Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2016; 22(38): 8497-8508
Published online Oct 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i38.8497
Published online Oct 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i38.8497
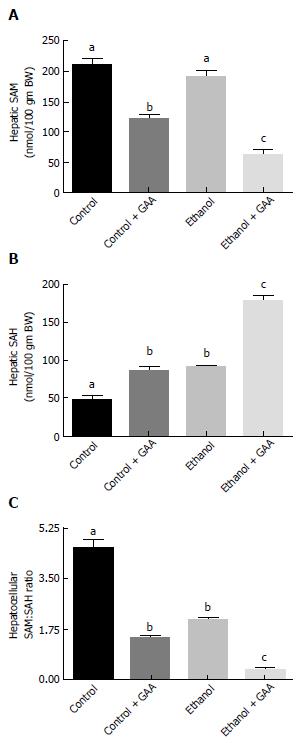
Figure 5 Effect of dietary ethanol and/or guanidinoacetate ingestion on hepatic S-adenosylmethionine, S-adenosylhomocysteine and S-adenosylmethionine: S-adenosylhomocysteine ratio.
Rats were fed the Lieber DeCarli control or ethanol diet with or without 0.36% GAA supplementation. After 6 wk of feeding, Hepatocellular SAM (A) and SAH (B) levels were determined by HPLC analysis as detailed in the “MATERIALS AND METHODS” section and (C) SAM:SAH ratio calculated. The data shown are mean ± SEM of 5 determinations. Values not sharing a common subscript letter are statistically different, P < 0.05 vs control. GAA: Guanidinoacetate; SAM: S-adenosylmethionine; SAH: S-adenosylhomocysteine.
- Citation: Osna NA, Feng D, Ganesan M, Maillacheruvu PF, Orlicky DJ, French SW, Tuma DJ, Kharbanda KK. Prolonged feeding with guanidinoacetate, a methyl group consumer, exacerbates ethanol-induced liver injury. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(38): 8497-8508
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i38/8497.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i38.8497