Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2021; 9(34): 10494-10506
Published online Dec 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i34.10494
Published online Dec 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i34.10494
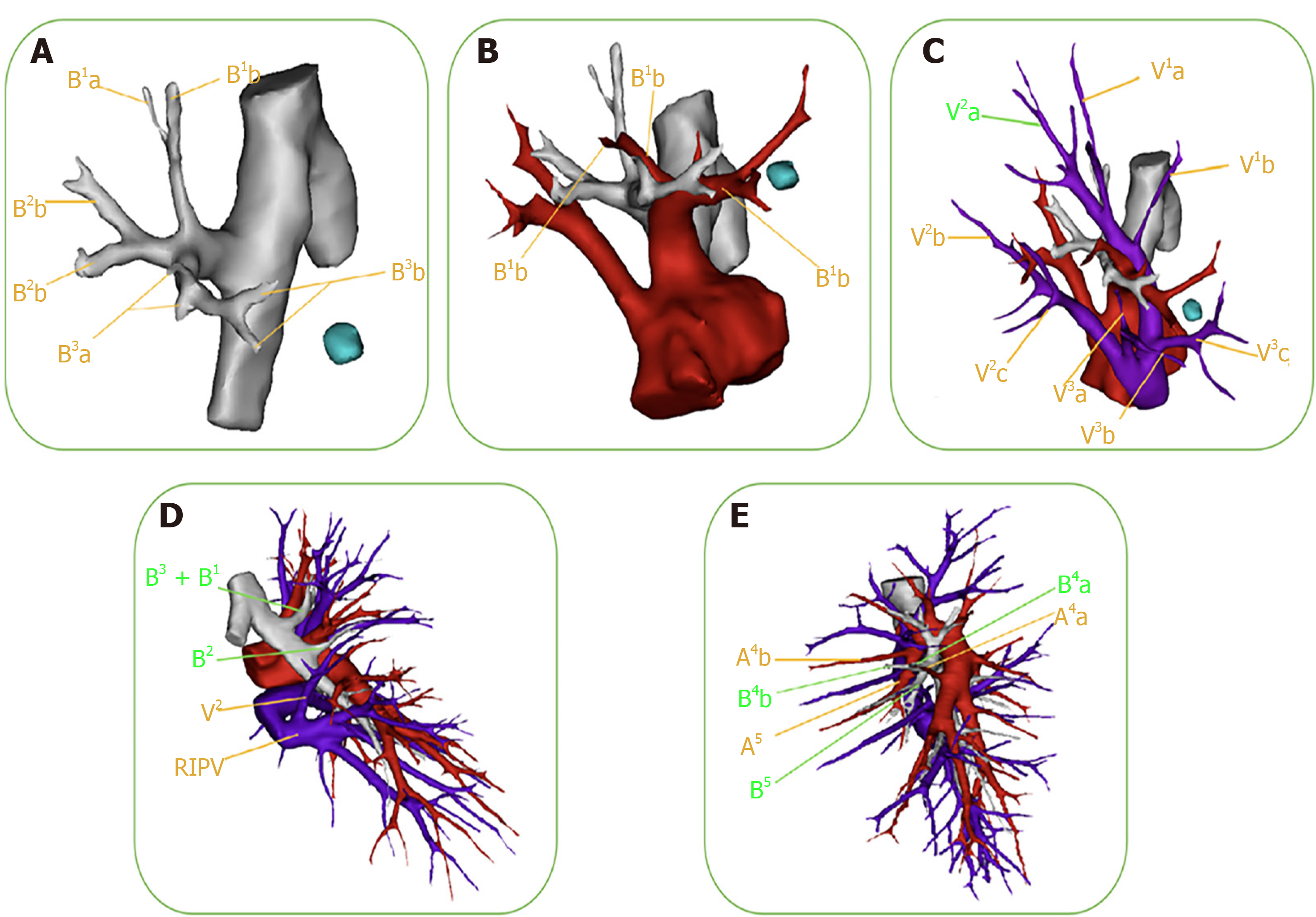
Figure 2 Presurgical confirmation of anatomical variations.
Preoperative three-dimensional (3D) computed-tomography bronchography and angiography images can clearly and vividly display the targeted segmental structure and variations of vessels and bronchi. A: The bronchus of the right upper lobe is divided into the apical segmental bronchus (B1), posterior segmental bronchus (B2), and anterior segmental bronchus (B3). The distance between the B3a and B3b of the anterior segmental bronchus is very great; B: The 3D image reveals the variations of the right upper-lobe artery: the A3a originates from the distal end of the A1, while the enlarged A3b coexists with the proximal end of the A1. Care should be taken to protect A1 when dealing with the A3b during the surgery; C: The segmental and sub-segmental veins of the right upper lobe are labeled successively in the 3D image. There was no central vein, and the V2 a flowed into the apex vein (V1) through the upper pulmonary hilum; D: The 3D image reveals the variations of the B2 and V2 in the right upper lobe. The B2 branched out separately, but the B1 and B3 arose from a common stem. When the B1 is resected, the surgeon often accidentally resects the B3 as well. Additionally, the right upper posterior pulmonary vein (V2) merged into the right inferior pulmonary vein (RIPV). When the surgeon deals with the right lower pulmonary vein, the V2 could be mistakenly cut off altogether, leading to postoperative hemoptysis; E: The 3D image demonstrates the variation of the mediastinal lingual-segment artery (Med A4+5) in the left upper lobe. The A4b and A5 of the left upper lingual-segment artery originated from the upper pulmonary trunk, while the A4a originated from the interlobar-fissure artery separately. When left superior segmentectomy is performed, it is possible to cut off the A4b and A5 at the same time, resulting in decreased pulmonary blood flow to lingular-segment lung tissue and an imbalanced ventilation: Blood flow ratio.
- Citation: Wu YJ, Shi QT, Zhang Y, Wang YL. Thoracoscopic segmentectomy and lobectomy assisted by three-dimensional computed-tomography bronchography and angiography for the treatment of primary lung cancer. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(34): 10494-10506
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i34/10494.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i34.10494