Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Oct 27, 2021; 13(10): 1190-1201
Published online Oct 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i10.1190
Published online Oct 27, 2021. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i10.1190
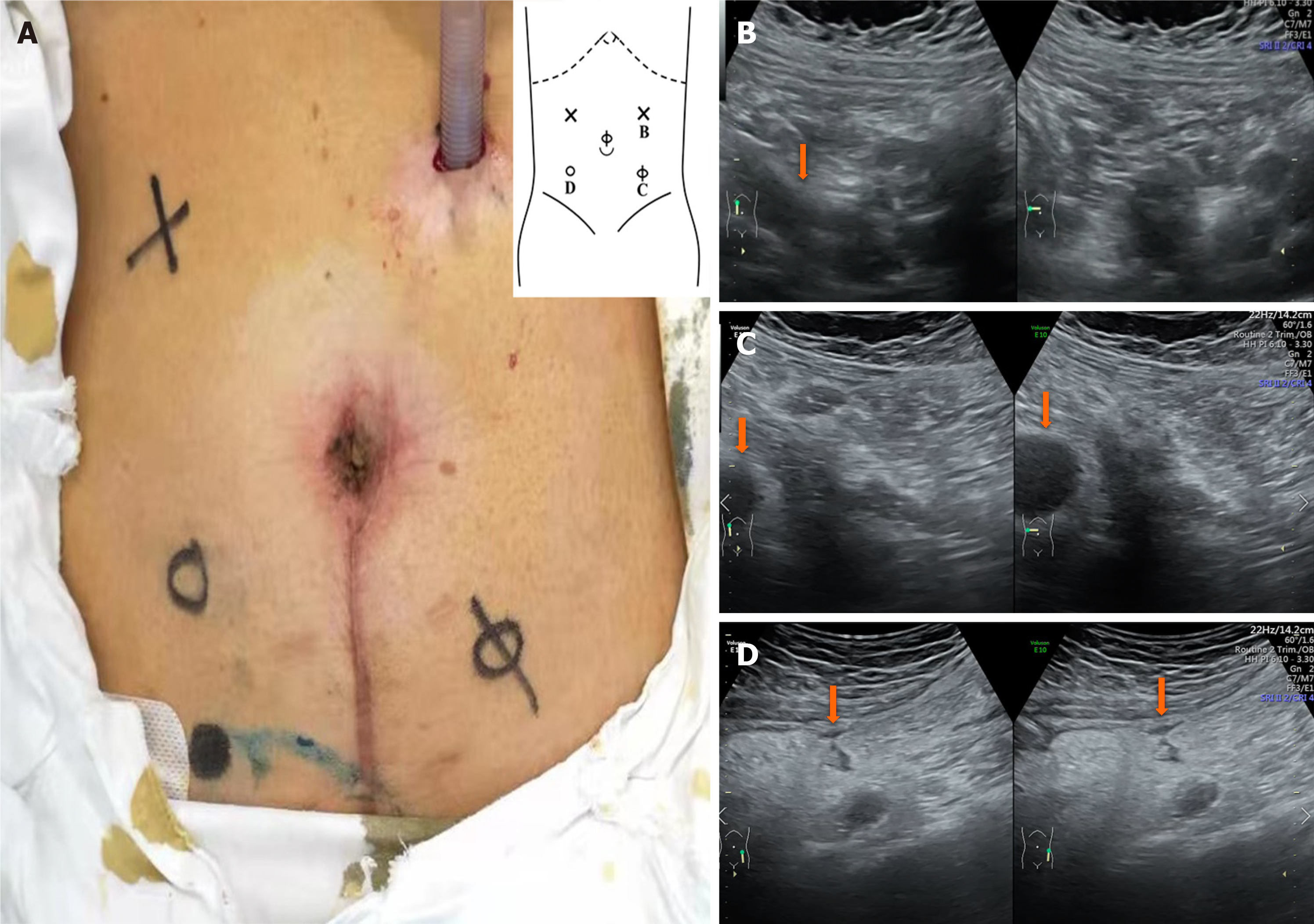
Figure 3 With the changes during respiration, B-ultrasonography was used to examine different areas to determine the activity between the abdominal wall and viscera.
A: The degree of intraperitoneal adhesion is indicated by the annotations "×", "Φ", and "loop". "×" means that the activity is greater than 30 mm, the activity is better in the abdominal cavity, and no adhesion is considered. "Φ" means that the activity is greater than 5 mm, but less than 30 mm, and moderate intraperitoneal activity and moderate adhesion are considered. "loop" means that the activity is less than 5 mm, and severe adhesion is considered; B: In (A), the area denoted "×" in the left upper abdomen is seen under ultrasound. The blood vessels disappear from the screen, as shown in the arrow. Considering that there is no adhesion, it is the first place to puncture; C: In (A), the area denoted "Φ" in the right lower abdomen is seen under ultrasound. The range of intraperitoneal vessels with respiration is shown by the arrow; D: In (A), the area denoted "loop" in the right lower abdomen is seen under ultrasound. The range of intraperitoneal vessels with respiration is shown by the arrow.
- Citation: Wan J, Liu C, Yuan XQ, Yang MQ, Wu XC, Gao RY, Yin L, Chen CQ. Laparoscopy for Crohn's disease: A comprehensive exploration of minimally invasive surgical techniques. World J Gastrointest Surg 2021; 13(10): 1190-1201
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v13/i10/1190.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v13.i10.1190