Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Jul 19, 2025; 15(7): 104921
Published online Jul 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i7.104921
Published online Jul 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i7.104921
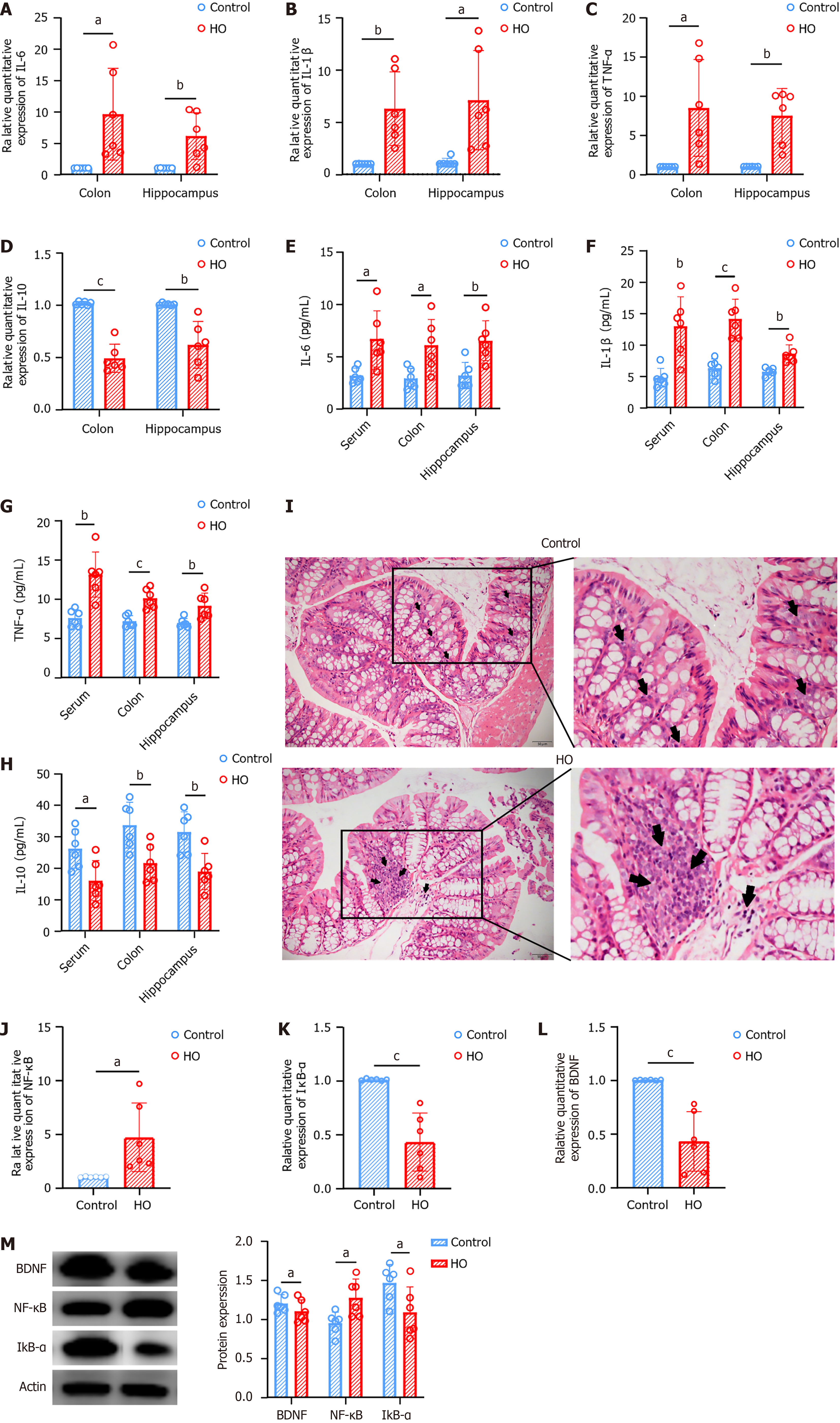
Figure 2 Inflammation is present in both peripheral and central regions of hypothyroid mice.
A-D: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis reveals elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines [interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-10] in both the colon and hippocampus of hypothyroid group (HO) mice; E-H: Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay results indicate higher concentrations of these cytokines in the serum, colon, and hippocampus of HO mice; I: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of colon tissue shows increased inflammatory cell infiltration in the HO group; J-L: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction demonstrates increased mRNA levels of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and decreased levels of inhibitor of NF-κB α and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hippocampus of HO mice; M: Western blot analysis confirms higher protein levels of NF-κB and lower levels of inhibitor of NF-κB α and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hippocampus. Results are presented as mean ± SEM, with aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 indicating statistical significance. HO: Hypothyroid group; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor κB; IκB: Inhibitor of nuclear factor κB; BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor.
- Citation: Guo HJ, Ma XQ, Li YT, Zhou ZH, Tao W, Jiang YH, Li XL, Zhang XL. Correlation between depressive-like behavior and gut microbiota in mice with hypothyroidism. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(7): 104921
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i7/104921.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i7.104921