Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jul 27, 2025; 17(7): 106672
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i7.106672
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i7.106672
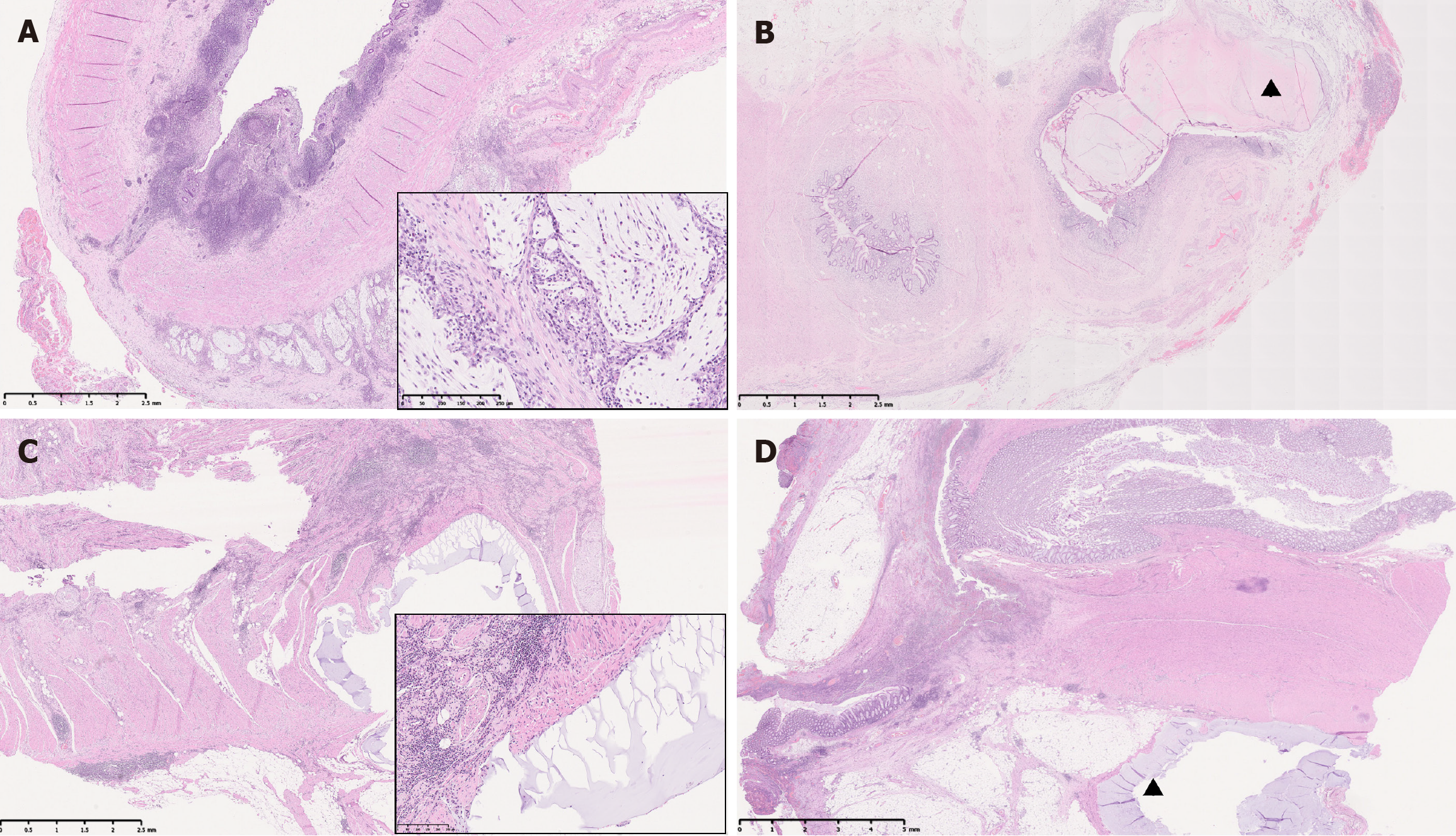
Figure 2 Acellular mucin in non-neoplastic conditions.
A: Interval appendectomy with subserosal acellular mucin mixed with inflammatory cells [hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)], inset: Higher magnification view of acellular mucin pools; B: Appendiceal diverticular disease with luminal acellular mucin (triangle) in the diverticulum (H&E); C: Ileum with acellular mucin pool at previous anastomosis site in a patient with Crohn’s disease (H&E), inset: Higher magnification view of acellular mucin pool; D: Acellular mucin pool (triangle) at previous diverticular pouch in colonic diverticulitis (H&E).
- Citation: Darwish N, Guo L, Park E, Lee H. Acellular mucin in neoplastic and non-neoplastic conditions of the lower gastrointestinal tract. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(7): 106672
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i7/106672.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i7.106672