Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. May 16, 2022; 10(14): 4541-4549
Published online May 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i14.4541
Published online May 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i14.4541
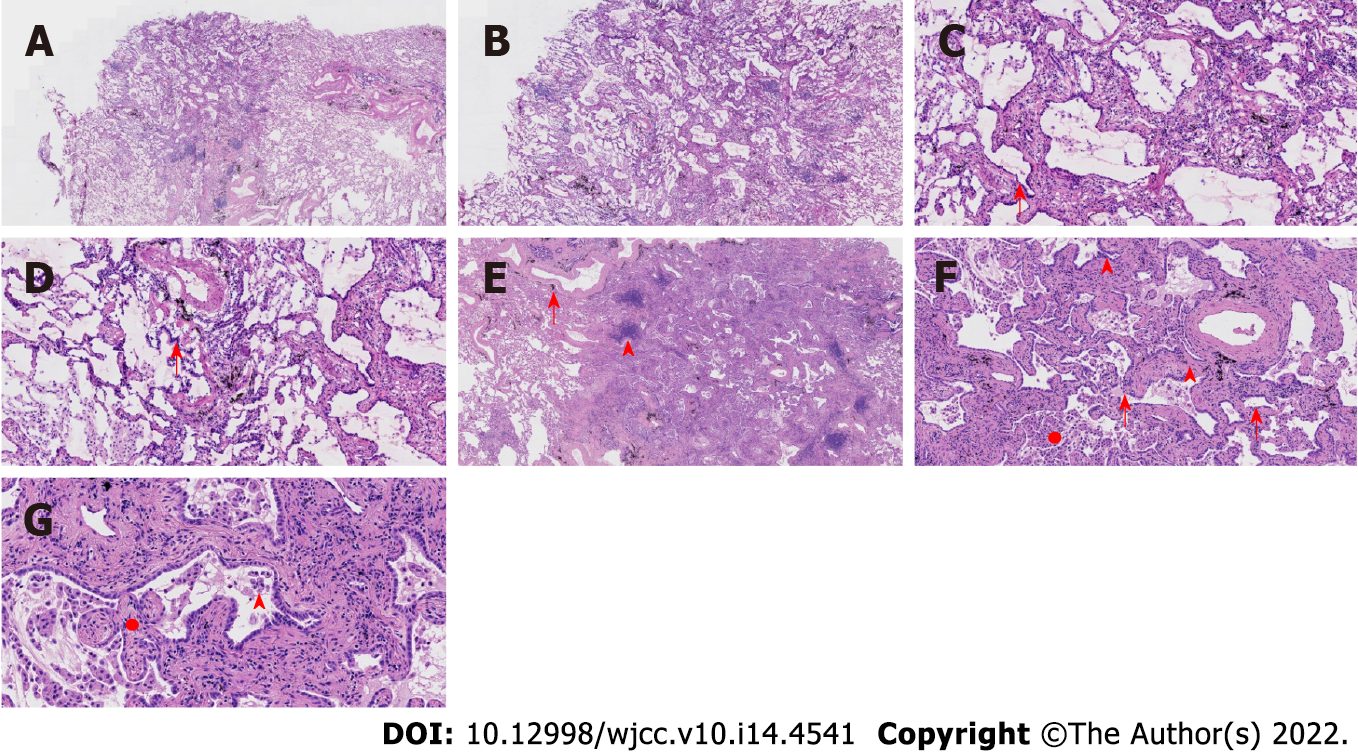
Figure 2 Pathological features of case 1.
A: At low magnification (40 ×, frozen section), the boundary of the tumor was relatively clear, and there was air cavities; B: At low magnification (100 ×, frozen section), the boundary of the tumor was relatively clear, and there was air cavities; C and D: Observations at high magnification (200 ×, frozen section) revealed that the tumor cells were mainly arranged in a monolayer structure, and the local part seemed to be a bilayer structure. Morphologically, the cells were observed to be medium sized, the nuclear chromatin was pale and homogeneous, and local cilia were seen (red arrow); E: At low magnification (100 ×), the relationship between the pulmonary lobular artery and bronchioles was close (arrow), and peripheral stromal lymphocytes were infiltrated in a focal shape (triangle); F and G: Observations at medium to high magnification (200 × and 400 ×, respectively) revealed that tumor cells were arranged as papillary and mural structures. The cell morphology is mild with visible cilia (arrows), bilayer structures (triangles), aggregation of phagocytes in the alveolar cavity (circle, F), and a fibrous non-cancerous stroma (circle, G).
- Citation: Du Y, Wang ZY, Zheng Z, Li YX, Wang XY, Du R. Bronchiolar adenoma with unusual presentation: Two case reports. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(14): 4541-4549
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i14/4541.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i14.4541