Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 26, 2023; 11(18): 4295-4305
Published online Jun 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i18.4295
Published online Jun 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i18.4295
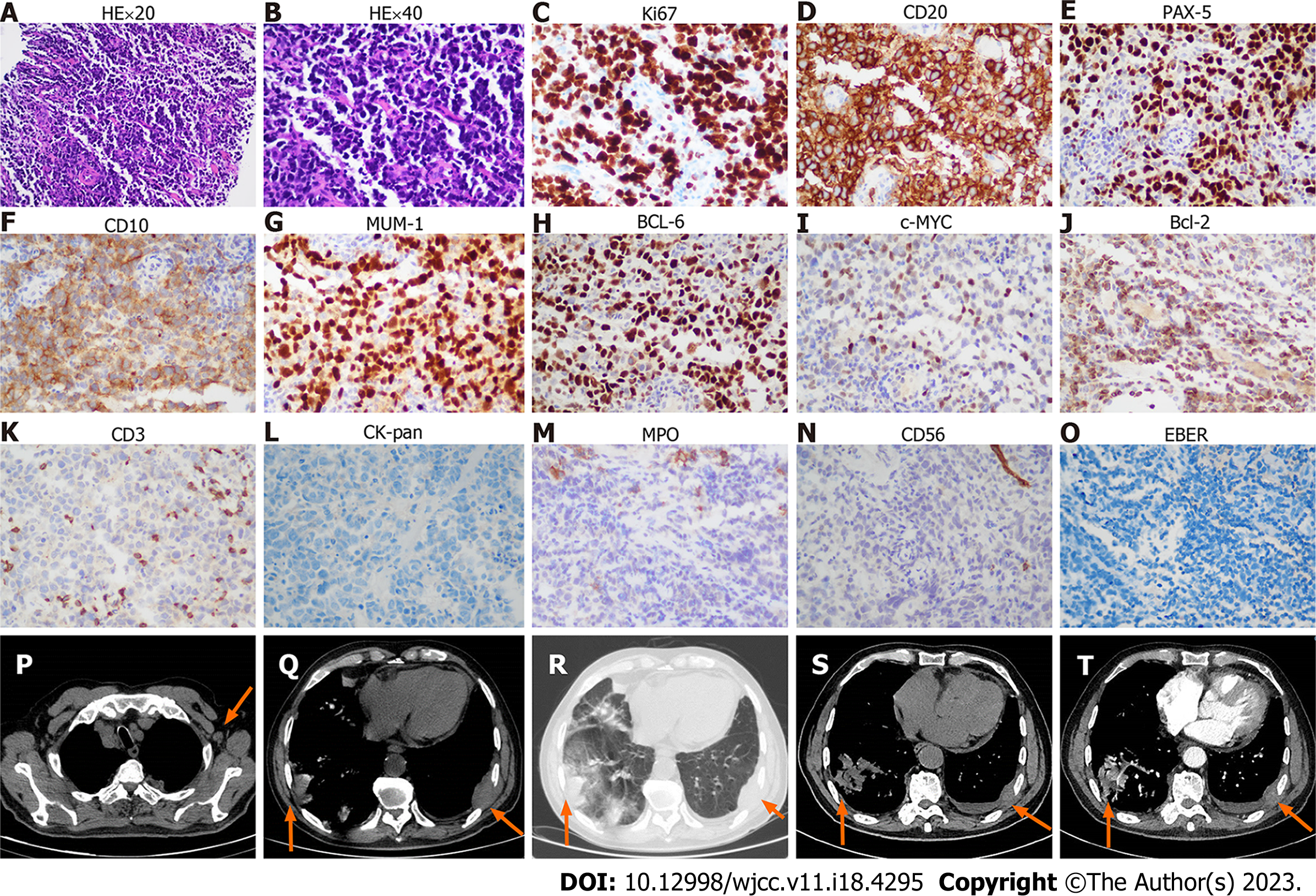
Figure 1 The biopsy and imaging of chest wall mass.
A-O: The HE and immunohistochemistry of chest wall mass; A: Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) staining × 20 objective; B: HE staining × 40 objective; C-O: The immunohistochemistry shows Ki-67 (++, approximately 70%), CD20 (++), PAX-5 (++), CD10 (+), MUM-1 (++), BCL-6 (++), c-MYC (+, < 40%), BCL-2 (+, < 50%), CD3 (T cells few +), CK-pan (-), myeloperoxidase (MPO) (-), CD 56 (-), and EBER (-). P: Enlarged axillary lymph node (arrow) in the chest computed tomography (CT) scan; Q and R: Infiltration of masses (arrows) to the lung and chest wall on mediastinum window (Q) and lung window (R). S and T: Unenhanced (S) and contrast-enhanced (T) CT images shows the infiltration of masses (arrows) to the lung and chest wall on mediastinal window.
- Citation: Zhang LB, Zhang L, Xin HL, Wang Y, Bao HY, Meng QQ, Jiang SY, Han X, Chen WR, Wang JN, Shi XF. Coexistence of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and untreated lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/waldenström macroglobulinemia in a same patient: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(18): 4295-4305
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i18/4295.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i18.4295