Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
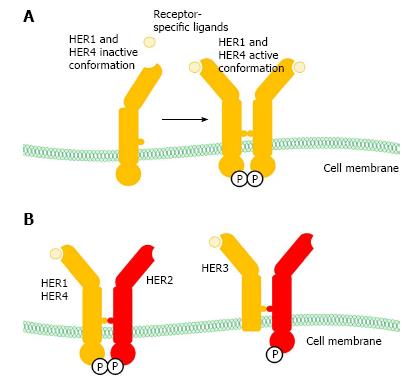
Figure 1 Characteristic features of ErbB receptors family.
A: Schematic representation of HER1 and HER4 conformational change upon ligand interaction; B: Schematic representation of HER2 heterodimers. HER: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; ErbB: erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog.
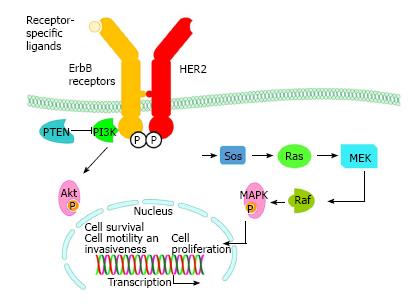
Figure 2 Schematic representation of HER2 physiological pathways.
Ras: Rat sarcoma protein; Sos: Son of sevenless; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; HER: Human epidermal growth factor receptor; ErbB: Erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog.
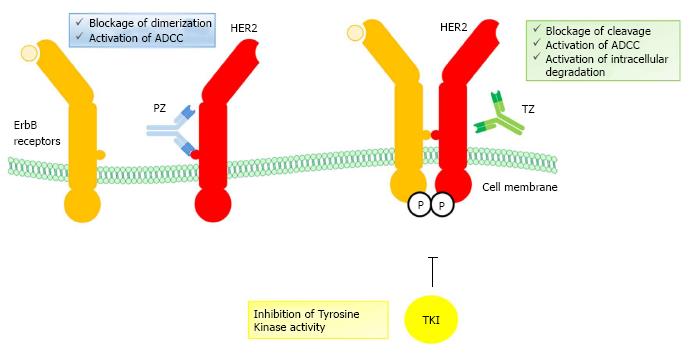
Figure 3 Schematic representation of mechanism of action of HER2-targeted drugs.
PZ recognizes an epitope within the HER2 dimerization domain, thus preventing interaction with other activated ErbB receptors. Moreover PZ recruits natural killer cells, which mediate ADCC. TKI act on HER2 tyrosine kinase activity, by blocking intracellular signaling. TZ binds the juxtamembrane portion of HER2, thus preventing receptor cleavage and stimulating ADCC response and receptor degradation after endocytosis of the HER2-TZ complex. PZ: Pertuzumab; TZ: Trastuzumab; TKI: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors; ADCC: Antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity; HER: Human epidermal growth factor receptor; ErbB: erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog.
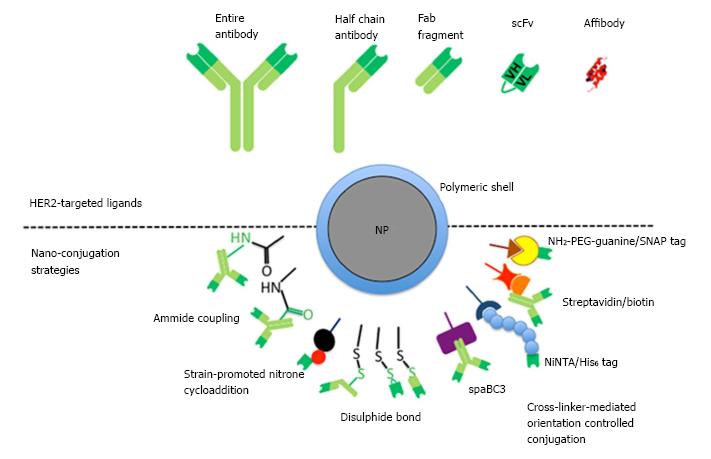
Figure 4 Schematic representation of HER2-targeting ligands and conjugation strategies employed for NPs functionalization.
HER: Human epidermal growth factor receptor; scFv: Single-chain fragment variable antibodies.
- Citation: Mazzucchelli S, Truffi M, Fiandra L, Sorrentino L, Corsi F. Targeted approaches for HER2 breast cancer therapy: News from nanomedicine? World J Pharmacol 2014; 3(4): 72-85
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3192/full/v3/i4/72.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5497/wjp.v3.i4.72