Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Biol Chem. Nov 26, 2015; 6(4): 324-332
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.324
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.324
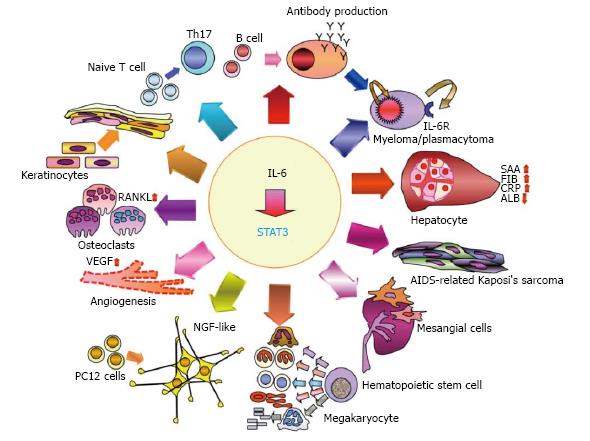
Figure 1 Interleukin 6 modulates a variety of physiological events, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, and apoptosis, through signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
IL-6-STAT3 axis plays roles in the immune, the endocrine, the nervous and the hematopoietic systems, and on bone metabolism. IL-6 has been implicated in the pathology of different diseases including multiple myeloma, rheumatoid arthritis, Castleman’s disease, AIDS, mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis, psoriasis, Kaposi’s sarcoma, sepsis and osteoporosis. SAA: Serum amyloid A; FIB: Fibrinogen; ALB: Albumin; CRP: C-reactive protein; NGF: Nerve growth factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; RANKL: Receptor activator of NF-κB ligand; Th17: T helper type 17; IL-6: Interleukin 6; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; AIDS: Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
- Citation: Matsuda T, Muromoto R, Sekine Y, Togi S, Kitai Y, Kon S, Oritani K. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 regulation by novel binding partners. World J Biol Chem 2015; 6(4): 324-332
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v6/i4/324.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.324