Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 16, 2014; 2(7): 240-249
Published online Jul 16, 2014. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i7.240
Published online Jul 16, 2014. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i7.240
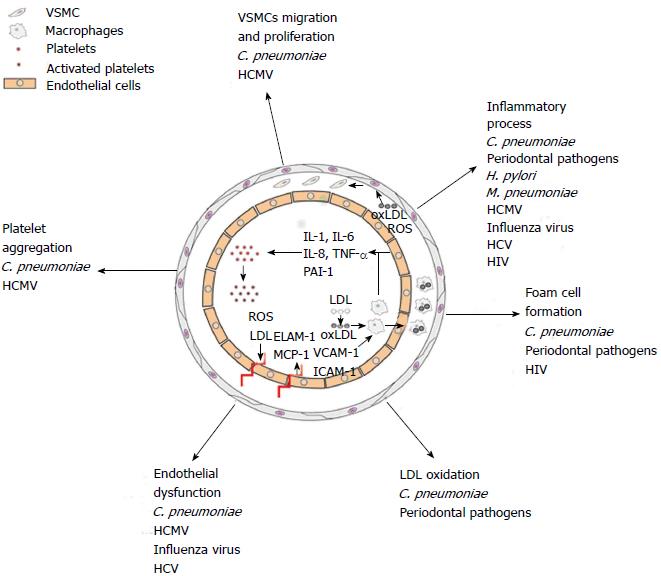
Figure 1 Schematic representation of transversal artery section.
Possible etiopathogenetic mechanisms of the infectious agents in atherosclerotic plaque development. C. pneumoniae: Chlamydia pneumoniae; HCMV: Human cytomegalovirus; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; M. pneumoniae: Mycoplasma pneumoniae; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus; SMC; Smooth muscle cell; ROS; Reactive oxygen species; LDL; Low-density lipoprotein; Ox-LDL: Oxidized low-density lipoprotein; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor; PAI: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; ELAM-1: Endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule-1; VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; ICAM-1: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1.
- Citation: Sessa R, Pietro MD, Filardo S, Turriziani O. Infectious burden and atherosclerosis: A clinical issue. World J Clin Cases 2014; 2(7): 240-249
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v2/i7/240.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v2.i7.240