Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 21, 2022; 10(3): 811-819
Published online Jan 21, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i3.811
Published online Jan 21, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i3.811
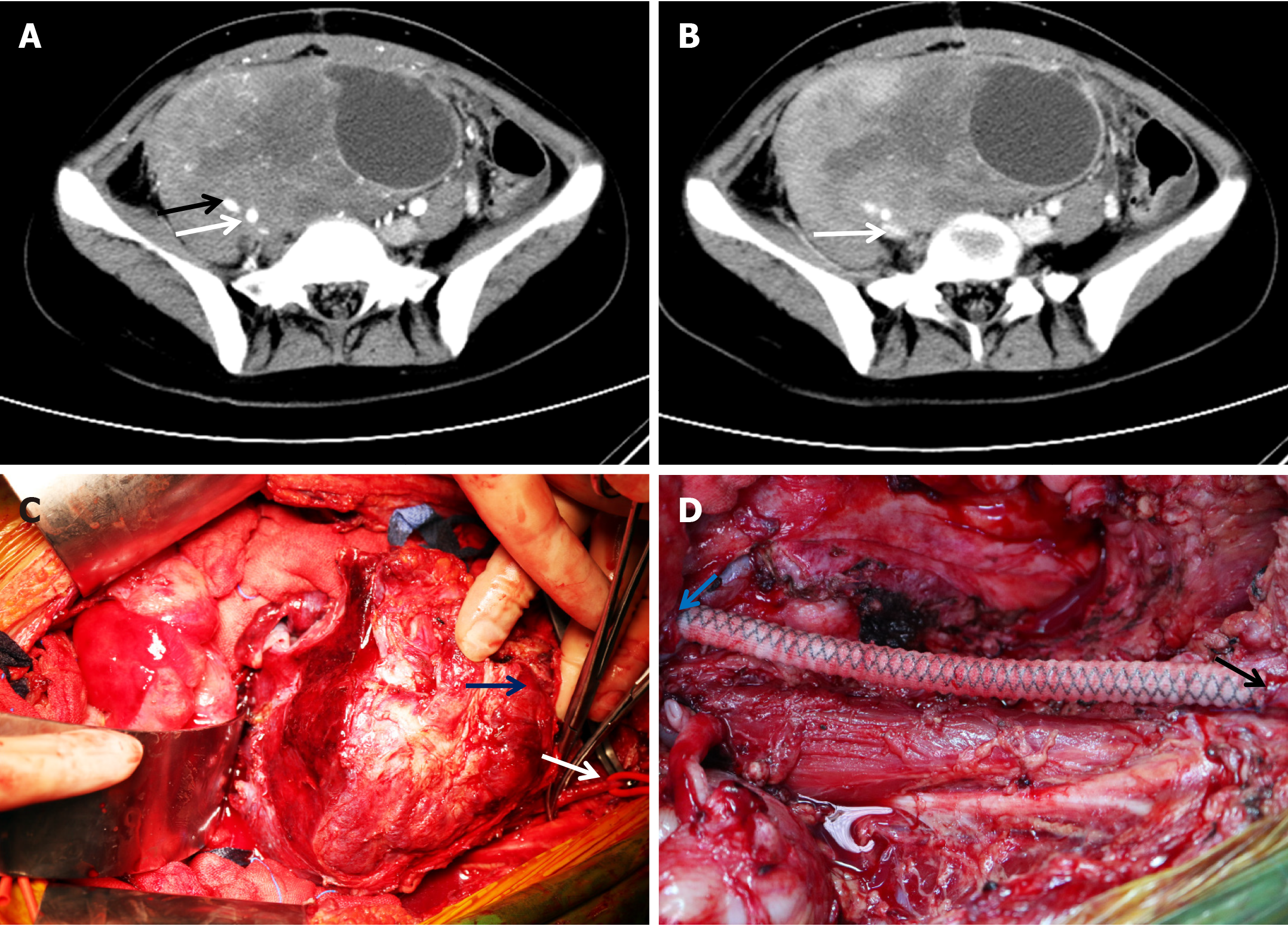
Figure 1 Computed tomography images from a case of retroperitoneal invasive fibroma and key steps in surgery.
A: The arterial phase of the computed tomography (CT) scan indicated a massive pelvic mass with a diameter of approximately 20 cm surrounding the right internal iliac artery (white arrow) and external iliac artery (black arrow); B: The venous phase of the CT scan indicated that the mass surrounded the right common iliac vein and caused compression occlusion (arrow); C: During surgery, the right femoral artery (white arrow) was dissociated; the blue arrow indicates the mass; D: Artificial vessel reconstruction between the right common iliac artery (blue arrow) and femoral artery (black arrow) was performed after tumor removal.
- Citation: Li WX, Tong HX, Lv CT, Yang H, Zhao G, Lu WQ, Zhang Y. Management of retroperitoneal sarcoma involving the iliac artery: Single-center surgical experience. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(3): 811-819
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i3/811.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i3.811