Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2018; 6(15): 882-891
Published online Dec 6, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i15.882
Published online Dec 6, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i15.882
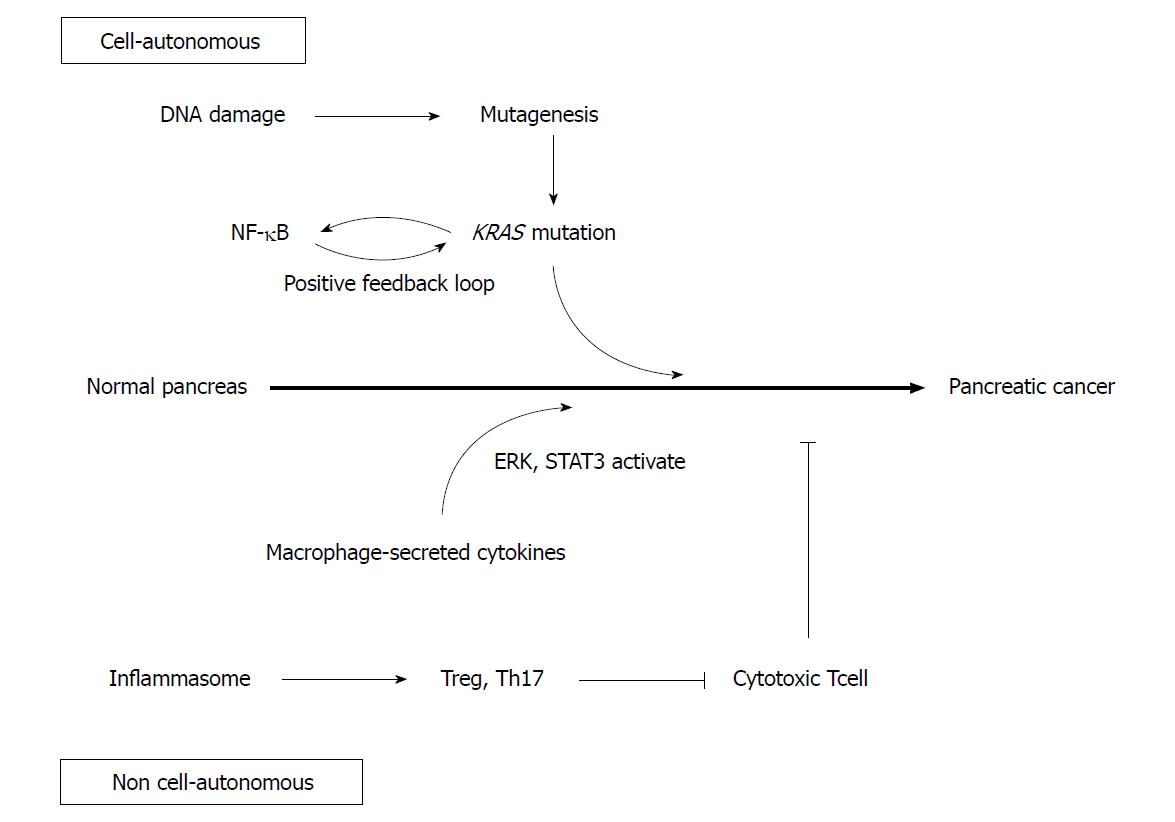
Figure 1 Inflammation induces carcinogenesis both cell-autonomously and non-cell-autonomously.
DNA damage caused by inflammation contributes to mutagenesis. Nuclear factor κB and KRAS activate each other and sustained KRAS activity promotes carcinogenesis. Macrophage-secreted cytokines activate the ERK and STAT3 signaling pathways in epithelial cells. Inflammasomes inactivate cytotoxic T cells via the activation of Th17 and regulatory T cells. NF-κB: Nuclear factor κB.
- Citation: Seimiya T, Otsuka M, Iwata T, Tanaka E, Suzuki T, Sekiba K, Yamagami M, Ishibashi R, Koike K. Inflammation and de-differentiation in pancreatic carcinogenesis. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(15): 882-891
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i15/882.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i15.882