Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 26, 2021; 9(6): 1433-1438
Published online Feb 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i6.1433
Published online Feb 26, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i6.1433
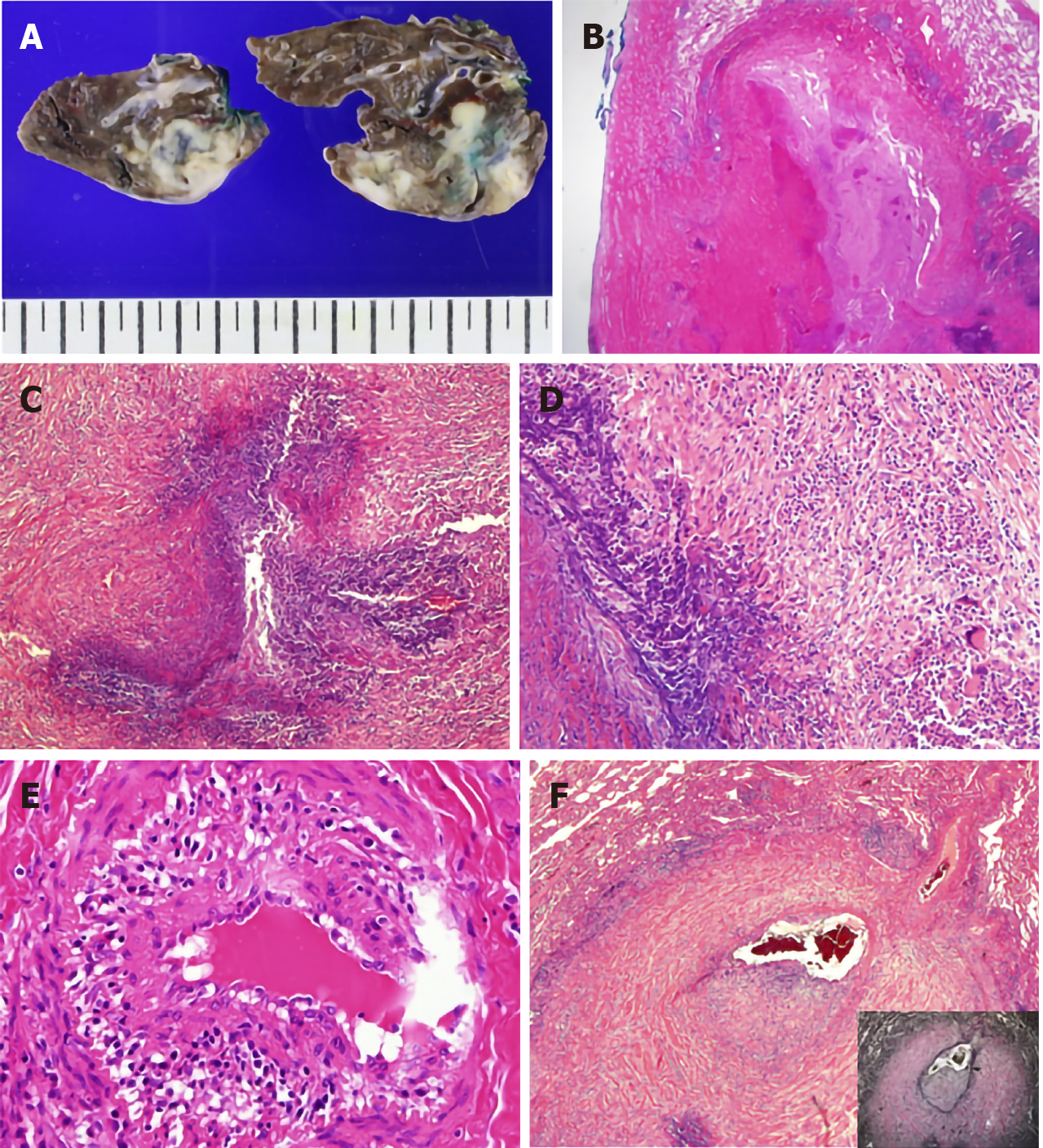
Figure 2 Pathology findings in the lung.
A: Gross sections of the wedged resected lung show pale-brown or ivory colored, irregularly shaped nodules. Areas of necrosis are grossly identifiable; B: The lung displayed extensive geographic necrosis areas with the total destruction of the normal lung parenchyma. Pleural plaque-like fibrosis was also present [Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) stain, × 12.5]; C: Smaller serpiginous abscesses were seen (HE stain, × 100); D: Granulomatous inflammation with a few multinucleated giant cells surrounded the necrotic area (HE stain, × 200); E: Some of the small vessels had many inflammatory cells infiltrating into the vessel wall (vasculitis) (HE stain, × 400); and F: Arterioles were markedly affected by vasculitis. The vessel wall was destroyed, and the lumen was partially occluded by infiltrating inflammatory cells and fibrosis. Cicatricial fibrosis surrounded the vessel wall (HE stain, inset: elastic stain, × 40).
- Citation: Cho U, Kim SK, Ko JM, Yoo J. Unusual presentation of granulomatosis with polyangiitis causing periaortitis and consequent subclavian steal syndrome: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(6): 1433-1438
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i6/1433.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i6.1433