Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2017; 8(2): 151-162
Published online May 26, 2017. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v8.i2.151
Published online May 26, 2017. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v8.i2.151
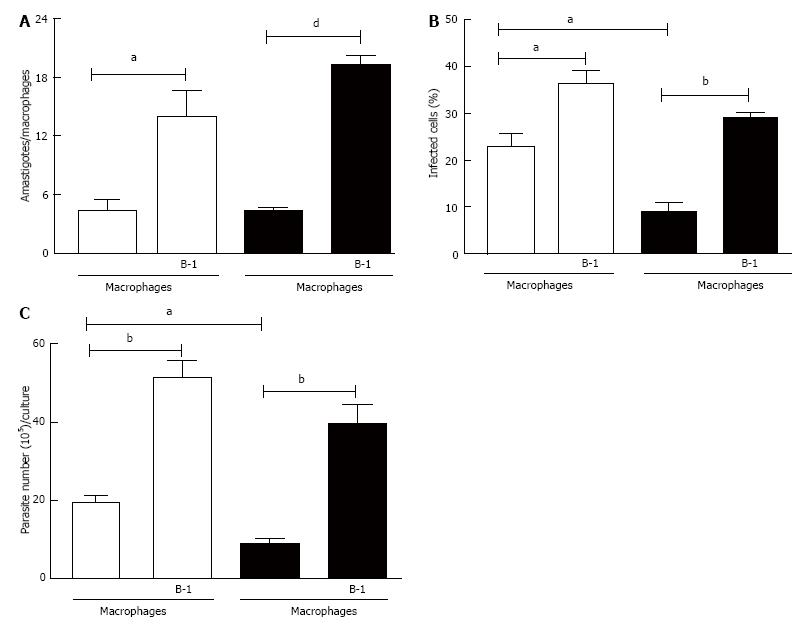
Figure 1 Effect of B-1 cells co-cultured with macrophages infected with Leishmania major.
B-1 cells and peritoneal macrophages from BALB/c mice (white bars) or XID mice (black bars) were cultured (105/well) and infected with metacyclic promastigotes of L. major. After 24 h, the cell culture was washed and phagocytes were cultured for another 3 d with DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS at 37 °C. After this period, cells were stained and amastigotes inside the phagocytes were counted under the light microscope (A) and set the percentage of infected cells (B). To quantify promastigotes forms in the supernatants, the cells were cultures and infected with L. major. After 24 h of infection, so were washed and cultured at a temperature of 27 °C in Schneider medium 20% FBS during 5 d. After this period, the promastigotes were quantified in the supernatant of the cultures of infected phagocytes (C). All cultures were performed in triplicate and bars show the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis were performed by t-test from representative results of three different experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.005 and dP < 0.0001.
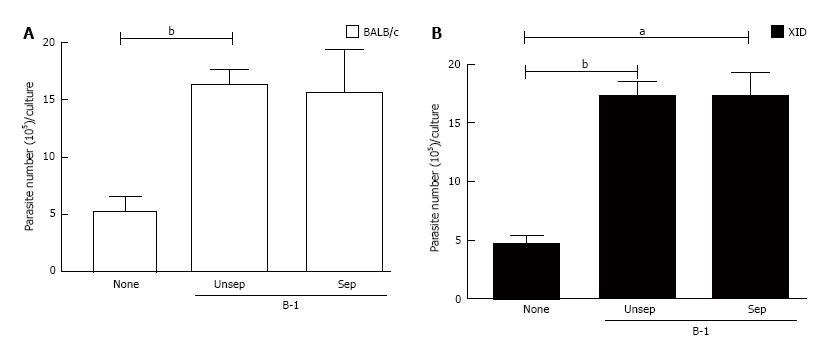
Figure 2 The immunomodulatory effect of co-cultured infected macrophages and B-1 cells is independent of contact.
Peritoneal macrophages from BALB/c (A) and XID (B) mice were plated in 24 wells vessels at 105 cells/well in complete culture medium and infected with L. major (106/well). After 24 h of infection, cells were washed and B-1 cells were added at same compartment (Unsep), or separated (Sep) by a cell-impermeable culture insert. The cells were cultured in Schneider medium for 5 d at a temperature of 27 °C. After this period, the promastigotes were quantified in the supernatant of the cultures of infected phagocytes. All cultures were performed in triplicate and bars show the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis were performed by t-test from representative results of three different experiments. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.005.
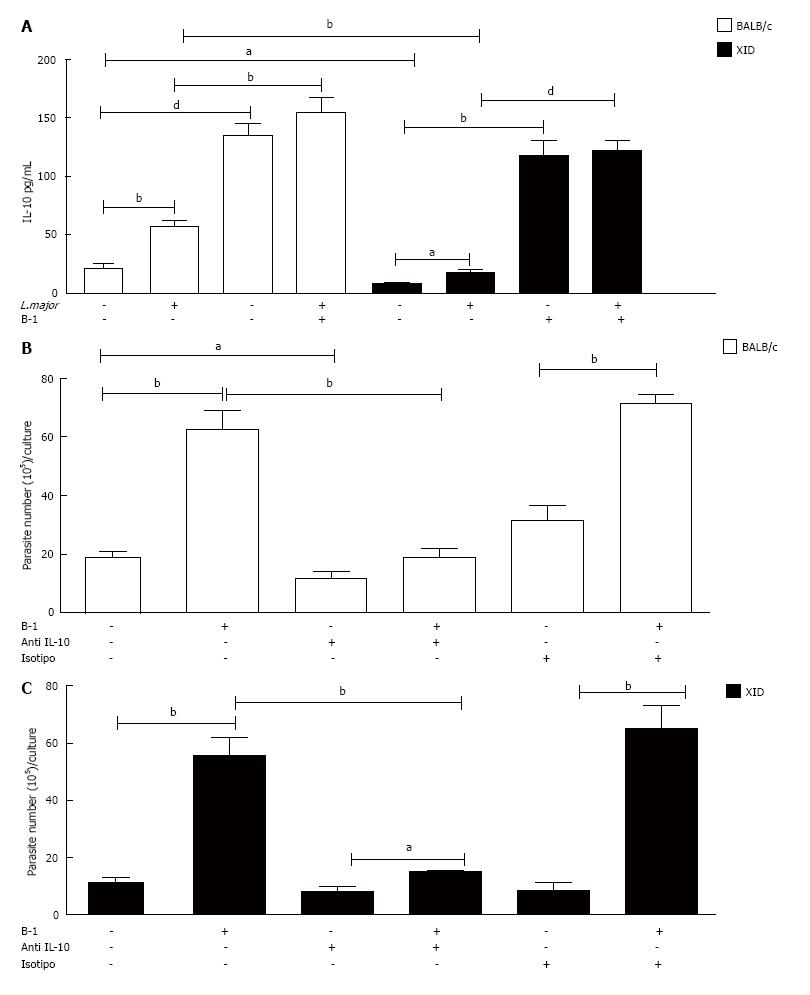
Figure 3 Interleukin-10 is a determinant factor for the increased parasite load in macrophages.
Peritoneal macrophages from BALB/c or XID mice co-cultured with B-1 cells were cultured in the presence or absence of L. major (MOI 10:1). After 24 h, the supernatant was collected and IL-10 was measured by ELISA (A). All cultures were performed in triplicate and bars show the mean ± SD. Representative result of three different experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.005 and dP < 0.0001. Co-cultures of B-1 cells and infected macrophages from BALB/c or XID mice were treated or not with doses of monoclonal neutralizing anti-IL-10 or control isotype. Once were infected with L. major, after 24 h, the cell cultures were washed with DMEM and incubated 3 d and then passed to Schneider medium. After 5 d in medium Schneider, promastigotes were counted in the supernatant (B). Statistical analysis were performed by t-test from representative results of three different experiments and bars show the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.005.
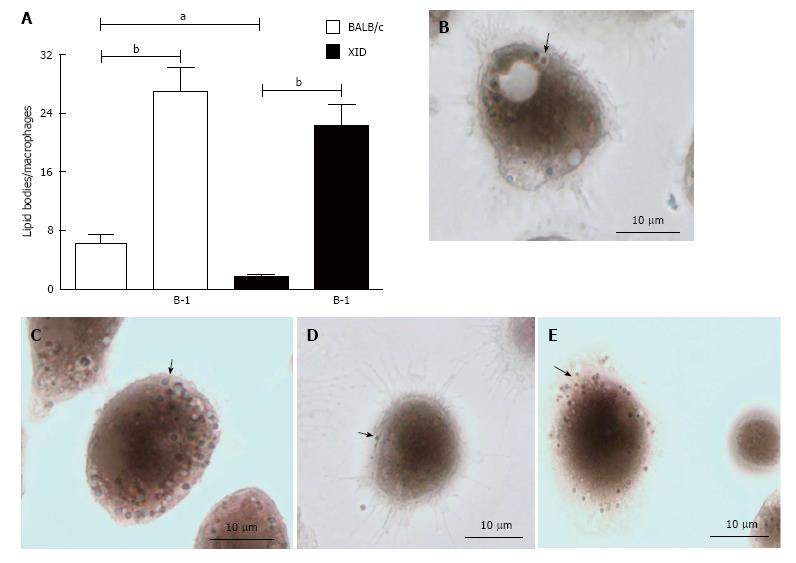
Figure 4 Presence of B-1 cells increased numbers of lipid bodies in infected macrophages.
Peritoneal macrophages from BALB/c or XID mice were incubated with glass coverslips; some cultures were infected with L. major. Stained with Osmium tetroxide, the slides were washed and stained with DAPI (Sigma). The morphology of fixed cells was observed, and Nile red LBs were counted by light microscopy with a 100 × objective lens in 50 consecutively scanned leukocytes (A). Representative images of lipid body formation in infected macrophages from BALB/c mice (B), infected macrophages from BALB/c mice cultured in the presence of B-1 cells (C), infected macrophages from XID mice (D) and infected macrophages from XID mice co-cultured with B-1 cells (E). Black arrows pointing to the LB. Statistical analysis were performed by t-test from representative results of three different experiments. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.005.
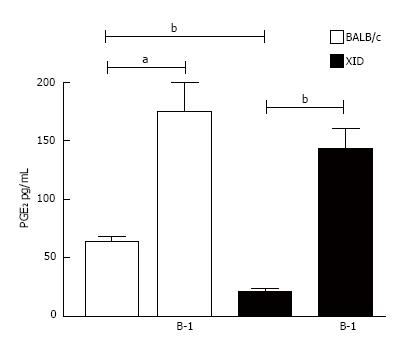
Figure 5 Infected macrophages co-cultured with B-1 cells secret high levels of prostaglandin E2.
Infected macrophages from BALB/c or XID mice were incubated in the presence or absence of L. major (MOI 10:1). After 24 h of infection the supernatant was collected, and B-1 cells were added to the culture. After 24 h the level of PGE2 secreted was measured by EIA. All cultures were performed in triplicate and bars show the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis were performed by t-test from representative results of three different experiments and bars show the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.005.
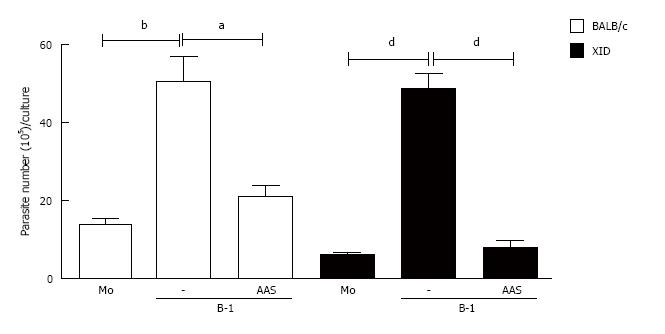
Figure 6 Blockage of the cyclooxygenase pathway induces protective phenotype in the Leishmania major infection.
Infected macrophages from BALB/c or XID mice macrophages were incubated in the presence or absence of L. major, 24 h after the cellular cultures were washed and B-1 cells were added. The co-culture was treated or not with aspirin (AAS) (10 mg/mL). After 24 h of incubation, the cells were washed and incubated again for 3 d. After this time, the promastigotes were counted in the culture supernatant. All cultures were performed in triplicate and bars show the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis were performed by t-test from representative results of three different experiments and bars show the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.005 and dP < 0.0001.
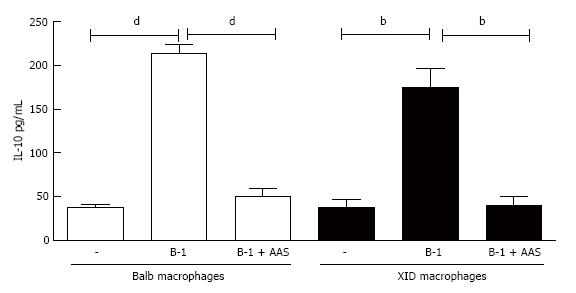
Figure 7 Effect of prostaglandin E2 inhibition on interleukin-10 production.
Infected peritoneal macrophages from BALB/c or XID mice were co-cultured with B-1 cells and incubated with or without aspirin (AAS) (10 μg/mL). After 24 h of incubation, the supernatant was collected and interleukin-10 measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. All cultures were performed in triplicate and bars show the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis were performed by t-test from representative results of three different experiments and bars show the mean ± SD. bP < 0.005 and dP < 0.0001.
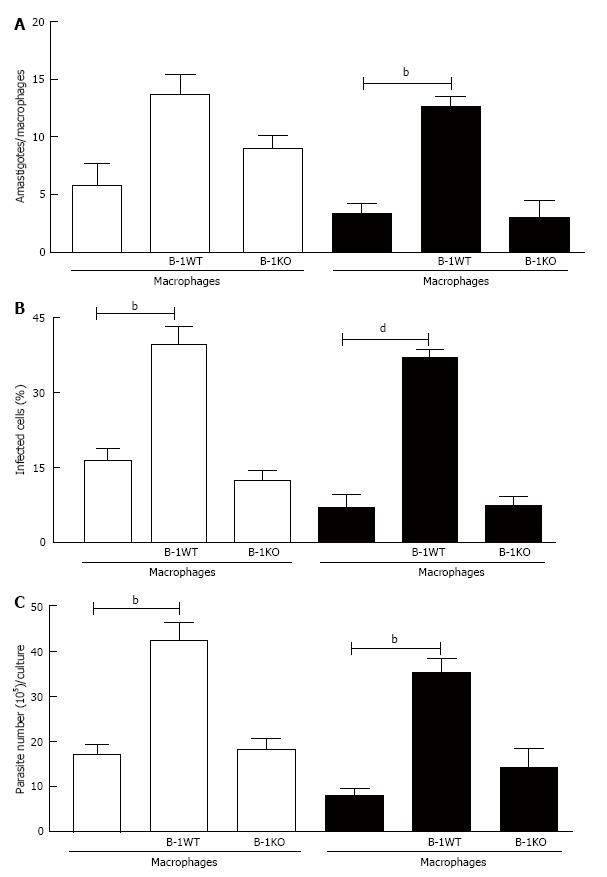
Figure 8 B-1 cells from interleukin-10 deficient mice are more competent to control Leishmania major infection in macrophages.
To confirm the production of IL-10 is involved in the susceptibility to infection by L. major, we used B-1 cells from BALB/c (white bars) and from IL-10 KO mice (black bars). Our data demonstrate decreased in the number of intracellular amastigotes (A) and percentage of infected cells (B). We also observed the significant decrease in the liberated promastigotes forms by infected macrophages co-cultured with B-1 cells from IL-10 KO mice (C). Statistical analysis was performed by t-test from representative results of three different experiments and bars show the mean ± SD. bP < 0.005 and dP < 0.0001.
- Citation: Arcanjo AF, Nunes MP, Silva-Junior EB, Leandro M, Rocha JDBD, Morrot A, Decote-Ricardo D, Freire-de-Lima CG. B-1 cells modulate the murine macrophage response to Leishmania major infection. World J Biol Chem 2017; 8(2): 151-162
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v8/i2/151.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v8.i2.151