Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Mar 27, 2024; 16(3): 882-892
Published online Mar 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i3.882
Published online Mar 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i3.882
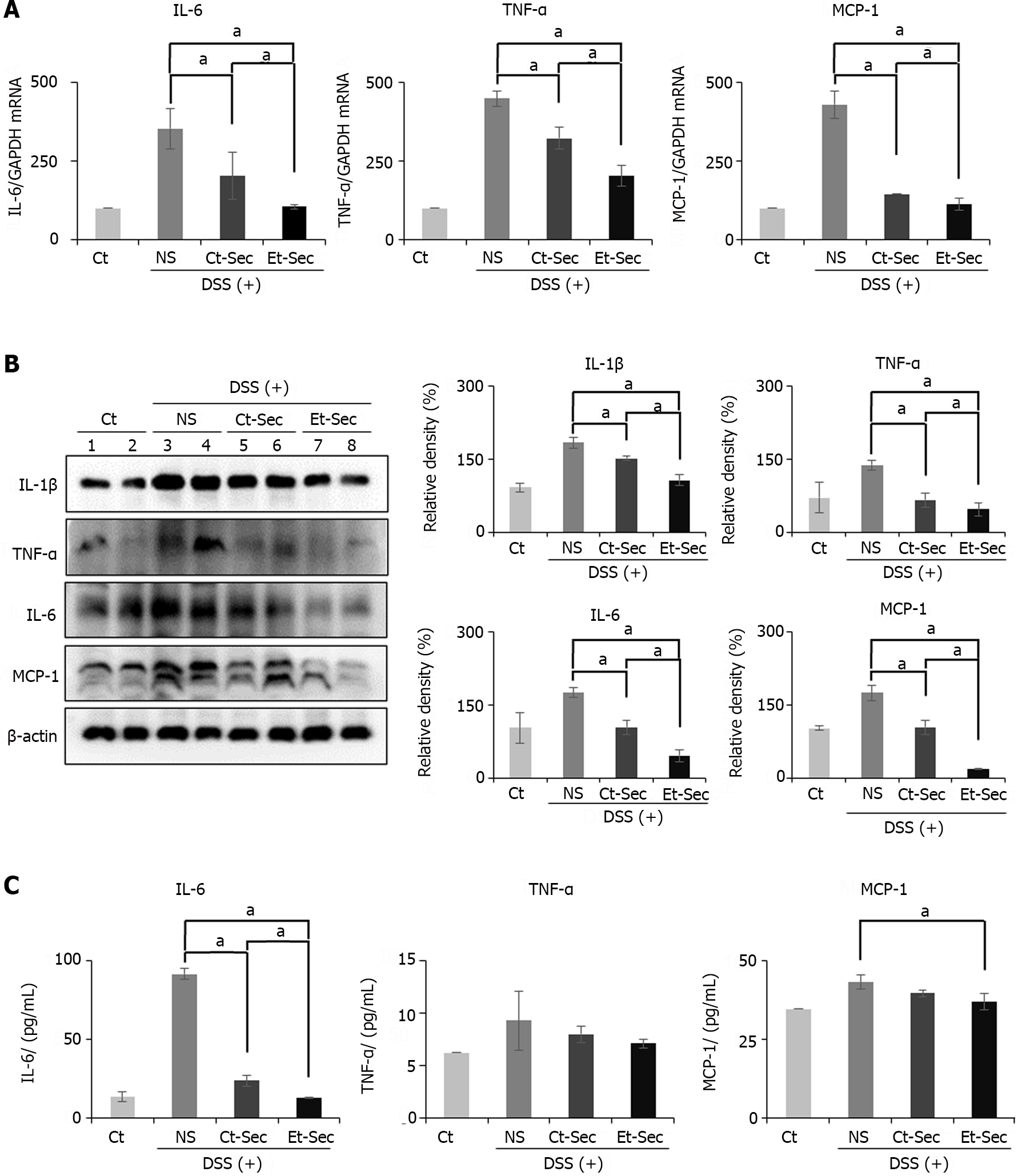
Figure 3 Determination of in vivo anti-inflammatory effects of etanercept-secretome.
A: Realtime polymerase chain reaction of inflammatory markers. Secretome-treated groups [control-secretome (Ct-Sec) and etanercept-secretome (Et-Sec)] showed reduced expression compared to normal saline (NS) (P < 0.05). Et-Sec group exhibited a more significant reduction than Ct-Sec group (P < 0.05); B: Western Blot Analysis of inflammatory markers. The Secretome-treated groups (Ct-Sec and Et-Sec) demonstrated reduced expression compared to NS (Ps < 0.05), with the Et-Sec group exhibiting a more significant reduction than the Ct-Sec group (P < 0.05); C: ELISA determing the levels of serum inflammatory markers. The Et-Sec group exhibited the most significant reduction in serum interleukin-6 and monocyte chemoattactant protein-1 levels in the inflammatory bowel disease mouse model (P < 0.05). Relative densities of individual markers had been quantified using Image J software and then were normalized to that of β-actin in each group. Values are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05. Et-Sec: Etanercept-secretome; Ct-Sec: Control-secretome; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; TNF: Tumor necreosis factor; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattactant protein-1; IL: Interleukin; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; DSS-treated group: Dextran sulfate sodium-treated group; ASCs: Adipose-derived stem cells; Ct: Control group; NS: Normal saline.
- Citation: Kim SJ, Kim OH, Hong HE, Ju JH, Lee DS. Etanercept-synthesizing adipose-derived stem cell secretome: A promising therapeutic option for inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(3): 882-892
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i3/882.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i3.882