (PNI) by promoting vascular regeneration, axonal regeneration, and myelin sheath repair, regulating the immune response, and inhibiting inflammation; C: Exosomes, lysates, and conditioned media from DPSCs are also effective in treating PNI. The figure was created with BioRender.com. DPSC: Dental pulp stem cell; NGF: Nerve growth factor; BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; GDNF: Glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor; NTF3: Neurotrophic factor 3.
Figure 4 Main models used to study the effect of dental pulp stem cells in treating peripheral nerve injury at present.
A: Rats; B: Rabbits; C: Pigs. D: Diabetic neuropathy; E: Nerve demyelination injury; F: Dental pulp injury; G: Nerve defect injury; H: Nerve crush injury; I: Nerve cells cultured in vitro are used. DPSC: Dental pulp stem cell. The figure was created with BioRender.com.
- Citation: Xing WB, Wu ST, Wang XX, Li FY, Wang RX, He JH, Fu J, He Y. Potential of dental pulp stem cells and their products in promoting peripheral nerve regeneration and their future applications. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(10): 960-978
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i10/960.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i10.960