Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 16, 2022; 10(35): 12980-12989
Published online Dec 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i35.12980
Published online Dec 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i35.12980
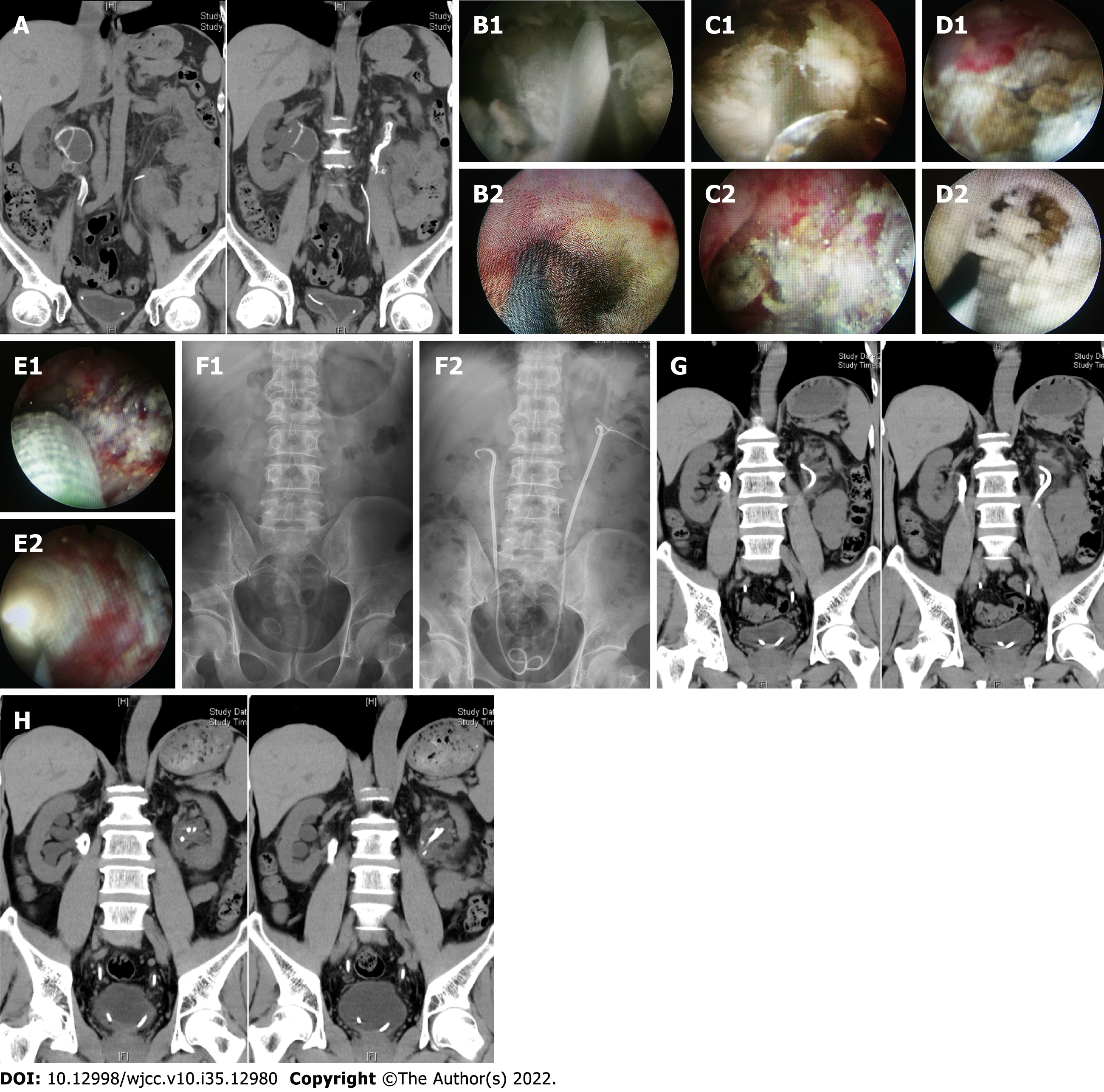
Figure 1 Imaging and endoscopic images of patient 1.
A: Preoperative coronal non-enhanced computed tomography (NCCT) showed annular calcification in the bilateral upper urinary tract; B: Extensive encrusted tissues can be seen within the right anterograde (B1) and retrograde (B2) lumina during the first-stage operation; C: Right anterograde (C1) and retrograde (C2) lumina after encrusted tissue removal during the first-stage operation; D: Extensive encrusted tissues can be seen within the left anterograde (D1) and retrograde (D2) lumina during the first-stage operation; E: Left anterograde (E1) and retrograde (E2) lumina after encrusted tissue removal and balloon dilation during the first-stage operation; F: Preoperative and postoperative kidney, ureter, and bladder (KUB) scans. Preoperative KUB scan showed bilateral upper urinary tract calcification with the stent tube moving downward on the left (F1), and postoperative KUB scan showed bilateral stents in good positions; G: Coronal NCCT performed 3 mo postoperatively showed little bilateral renal pelvis calcification and the indwelling bilateral stents; H: Coronal NCCT scan performed 6 mo postoperatively showed that the initial calcification on the left side disappeared and that on the right side decreased significantly.. NCCT: Non-enhanced computed tomography); KUB: Kidney, ureter, and bladder.
- Citation: Liu YB, Xiao B, Hu WG, Zhang G, Fu M, Li JX. Endoscopic treatment of urothelial encrusted pyelo-ureteritis disease: A case series. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(35): 12980-12989
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i35/12980.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i35.12980