修回日期: 2007-02-01
接受日期: 2007-02-09
在线出版日期: 2007-04-18
目的: 分析STAT5及其靶基因产物Cyclin D1与Caspase-3在结直肠癌组织中的表达情况, 探讨STAT5及其靶基因产物在结直肠癌发病机制中的作用.
方法: 收集北京海淀医院外科2003-12/2005-12经手术切除的结直肠癌标本60例, 应用Western blot检测60例结直肠癌组织、正常黏膜中STAT5及其靶基因产物Cyclin D1与Caspase-3表达.
结果: p-STAT5, Cyclin D1及Caspase-3表达水平在结直肠癌组织中明显高于正常黏膜(P = 0.028, 0.035, 0.046); p-STAT5表达水平与分期相关(P = 0.026); Caspase-3与分期相关(P = 0.041). p-STAT5与Caspase-3在结直肠癌组织中表达情况呈线性相关(r = 0.412, P<0.05).
结论: STAT5信号转导通路可能在结直肠癌发生过程中起重要作用, 检测结直肠癌中STAT5及其靶基因产物的表达可以反映肿瘤的恶性潜能.
引文著录: 欧云菘, 马向涛, 余力伟. STAT5信号转导通路及其靶基因产物与结直肠癌恶性潜能的关系. 世界华人消化杂志 2007; 15(11): 1306-1309
Revised: February 1, 2007
Accepted: February 9, 2007
Published online: April 18, 2007
AIM: To investigate the expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) and target gene products including Cyclin D1 and Caspase-3 in human colorectal carcinoma (CRC), and to explore the mechanism in the tumorigenesis of CRC.
METHODS: Primary colorectal cancer and adjacent normal mucosal specimens were obtained from 60 patients undergoing CRC resection at Beijing Haidian Hospital from December 2003 to December 2005. Western blot analysis was used to measure the expression of STAT5, p-STAT5, Cyclin D1, and Caspase-3 in the cancerous and adjacent normal tissues.
RESULTS: The levels of p-STAT5, Cyclin D1, and Caspase-3 protein were increased in the cancer tissues as compared with those in the normal ones (P = 0.028, 0.035, 0.046). Over-expression of p-STAT5 was correlated with TNM staging (P = 0.026), and Caspase-3 expression was also associated with TNM staging in CRC (P = 0.041). Caspase-3 was in a positive linear correlation with p-STAT5 in tumor (r = 0.412, P < 0.05).
CONCLUSION: STAT5 signaling pathway may play an important role in the tumorigenesis of CRC, and detection of STAT5 and its target gene products may predict the malignant potential of CRC.
- Citation: Ou YS, Ma XT, Yu LW. Constitutive activation of STAT5 pathway and overexpression of target gene products correlate with malignant potential in human colorectal carcinoma. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi 2007; 15(11): 1306-1309
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1009-3079/full/v15/i11/1306.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v15.i11.1306
STAT5是转录信号转导子与激活子家族(signal transducers and activators of transcription, STATs)的重要成员, 该通路接受生长因子、细胞因子等细胞外信号刺激, 作用于细胞核内特异的DNA片段, 调控靶基因转录, 影响细胞的增殖、分化和凋亡[1-2]. STAT5蛋白异常激活与多种恶性肿瘤发生、发展及预后密切相关, 但是关于STAT5信号转导通路与结直肠癌的研究尚处于初期[3-4]. 本研究应用Western blot检测STAT5(p-STAT5)及其靶基因产物Cyclin D1与Caspase-3在结直肠癌组织中的表达, 分析STAT5及其靶基因产物与结直肠癌恶性潜能的关系.
收集北京海淀医院外科2003-12/2005-12经手术切除的结直肠癌标本60例, 年龄27-81(中位65)岁; 术后病理组织学类型包括: 高分化腺癌16例, 中分化腺癌30例, 低分化腺癌14例; 肿瘤分期按照国际抗癌联盟(UICC)的TNM分期, 分为Ⅰ期1例、Ⅱ期30例、Ⅲ期19例、Ⅳ期10例. 于手术切除肿瘤后15-20 min内采集结直肠癌组织及癌旁肠黏膜组织作为对照(距肿瘤边缘大于5 cm), 立即置于液氮中保存. 患者在手术前未接收化疗或者放疗并且签署知情同意书. Western blot中用的PVDF膜购自美国Millipore公司, 显影用的胶片购自美国Kodak公司. 所有抗体购自美国Santa Cruz公司. 预染标准分子质量蛋白购自美国GIBCO/BRL公司. ECL化学发光试剂盒购自英国Amersham公司. 浓缩蛋白分析液购自美国Bio-Rad公司. 其他试剂均为分子生物学纯度购自美国Sigma公司.
组织于裂解缓冲液中裂解(150 mmol/L NaCl; 10 g/L过氧胆酸钠; 10 g/L Triniton X-100; 1 g/L十二烷基磺酸钠; 10 mmol/L Tris, pH7.2; 1 mmol/L正钒酸钠; 1 mmol/L苯甲磺酰氟; 1 mmol/L氟化钠; 0.1 mmol/L抑肽酶, 1 mmol/L亮抑蛋白酶肽). 裂解液在4 ℃条件下13000 g离心30 min. 蛋白浓度测定Bradford法: 以牛血清蛋白(BSA)作为标准品, 根据蛋白定量试剂盒(美国Bio-Rad公司)说明绘制蛋白定量标准曲线, 用分光光度计595 nm下测光密度值, 计算提取液蛋白浓度.
1.2.1 Western blot将蛋白提取物与2×十二烷基磺酸钠(SDS): 上样缓冲液按1:1混合(125 mmol/L Tris·HCl, pH6.8; 40 g/L十二烷基磺酸钠; 200 mL/L甘油; 100 g/L 2-巯基乙醇)后100 ℃水浴下加热5 min. 取总蛋白50 μg, 100 g/L聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳分离后电转移到PVDF膜上. 电泳时在聚丙烯酰胺凝胶中加入预染标准分子质量蛋白作为指示. 转膜后用TBST缓冲液(10 mmol/L Tris·HCl, pH7.5, 150 mmol/L氯化钠, 5 g/L Tween-20)与50 g/L牛血清白蛋白封闭30 min. 封闭后, 加入一抗STAT5, p-STAT5, Cyclin D1, Caspase-3, 工作浓度1:1000, GAPDH作为内参照, 于4 ℃条件下孵育过夜, 用TBST(每次5 min)洗膜后, 与辣根过氧化物酶结合的二抗孵育30 min, 工作浓度1:1000. 然后用ECL化学发光试剂盒检测杂交信号. 用PhosphoImager图像分析仪(美国Molecular Dynamics公司)测定条带的吸光度(A值), 以A值代表蛋白的相对表达量.
统计学处理 用SPSS12.0软件完成. 采用独立样本t检验、配对样本t检验, Pearson相关性分析, P<0.05时表示差异有显著性.
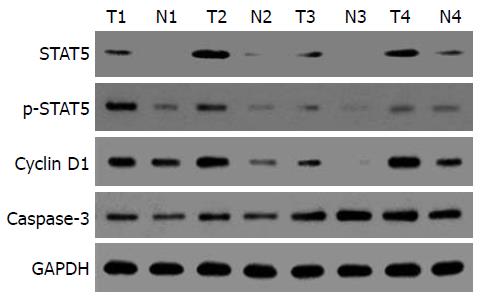
结直肠癌组织中p-STAT5, Cyclin D1及Caspase-3蛋白表达水平明显高于癌旁肠黏膜(图1, 表1). 结直肠癌组织中p-STAT5与Caspase-3表达水平与TNM分期相关(P<0.05). Pearson相关性分析显示p-STAT5与Caspase-3在结直肠癌组织中表达情况呈线性相关(r = 0.412, P<0.05), 而p-STAT5与Cyclin D1在结直肠癌组织中表达情况无相关性(r = 0.127, P>0.05).
| 项目 | n | p-STAT5 | Cyclin D1 | Caspase-3 | |||
| 平均倍数1 | P值 | 平均倍数1 | P值 | 平均倍数1 | P值 | ||
| 性别 | |||||||
| 男性 | 32 | 2.7±0.4 | 0.821 | 4.1±0.4 | 0.913 | 3.7±0.4 | 0.746 |
| 女性 | 28 | 2.5±0.3 | 4.3±0.5 | 3.3±0.3 | |||
| 年龄(岁) | |||||||
| ≥65 | 26 | 2.8±0.4 | 0.736 | 4.8±0.3 | 0.825 | 3.4±0.3 | 0.870 |
| <65 | 34 | 2.4±0.2 | 3.6±0.3 | 3.6±0.4 | |||
| TNM | |||||||
| Ⅲ+Ⅳ | 29 | 3.6±0.4 | 0.026 | 5.2±0.5 | 0.085 | 4.2±0.5 | 0.041 |
| Ⅰ+Ⅱ | 31 | 1.8±0.2 | 3.4±0.3 | 2.1±0.2 | |||
| 组织学分级 | |||||||
| G1 | 16 | 2.3±0.4 | 0.778 | 4.7±0.4 | 0.732 | 3.9±0.4 | 0.894 |
| G2 | 30 | 2.4±0.3 | 0.645 | 4.2±0.3 | 0.627 | 3.3±0.3 | 0.771 |
| G3 | 14 | 3.4±0.4 | 0.530 | 3.6±0.4 | 0.565 | 3.6±0.3 | 0.832 |
| 远处转移 | |||||||
| M1 | 10 | 3.8±0.4 | 0.418 | 5.5±0.4 | 0.211 | 4.4±0.4 | 0.162 |
| M0 | 50 | 2.6±0.3 | 3.3±0.3 | 2.9±0.2 | |||
| 肿瘤大小 | |||||||
| >5 cm | 25 | 3.6±0.4 | 0.638 | 5.4±0.5 | 0.612 | 5.2±0.4 | 0.324 |
| ≤5 cm | 35 | 2.5±0.2 | 4.0±0.4 | 3.3±0.3 | |||
| 性别 | |||||||
| 男性 | 32 | 3.0±0.3 | 0.582 | 4.5±0.4 | 0.776 | 3.8±0.3 | 0.735 |
| 女性 | 28 | 2.2±0.2 | 3.9±0.3 | 3.2±0.3 | |||
JAKs/STATs信号转导通路与细胞的增殖、分化及凋亡关系密切, 该通路异常活化可导致细胞异常增殖和恶性转化. 目前, 在哺乳动物中发现STATs家族由7个成员组成: STAT1-STAT4, STAT5a, STAT5b及STAT6. STAT5最初被称为泌乳素诱导的乳腺因子(mammary gland factor, MGF), 在乳腺上皮细胞增殖与分化中起重要作用[5-6]. STAT5包括STAT5a与STAT5b两种异构体, 结构上具有95%的同源性. STAT5表达与活化不仅与乳腺癌发生、发展密切相关, 而且在髓样白血病、前列腺癌及头颈部鳞状细胞癌中均发现STAT5异常表达与活化[7-10].
STAT5作为上游酪氨酸激酶通过调控靶基因而诱导某些关键产物的表达来影响肿瘤的发生, 重要的靶基因产物包括Cyclin D1与Caspase家族成员. Calo et al[11]发现, STAT5在卵巢癌细胞系MDAH 2774与Caov-3中持续激活, 阻断STAT5活化可以抑制CyclinD1表达. 胱冬肽酶(Caspase)是一类天冬氨酸残基特异性的半胱氨酸蛋白酶, 在细胞凋亡过程中起关键作用. 他们对Bcl-2家族的蛋白质具有重要的酶解修饰作用, 目前已发现的属于这类蛋白酶家族的成员已有十余种, 包括Caspase1-10等, 而Caspase-3是此家族的重要成员[12-14]. Yamashita et al[15]应用STAT5显性负性异构体STAT5aDelta740转染乳腺癌细胞系T47D与MCF7, 发现STAT5aDelta740可以诱导Caspase-3阳性的T47D细胞发生凋亡, 而Caspase-3阴性的MCF7细胞未受影响. 我们通过检测结直肠癌组织中活化状态STAT5(p-STAT5)发现p-STAT5与分期晚(Ⅲ+Ⅳ)相关(P<0.05); Caspase-3与分期晚(Ⅲ+Ⅳ)相关(P<0.05), Pearson相关性分析显示p-STAT5与Caspase-3在结直肠癌组织中表达情况呈线性相关(r = 0.482, P<0.05). 本研究前期工作应用STAT5反义寡核苷酸(20 μmol/L)转染结肠癌细胞HCT116后, 可以阻断其内源性STAT5信号转导通路, Caspase-3表达随STAT5活性受抑制而下降, 凋亡细胞增加, 其可能机制是失活状态的STAT5不能与Caspase-3启动子结合, 从而抑制Caspase-3表达, 细胞出现凋亡[16-17].
总之, STAT5信号转导通路在结肠癌细胞中的转录调控机制尚不清楚, STAT5的异常激活与结肠癌细胞凋亡关系还有待于进一步明确. 实验动物模型及临床观察中发现肿瘤细胞耐受化疗与STAT5与Caspase成员异常增高有关, 阻断STAT5通路可诱导耐药肿瘤细胞凋亡[18-19]. 深入研究STAT5信号转导通路作用机制有可能为治疗结肠癌提供新的理论和实验基础[20-21].
STAT5蛋白异常激活与多种恶性肿瘤发生、发展及预后密切相关, 但是关于STAT5信号转导通路与结直肠癌的研究尚处于初期. 深入研究STAT5信号转导通路作用机制有可能为治疗结肠癌提供新的理论和实验基础.
STAT5蛋白异常激活与多种恶性肿瘤发生、发展及预后密切相关, 本文进一步研究了2年内的60例结直肠癌患者STAT5及其靶基因产物的表达情况与临床病理的关系, 有一定临床和科学意义.
编辑: 张焕兰 电编:张敏
| 1. | Barash I. Stat5 in the mammary gland: controlling normal development and cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2006;209:305-313. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 2. | Buitenhuis M, Coffer PJ, Koenderman L. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5). Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36:2120-2124. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 3. | 马 向涛, 余 力伟, 王 杉, 张 辉, 杜 如昱, 崔 志荣. 环氧合酶-2抑制剂调控Stat5信号转导通路抑制结肠癌细胞增殖的分子机制. 中华医学杂志. 2005;85:2566-2569. |
| 5. | Haura EB, Turkson J, Jove R. Mechanisms of disease: Insights into the emerging role of signal transducers and activators of transcription in cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2005;2:315-324. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 6. | Turkson J. STAT proteins as novel targets for cancer drug discovery. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2004;8:409-422. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 7. | Debierre-Grockiego F. Anti-apoptotic role of STAT5 in haematopoietic cells and in the pathogenesis of malignancies. Apoptosis. 2004;9:717-728. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 8. | Ni Z, Lou W, Lee SO, Dhir R, DeMiguel F, Grandis JR, Gao AC. Selective activation of members of the signal transducers and activators of transcription family in prostate carcinoma. J Urol. 2002;167:1859-1862. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 9. | Li H, Zhang Y, Glass A, Zellweger T, Gehan E, Bubendorf L, Gelmann EP, Nevalainen MT. Activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-5 in prostate cancer predicts early recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:5863-5868. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 10. | Lai SY, Childs EE, Xi S, Coppelli FM, Gooding WE, Wells A, Ferris RL, Grandis JR. Erythropoietin-mediated activation of JAK-STAT signaling contributes to cellular invasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2005;24:4442-4449. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 11. | Calò V, Migliavacca M, Bazan V, Macaluso M, Buscemi M, Gebbia N, Russo A. STAT proteins: from normal control of cellular events to tumorigenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2003;197:157-168. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 12. | Oliver L, Vallette FM. The role of caspases in cell death and differentiation. Drug Resist Updat. 2005;8:163-170. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 13. | Bröker LE, Kruyt FA, Giaccone G. Cell death independent of caspases: a review. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:3155-3162. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 14. | Riedl SJ, Shi Y. Molecular mechanisms of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:897-907. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 15. | Yamashita H, Iwase H, Toyama T, Fujii Y. Naturally occurring dominant-negative Stat5 suppresses transcriptional activity of estrogen receptors and induces apoptosis in T47D breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2003;22:1638-1652. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 16. | 马 向涛, 余 力伟, 王 杉, 杜 如昱, 崔 志荣. Stat5反义寡核苷酸联合Jak激酶抑制剂AG490调控结肠癌细胞增殖与凋亡的分子机制. 肿瘤防治研究. 2006;33:883-886. |
| 17. | 马 向涛, 余 力伟, 王 杉, 杜 如昱, 崔 志荣. Stat5b信号通路调控bcl-2成员表达抑制结肠癌细胞凋亡的作用及其机制. 中华实验外科杂志. 2005;22:1167-1169. |
| 18. | Klampfer L. Signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs): Novel targets of chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic drugs. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2006;6:107-121. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 19. | Scherr M, Chaturvedi A, Battmer K, Dallmann I, Schultheis B, Ganser A, Eder M. Enhanced sensitivity to inhibition of SHP2, STAT5, and Gab2 expression in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Blood. 2006;107:3279-3287. [PubMed] [DOI] |
| 20. | 马 向涛, 余 力伟, 王 杉, 杜 如昱, 崔 志荣. Stat5反义寡核苷酸联合5-氟尿嘧啶对胃癌细胞增殖与凋亡的影响. 世界华人消化杂志. 2006;14:1257-1261. [DOI] |
| 21. | Wittig I, Groner B. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5), a crucial regulator of immune and cancer cells. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2005;5:449-463. [PubMed] [DOI] |