Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jan 27, 2024; 16(1): 13-20
Published online Jan 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i1.13
Published online Jan 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i1.13
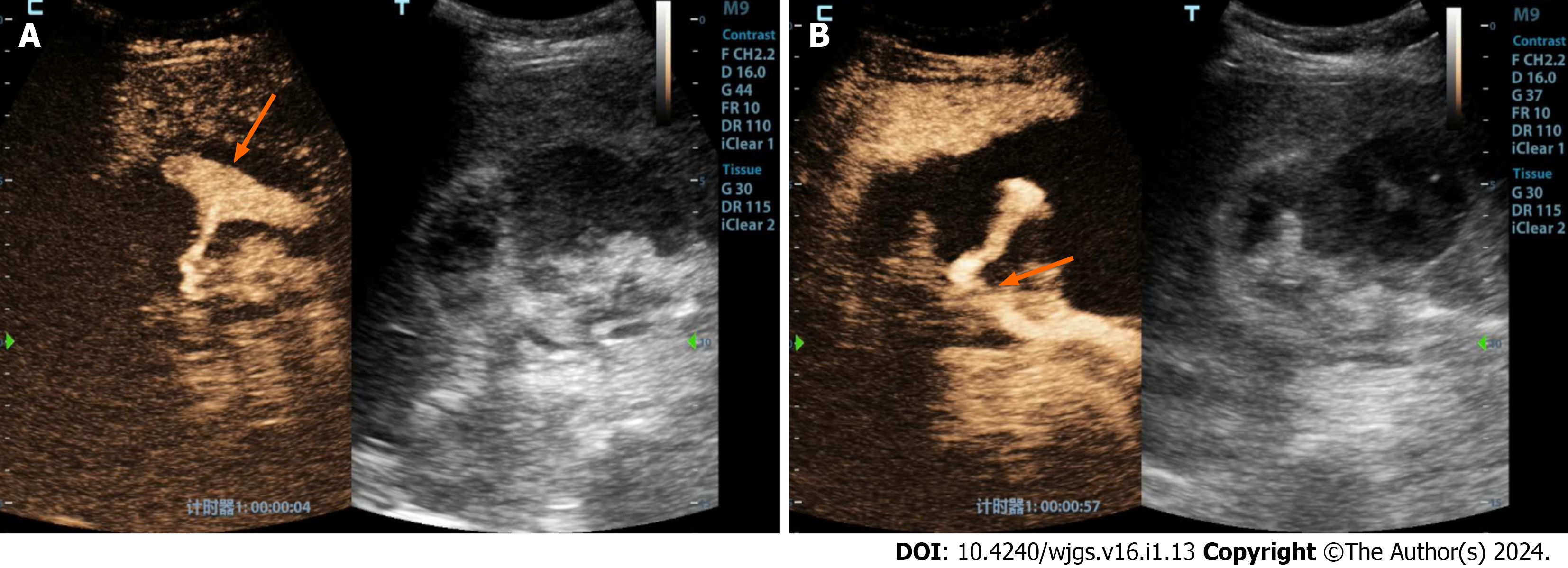
Figure 4 A 48-year-old female patient underwent a piggyback liver transplantation procedure due to decompensated cirrhosis resulting from hepatitis B.
A: Evaluated 13 d postoperatively, the patient’s clinical history revealed a progressive decline in blood pressure and red blood cell count, accompanied by the accumulation of a significant volume of intraperitoneal fluid. Conventional ultrasound examination demonstrated a substantial accumulation of fluid in the porta hepatis region, characterized by hypoechoic features and the presence of numerous fine, low-level echogenic particles suspended within. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound revealed enhanced contrast agent pooling within the intraperitoneal fluid of the porta hepatis, exhibiting a morphology resembling a mushroom cloud (highlighted by the orange arrow); B: Notably, further tracking of the contrast agent leakage within the porta hepatis area (indicated by the orange arrow) indicated that it originated from the hepatic artery anastomosis site.
- Citation: Zhao NB, Chen Y, Xia R, Tang JB, Zhao D. Prognostic value of ultrasound in early arterial complications post liver transplant. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(1): 13-20
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i1/13.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i1.13