Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2013; 19(24): 3781-3791
Published online Jun 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i24.3781
Published online Jun 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i24.3781
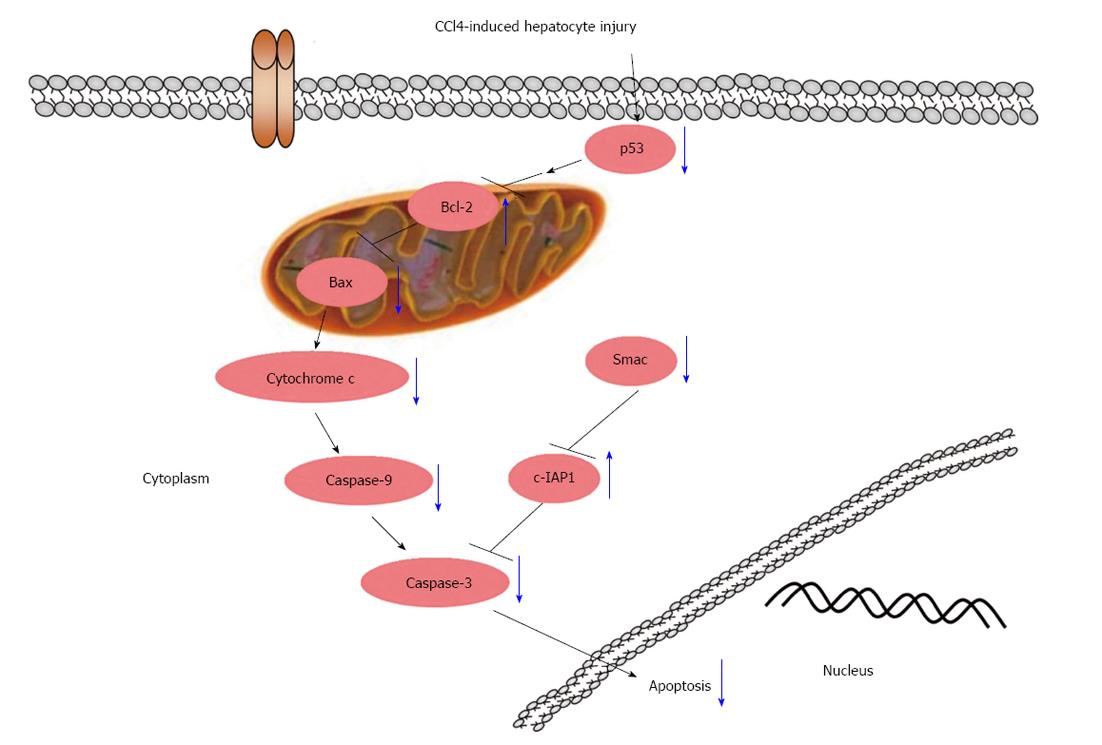
Figure 5 Schematic diagram of the effect of glycyrrhizic acid on the interruption of p53 signaling in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatocyte apoptosis (blue arrows).
Glycyrrhizic acid (GA) suppressed the activation of p53, decreased the expression level of Bax and increased the expression level of Bcl-2, which resulted in reduced cytochrome C release from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm, and inactivated caspase-9 and -3; GA also significantly inhibited Smac release from mitochondria into the cytoplasm and elevated the expression level of c-IAP1, resulting in inhibition of caspase-3 activity. Ultimately, GA suppressed the apoptosis of hepatocytes.
-
Citation: Guo XL, Liang B, Wang XW, Fan FG, Jin J, Lan R, Yang JH, Wang XC, Jin L, Cao Q. Glycyrrhizic acid attenuates CCl4-induced hepatocyte apoptosis in rats
via a p53-mediated pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(24): 3781-3791 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i24/3781.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i24.3781