Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
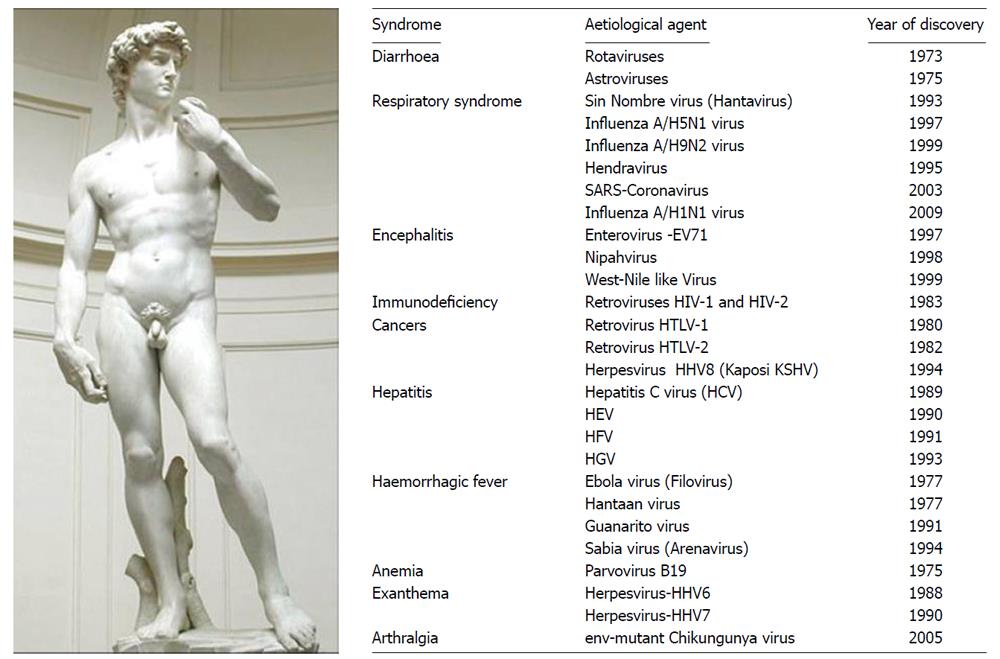
Figure 1 Major emerging and re-emerging virus-associated diseases in human.
The etiological agents of infectious diseases identified since 1973, as newly discovered viruses of public health importance. It includes a few arboviruses that are transmitted to humans by arthropod vectors, upon biting. Among known arboviruses, some are transmitted by mosquitoes (Bunyaviridae: La Crosse encephalitis, California encephalitis, Rift Valley fever; Flaviviridae: Dengue fever, Yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis, West Nile; Togaviridae: Eastern equine encephalomyelitis, Western equine encephalomyelitis, Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis; Ross River fever, O’Nyong-nyong fever, Chikungunya), others by ticks (Bunyaviridae: Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever; Flaviviridae: Tick-borne encephalitis; Omsk hemorrhagic fever; Reoviridae: Colorado tick fever). Most of the emerging pathogens in humans originate from zoonosis.
- Citation: Devaux CA. Emerging and re-emerging viruses: A global challenge illustrated by Chikungunya virus outbreaks. World J Virol 2012; 1(1): 11-22
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v1/i1/11.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v1.i1.11