Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Jun 24, 2025; 16(6): 105996
Published online Jun 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i6.105996
Published online Jun 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i6.105996
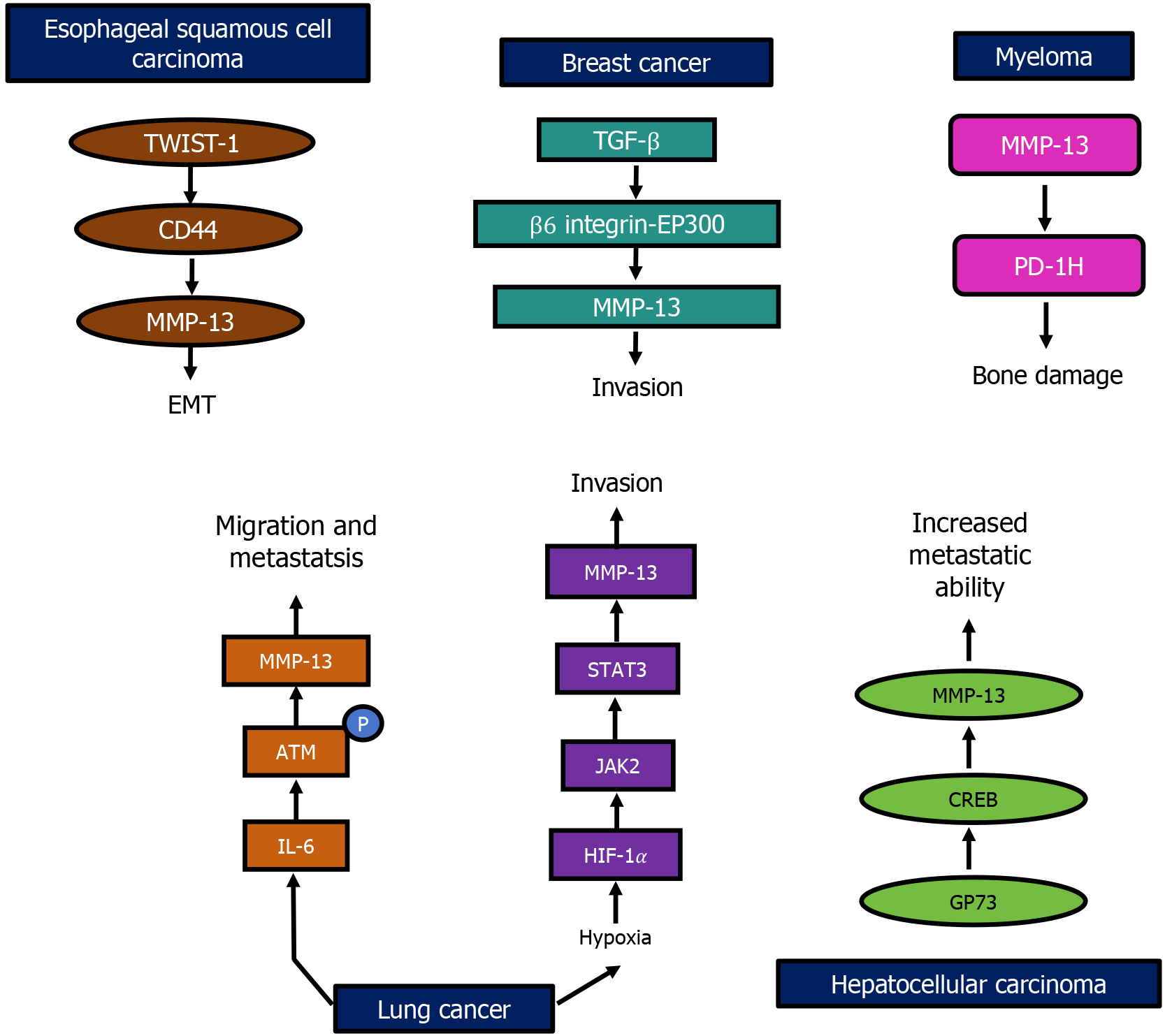
Figure 3 Matrix metalloproteinase-13-mediated cancer progression.
The overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) has been associated with increased invasion, migration, and metastasis in different types of cancer. In breast cancer, transforming growth factor-β/β6 integrin-histone acetyltransferase p300/MMP-13 axis increases the invasive potential, and in lung cancer, hypoxia-inducible factor 1/ Janus kinase 2/signal transducers and activators of transcription 3/MMP-13 and interleukin 6/ataxia telangiectasia mutated protein/MMP-13 axes are involved in tumor aggressiveness. Then, the Golgi protein 73/cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein/MMP-13 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma further accelerates metastasis. TWIST 1: Twist family basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor 1; MMP-13: Matrix metalloproteinase-13; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; EP-300: Histone acetyltransferase p300; PD-1H: Programmed death-1 homolog; ATM: Ataxia telangiectasia mutated protein; EMT: Epithelial mesenchymal transition; IL-6: Interleukin 6; HIF-1: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1; JAK2: Janus kinase 2; STAT3: Signal transducers and activators of transcription 3; GP73: Golgi protein 73; CREB: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein.
- Citation: Chidambaram D, Subashini V, Nanthanalaxmi M, Saranya I, Selvamurugan N. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in cancer: Signaling pathways and non-coding RNAs in tumor progression and therapeutic targeting. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(6): 105996
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i6/105996.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i6.105996