Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Jun 19, 2025; 15(6): 104809
Published online Jun 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i6.104809
Published online Jun 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i6.104809
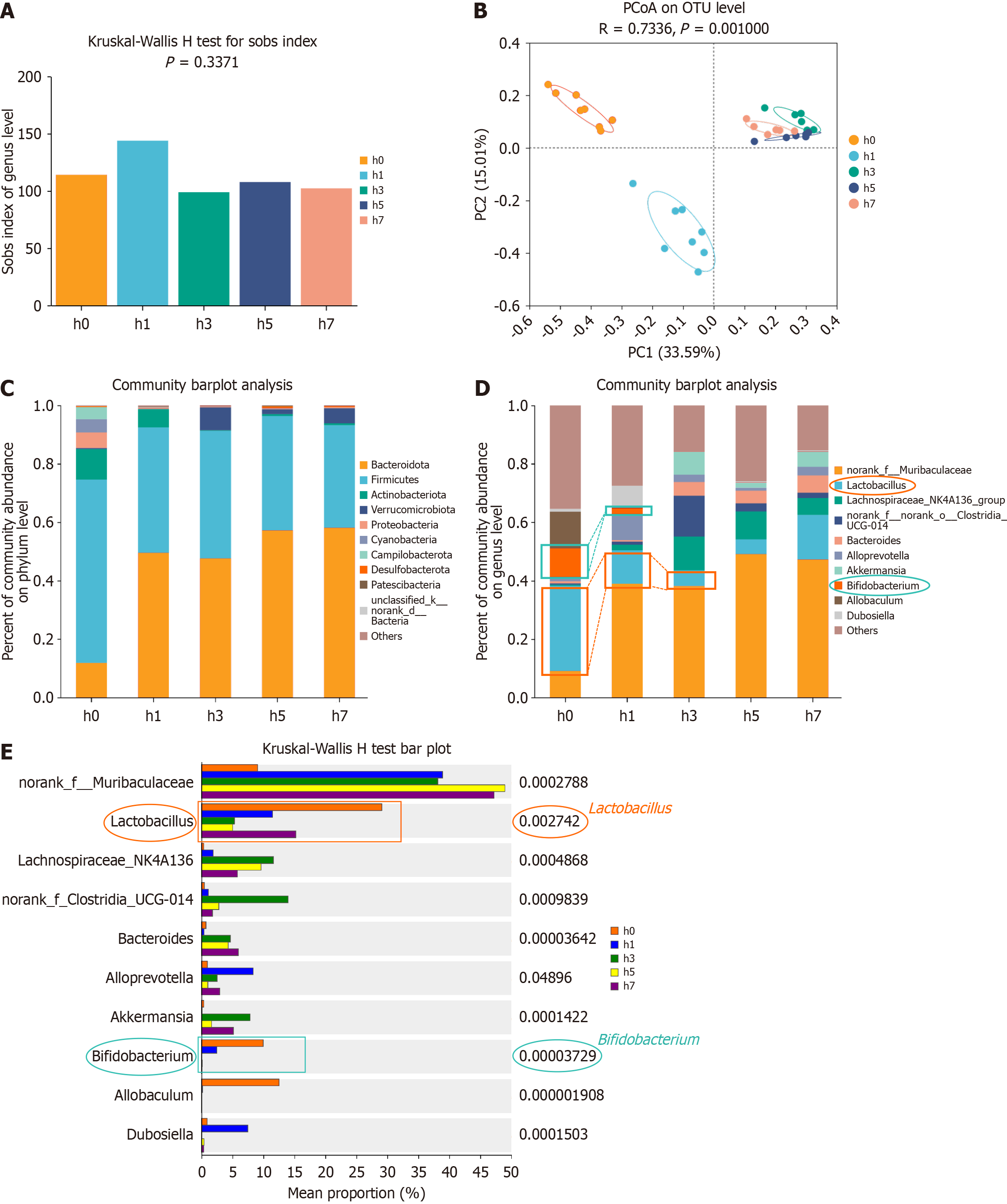
Figure 6 Hypobaric hypoxia exposure leads to changes in the fecal microbiota.
A: Α-diversity is represented by the Sobs index for fecal flora samples in each group; B: Principal coordinate analysis was performed, and statistical significance between groups was evaluated using PERMANOVA for fecal flora samples in each group; C: Richness of fecal flora in each group at the phylum level; D: Richness of fecal flora in each group at the genus level; E: Differences in microbial communities among groups were assessed using a multigroup comparison of species composition. PCoA: Principal coordinate analysis; OTU: Operational taxonomic unit.
- Citation: Chang WY, Qin QZ, Li XT, Wang JJ, Chen Y, Ruan HQ, Qu YN, Jiang XX, He HX. Modulating oral microbiota ameliorates hypobaric hypoxia-induced anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in mice. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(6): 104809
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i6/104809.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i6.104809