Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Jun 19, 2025; 15(6): 104809
Published online Jun 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i6.104809
Published online Jun 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i6.104809
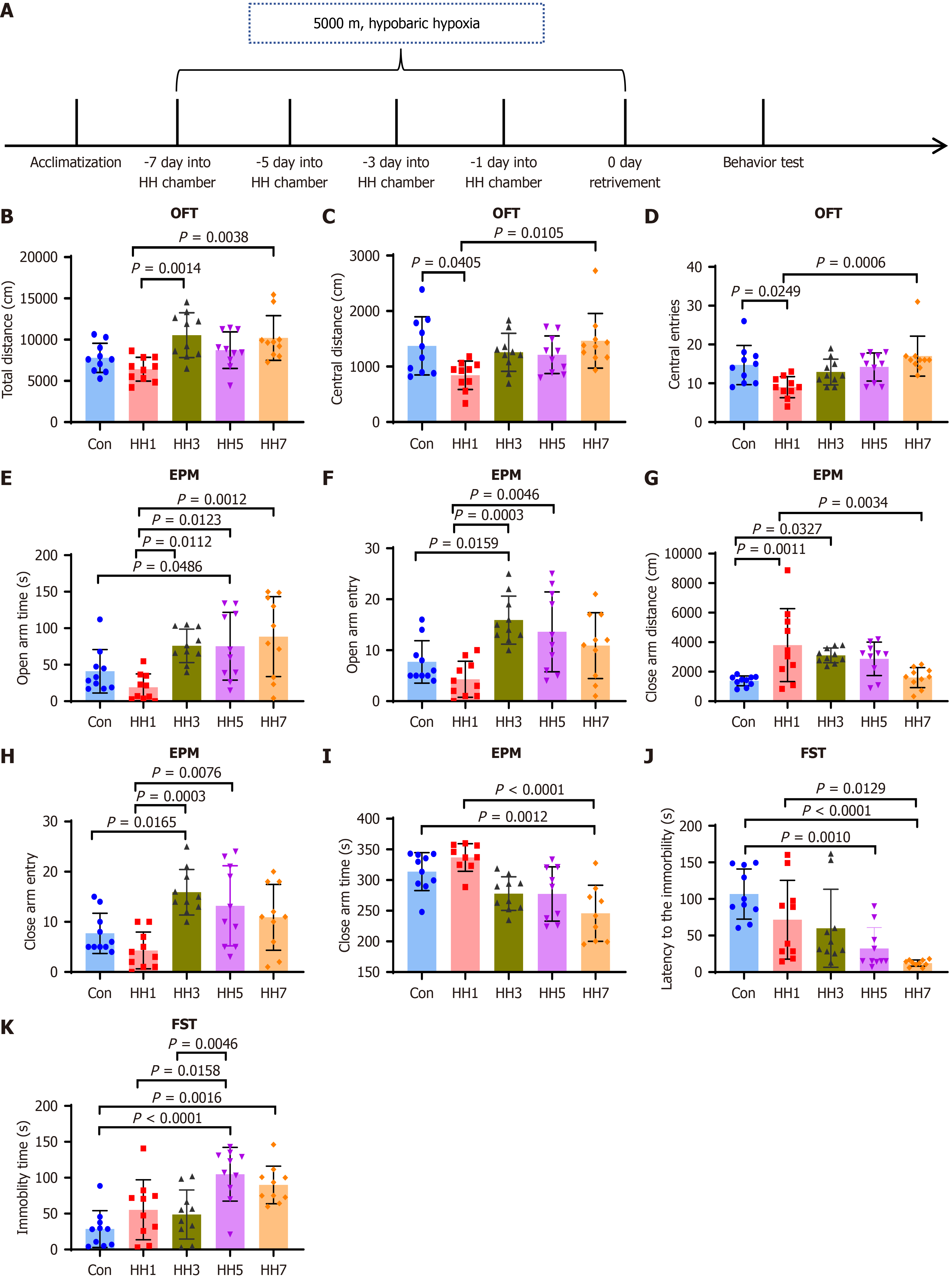
Figure 2 Effects of hypobaric hypoxia exposure on anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in mice.
A: Paradigm of hypobaric hypoxia exposure for 0, 1, 3, 5, and 7 days; B-D: Total distance, central distance, and number of entries into the central zone for each group in the open field test (n = 10); E-I: Time spent in the open arm, number of entries into the open arm, distance traveled in the close arm, number of entries into the close arm, and time spent in the close arm for each group in the elevated plus maze test (n = 10); J: Immobility latency for each group in the forced swim test (n = 10); K: Immobility time for each group in the forced swim test (n = 10). aP ≤ 0.05, bP ≤ 0.01, cP ≤ 0.001, dP ≤ 0.0001. HH: Hypobaric hypoxia; OFT: Open field test; EPM: Elevated plus maze; FST: Forced swim test; Con: Control group; HH1: One day of hypobaric hypoxia exposure; HH3: Three days of hypobaric hypoxia exposure; HH5: Five days of hypobaric hypoxia exposure; HH7: Seven days of hypobaric hypoxia exposure.
- Citation: Chang WY, Qin QZ, Li XT, Wang JJ, Chen Y, Ruan HQ, Qu YN, Jiang XX, He HX. Modulating oral microbiota ameliorates hypobaric hypoxia-induced anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in mice. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(6): 104809
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i6/104809.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i6.104809