Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jun 27, 2025; 17(6): 106155
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i6.106155
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i6.106155
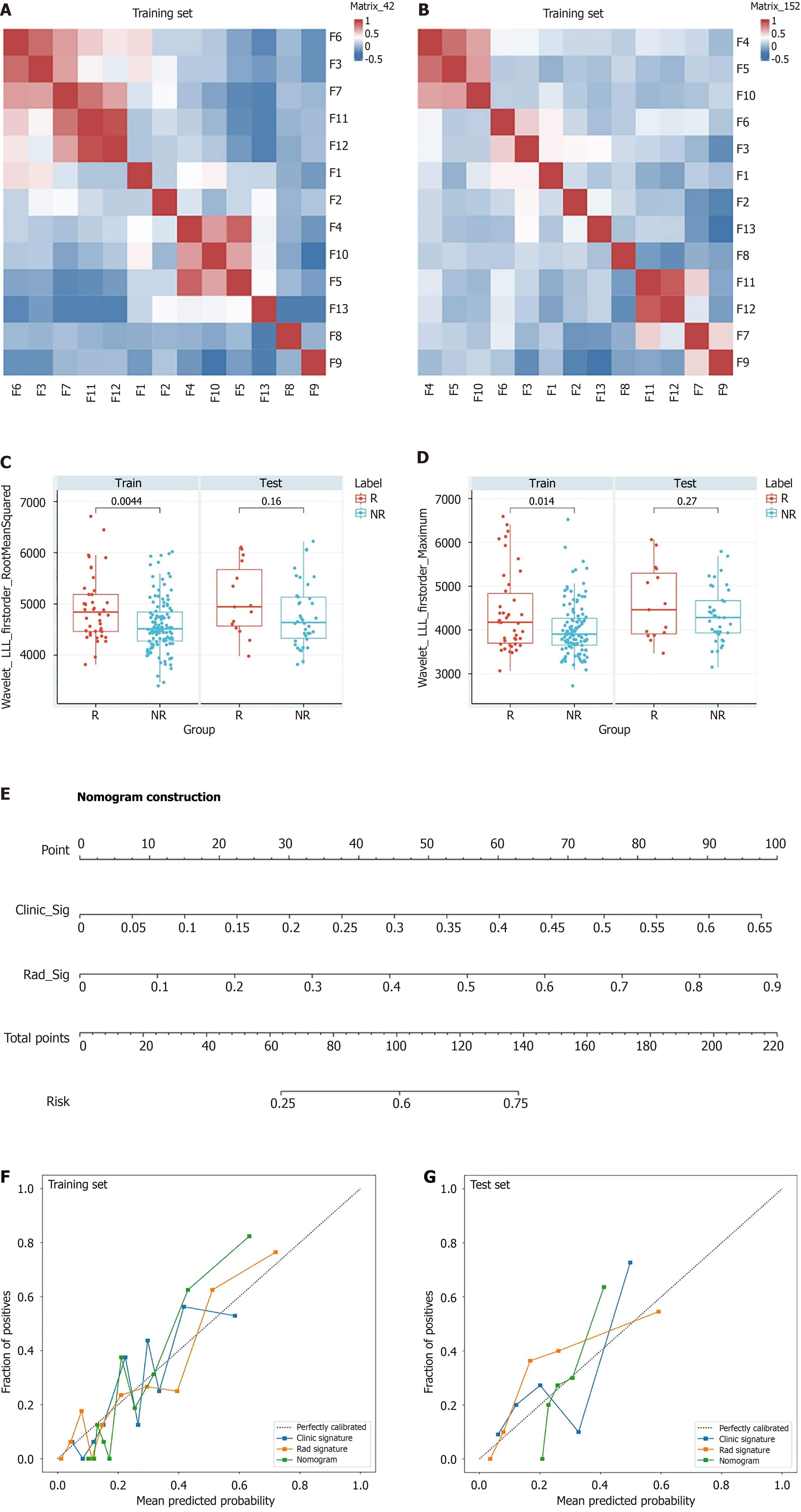
Figure 3 A nomogram based on Rad-score and clinical indicators for predicting bowel resection risk in patients with incarcerated inguinal hernia.
A and B: Heatmaps illustrating the distribution of the 13 selected radiomic features in both cohorts; C and D: Box plots of the most significantly different radiomic features in the training and test cohorts; E: Construction of the radiomic-clinical nomogram; F and G: Calibration curves for the radiomic nomogram in the training and test sets. R: Bowel resection group; NR: Non-bowel resection group.
- Citation: Li DL, Zhu L, Liu SL, Wang ZB, Liu JN, Zhou XM, Hu JL, Liu RQ. Machine learning-based radiomic nomogram from unenhanced computed tomography and clinical data predicts bowel resection in incarcerated inguinal hernia. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(6): 106155
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i6/106155.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i6.106155