Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Biol Chem. Nov 26, 2015; 6(4): 290-300
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.290
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.290
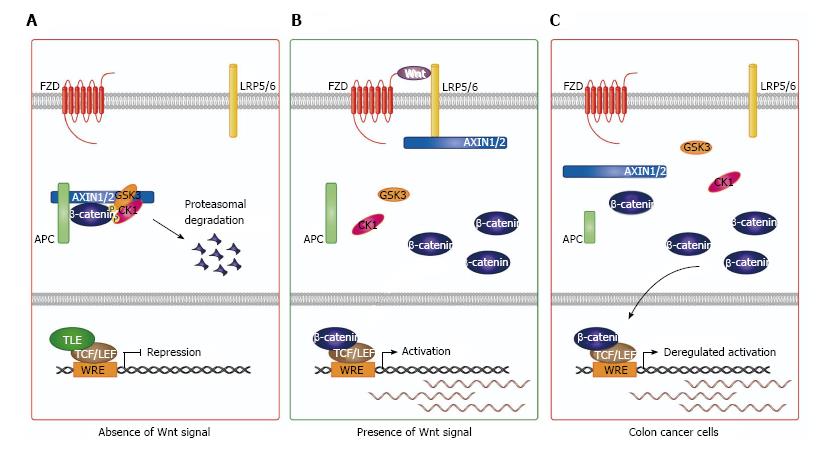
Figure 1 The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
A: In the absence of a Wnt ligand, cytoplasmic β-catenin is targeted for proteasomal degradation by a multi-protein “destruction complex”. Within the nucleus, TCF/Lef at WREs associates with the TLE co-repressor to repress Wnt/β-catenin target gene expression; B: Upon Wnt ligand binding to the FZD and LRP5/6 co-receptor complex, AXIN1/2 is recruited to the plasma membrane and the destruction complex is inactivated. β-Catenin subsequently translocates to the nucleus where it binds TCF/Lef assembled at WREs and recruits co-activator complexes to activate Wnt/β-catenin target gene expression; C: In CRCs, truncations of the APC protein prevent efficient targeting of β-catenin for proteasomal degradation. Therefore, nuclear β-catenin levels are elevated and aberrantly associate with TCF/Lef at WREs to drive deregulated expression of Wnt/β-catenin target genes. WRE: Wnt responsive DNA element; TCF/Lef: T-cell factor/Lymphoid enhancer factor; TLE: Transducin-like enhancer; FZD: Frizzled; LRP5/6: Lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 or 6; AXIN1/2: Axis inhibition proteins 1 and/or 2; CRC: Colorectal cancer; APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; GSK3: Glycogen synthase kinase three; CK1: Casein kinase 1.
-
Citation: Rennoll S, Yochum G. Regulation of
MYC gene expression by aberrant Wnt/β-catenin signaling in colorectal cancer. World J Biol Chem 2015; 6(4): 290-300 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v6/i4/290.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.290