Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Biol Chem. Nov 26, 2015; 6(4): 281-289
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.281
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.281
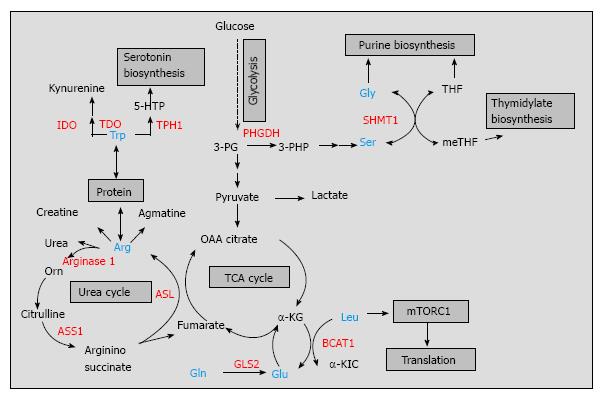
Figure 1 Schematic representation of amino acid metabolic pathways targeted in cancer therapy.
The amino acid metabolism of Arg, Trp, Ser, Gly, Gln, Glu, and BCAAs interconnects with major catabolic and biosynthetic pathways shown in gray. Arg is an important precursor for creatine, urea, and agmatine synthesis while Trp is important for kynurenine and serotonin biosynthesis; Ser and Gly are major sources of methyl groups during purine and thymidylate biosynthesis; Leu is a known activator of complex 1 of mTOR pathway and Gln/Glu provide intermediates for the TCA cycle and restore glutathione to its reduced form. Metabolic enzymes catalyzing important steps in the metabolism of these amino acids are involved in clinical and/or preclinical cancer studies and are denoted in red. 5-HTP: 5-hydroxytrytophan; 3-PG: 3-phosphoglycerate; 3-PHP: 3-phosphohydroxy pyruvate; THF: Tetrahydrofolate; meTHF: Methyltetrahydrofolate; OAA: Oxaloacetate; α-KG: α-ketoglutarate; α-KIC: α-ketoisocaproate; Trp: Tryptophan; Arg: Arginine; Gln: Glutamine; Glu: Glutamate; BCAAs: Branched chain amino acids; Ser: Serine; Gly: Glycine; mTORC1: Complex 1 of the mammalian target of rapamycin; IDO: Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase; TDO: Tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase; TPH1: Tryptophan hydroxylase-1; BCATc: Cytosolic branched chain aminotransferase; ASS1: Argininosuccinate synthetase 1; ASL: Argininosuccinate lyase; GLS2: Glutaminase 2; PHGDH: Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase; SHMT1: Serine hydroxymethyl transferase 1.
- Citation: Ananieva E. Targeting amino acid metabolism in cancer growth and anti-tumor immune response. World J Biol Chem 2015; 6(4): 281-289
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v6/i4/281.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.281