Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Sep 19, 2025; 15(9): 108382
Published online Sep 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i9.108382
Published online Sep 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i9.108382
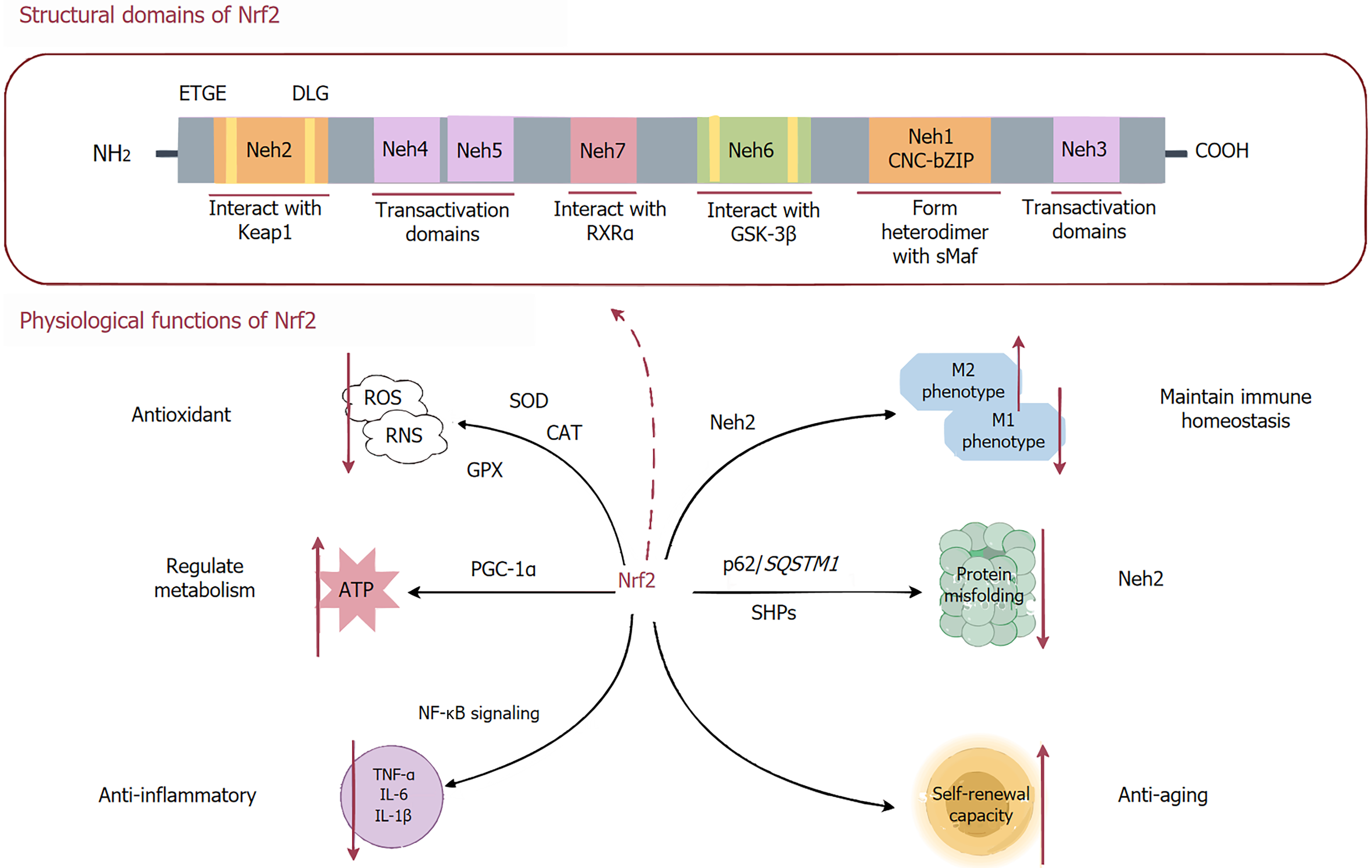
Figure 1 Structure and function of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2.
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is composed of seven conserved Nrf2-ECH homology (Neh) domains, each playing a distinct role in its regulation: Neh1 facilitates antioxidant response element binding via heterodimerization with Maf proteins, Neh2 mediates Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1)-dependent degradation through ETGE and DLG motifs, and Neh6 enables Keap1-independent degradation via glycogen synthase kinase-3β phosphorylation. Meanwhile, Neh3, Neh4, and Neh5 act as transactivation domains, while Neh7 fine-tunes Nrf2 activity by interacting with retinoid X receptor alpha. Nrf2 serves as a master regulator of cellular health, orchestrating antioxidant defense, metabolic regulation, anti-inflammatory responses, immune homeostasis, protein quality control, and anti-aging mechanisms to ensure cellular adaptation, survival, and longevity. Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; NH2: Amino; COOH: Carboxyl; RXR: Retinoid X receptor; GSK-3β: Glycogen synthase kinase-3β; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; RNS: Reactive nitrogen species; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; CAT: Catalase; GPX: Glutathione peroxidase; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; PGC-1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1α; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-B; SHP: Small heterodimer partner.
- Citation: Zhang YM, Zhang ZG. Modulating nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 and heme oxygenase-1 in liver-brain axis disorders. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(9): 108382
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i9/108382.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i9.108382