Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 16, 2025; 13(26): 104421
Published online Sep 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i26.104421
Published online Sep 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i26.104421
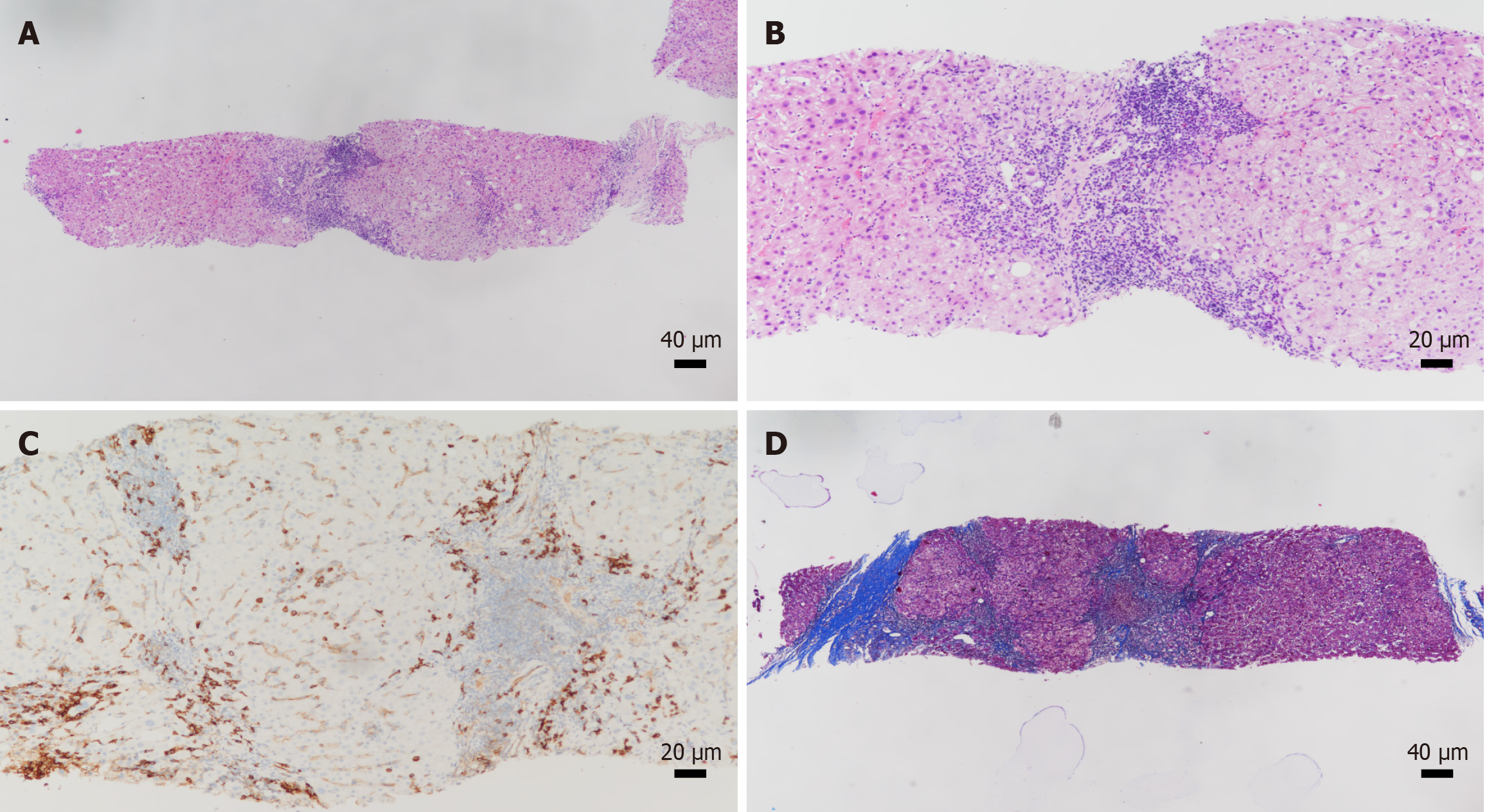
Figure 2 Liver biopsy pathological results for case 2.
A: The liver biopsy tissue revealed seven portal areas of medium to small size with disorganized lobular architecture (hematoxylin and eosin); B: The primary lesions include expansion of some portal areas, moderate inflammatory cell infiltration dominated by mononuclear cells (hematoxylin and eosin); C: Plasma cells are easily visible in small clusters (CD38), and moderate interface hepatitis observed in some portal areas; D: The bile ductules are discernible with disorganized epithelial lining and infiltration of inflammatory cells into the interductal epithelium, accompanied by a mild bile duct reaction around the portal areas. There is also proliferation of interstitial fibrous tissue in the portal areas, leading to the formation of local fibrous septa that segment the hepatic parenchyma and disrupt the lobular structure (Masson).
- Citation: Dou J, Zhao XY, Wang ZG, Ning ZH, Wang XZ, Guo F. Hepatitis B virus and hepatitis D virus co-infection complicated by autoimmune hepatitis: Two case reports. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(26): 104421
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i26/104421.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i26.104421