Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Apr 27, 2023; 15(4): 600-620
Published online Apr 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i4.600
Published online Apr 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i4.600
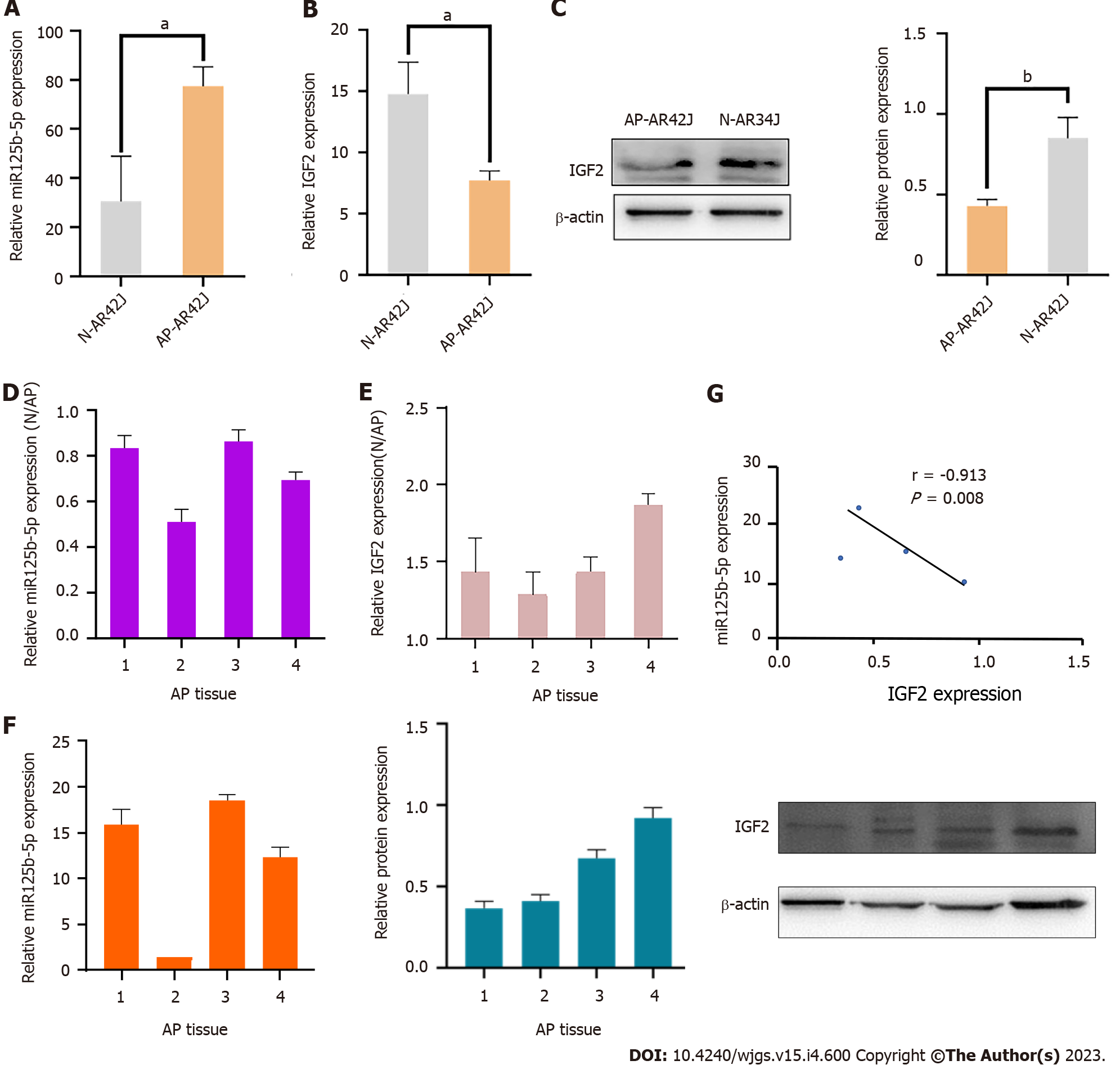
Figure 3 Expression of miR-125b-5p and insulin-like growth factor 2 in vitro and invivo.
A: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to detect the expression of miR-125b-5p in AR42J cell lines in activated and inactive state; B: RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression of insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) in AR42J cell lines under activated and inactive state; C: Western blot was used to detect the expression level of IGF2, and β-actin was used as the internal reference; D: RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression of miR-125b-5p in normal pancreatic tissues and pancreatitis tissues; E: RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression of IGF2 in normal pancreatic tissues and pancreatitis tissues; F: The mRNA and protein expression of miR-125b-5p and IGF2 in 4 cases of pancreatitis tissues were detected by RT-qPCR and Western blot. Among them, sample 2 was used as the standard to calculate the fold change of miR-125b-5p expression in other samples by comparing the miR-125b-5p/U6 ratio in sample 2. Western blot was used to detect the expression level of IGF2, and β-actin was used as the internal reference. The experiment was repeated three times and is expressed as mean ± SD; G: miR-125b-5p was negatively correlated with IGF2 protein expression level, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.005. AP: Acute pancreatitis; IGF2: Insulin-like growth factor 2; N: Normal.
- Citation: Zheng Z, Cao F, Ding YX, Lu JD, Fu YQ, Liu L, Guo YL, Liu S, Sun HC, Cui YQ, Li F. Acinous cell AR42J-derived exosome miR125b-5p promotes acute pancreatitis exacerbation by inhibiting M2 macrophage polarization via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. World J Gastrointest Surg 2023; 15(4): 600-620
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v15/i4/600.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v15.i4.600