Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Transplant. Jun 24, 2016; 6(2): 278-290
Published online Jun 24, 2016. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v6.i2.278
Published online Jun 24, 2016. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v6.i2.278
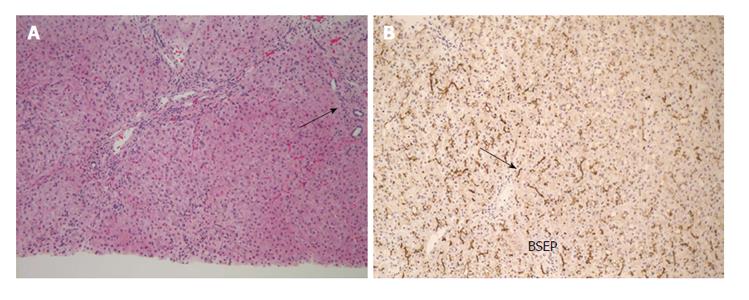
Figure 3 Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 2 is characterized by mutations in the ABCB11 gene.
A: Patients with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 2 (PFIC2) can initially present clinically similarly to PFIC1, but with more rapid progression of liver disease. Early on in the disease patients may present with neonatal giant cell hepatitis and lobular inflammation. However, there can be rapid progression with prominent duct reaction and progression to cirrhosis. This figure demonstrates prominent duct reaction in a patient with PFIC2 and advancing fibrosis (arrow). Duct reaction and cholestasis can also occur in patients with extrahepatic biliary obstruction so correlation with clinical findings is required; B: PFIC2 is also called BSEP disease and is characterized by mutations in the ABCB11 gene. ABCB11 encodes for the major canalicular bile salt exporter BSEP. Patients with normal BSEP expression show positive immunohistochemistry for BSEP with a canalicular pattern of staining (arrow). In some cases of PFIC2, there is complete lack of staining for BSEP. BSEP: Bile salt exporter pump.
- Citation: Mehl A, Bohorquez H, Serrano MS, Galliano G, Reichman TW. Liver transplantation and the management of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis in children. World J Transplant 2016; 6(2): 278-290
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v6/i2/278.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v6.i2.278