Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Transplantation. Sep 10, 2018; 8(5): 156-166
Published online Sep 10, 2018. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v8.i5.156
Published online Sep 10, 2018. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v8.i5.156
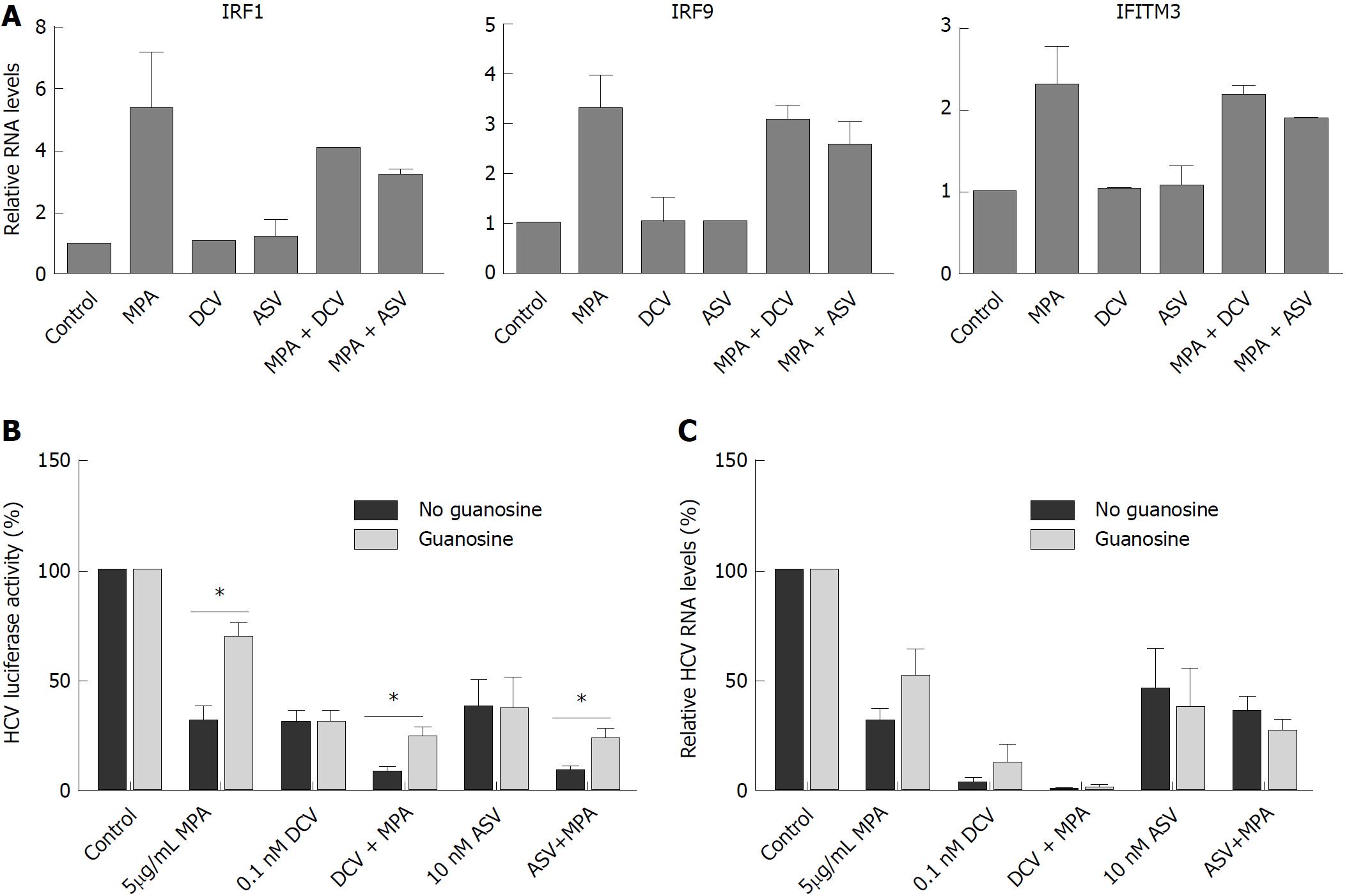
Figure 5 The combined antiviral action of DAAs with MPA is not caused by increased expression by ISGs and is partly reversed by guanosine.
A: The expression of IRF1, IRF9, and IFITM3 was upregulated after 48h culture with 5 mg/ml MPA. 0.1 nM DCV and 10 nM ASV had no effect on the expression of these genes and did not affect the MPA induced expression. The results are means ± SEM of 2 independent experiments, performed in duplicate; B: The effect of guanosine (GU) supplementation on the combined antiviral action of DCV and ASV with MPA was investigated in Huh7ET-luc cells: MPA inhibited HCV replication by 69% of control, and this was significantly reversed by the addition of 50 μmol/ml guanosine by 30% of control (Mann-Whitney test, P = 0.03). Guanosine did not affect the antiviral action of DSV or ASV, and significantly reversed the combined antiviral effect of DSV or ASV with MPA (Mann-Whitney test P = 0.03 for DSV + MPA and P = 0.03 for ASV + MPA) Results are mean of 4 independent experiments performed in triplicate; C: In the infectious JFH model, HCV replication was effectively inhibited by 5mg/ml MPA, 0.1 nM DCV and 10nM ASV (by 68%, 96.5% and 54% of control respectively).The addition of 50 μmol/ml guanosine partly reversed the antiviral action of MPA by 49% of control, and had no effect on the antiviral action of DSV or ASV, either in the absence or presence of MPA. Results are mean ± SEM of 4-6 independent experiments, performed in duplicate.
- Citation: de Ruiter PE, Gadjradj Y, de Knegt RJ, Metselaar HJ, Ijzermans JN, van der Laan LJ. Interaction of immunosuppressants with HCV antivirals daclatasvir and asunaprevir: combined effects with mycophenolic acid. World J Transplantation 2018; 8(5): 156-166
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v8/i5/156.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v8.i5.156