Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. Jul 26, 2010; 1(7): 209-220
Published online Jul 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i7.209
Published online Jul 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i7.209
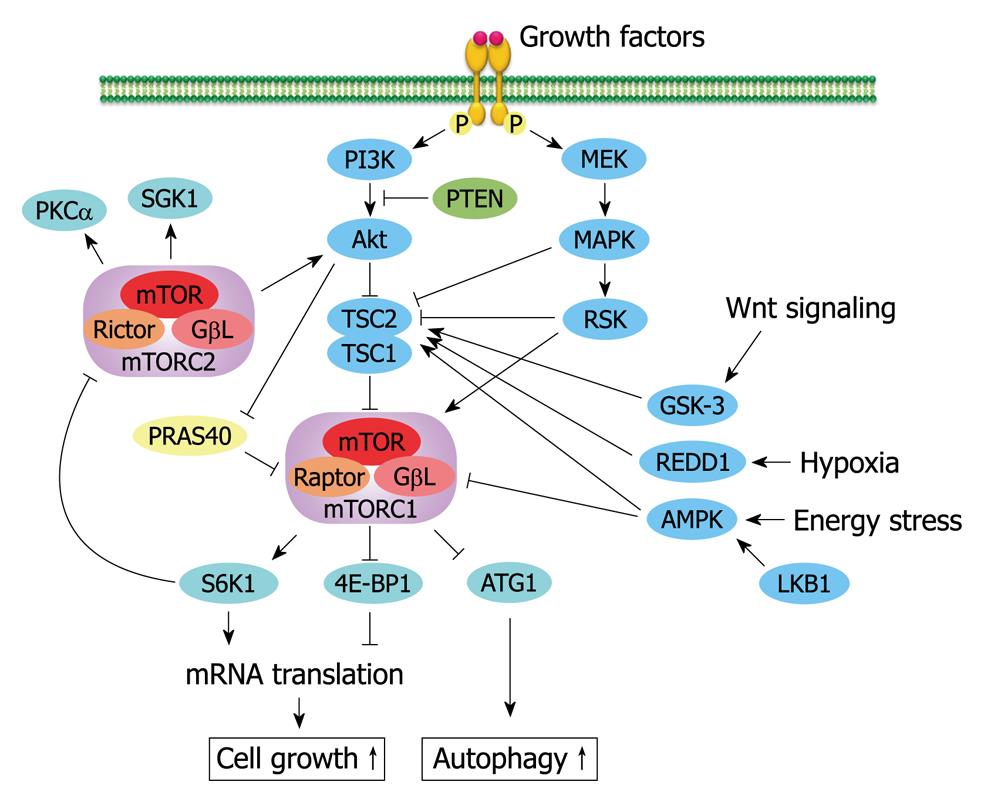
Figure 5 Key regulators of the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway.
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) forms the catalytic core of two functionally distinct complexes, mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) and mTORC2. Diverse environmental factors, including growth factors (e.g. insulin, insulin-like growth factor 1 and epidermal growth factor) and stresses (e.g. hypoxia or energy) promote mTORC1-dependent cell growth and down-regulate autophagy. The negative feedback loop signals of mTORC1/p70-S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) suppress the mTORC2/Akt signaling pathway. PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted from chromosome 10; TSC: Tuberous sclerosis complex; Raptor: Regulatory-associated protein of mTOR; Rictor: Rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; RSK: Ribosomal s6 kinase; PRAS40: Proline-rich PKB/Akt substrate of 40 kDa; ATG1: Autophagy-related gene 1; PKCα: Protein kinase C α; SGK1: Serine/threonine-protein kinase 1; GSK-3: Glycogen synthase kinase 3; REDD1: Regulated in development and DNA damage responses 1; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; LKB1: Liver kinase B1; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-kinase; P: Phosphate.
- Citation: Itamochi H. Targeted therapies in epithelial ovarian cancer: Molecular mechanisms of action. World J Biol Chem 2010; 1(7): 209-220
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v1/i7/209.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v1.i7.209