Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2014; 20(13): 3418-3430
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3418
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3418
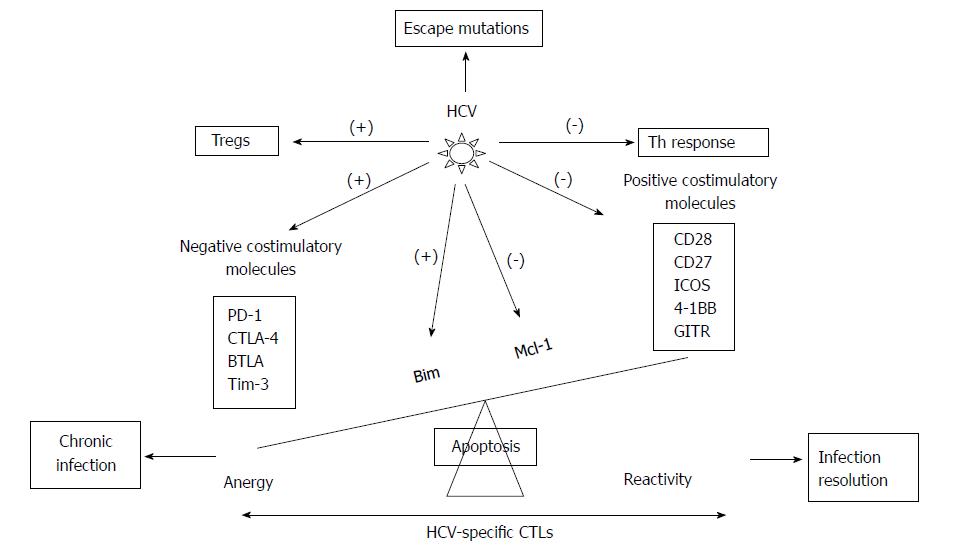
Figure 3 Scheme showing the hepatitis C virus strategies to escape from hepatitis C virus-specific cytotoxic T cells control.
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) modulates the balance between positive and negative co-stimulatory molecules, between pro- and anti-apoptotic molecules, and between Th and Treg cells and develops escape mutations at TCR recognition site. PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1; CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4; BTLA: B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator; Tim-3: T-cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin domain 3; ICOS: Inducible T-cell Costimulator; GITR: Glucocorticoid induced tumor necrosis factor receptor family related gene; Bim: Bcl-2-interacting mediator; Mcl-1: Myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein; (-) inhibition; (+) induction.
- Citation: Larrubia JR, Moreno-Cubero E, Lokhande MU, García-Garzón S, Lázaro A, Miquel J, Perna C, Sanz-de-Villalobos E. Adaptive immune response during hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(13): 3418-3430
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i13/3418.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3418