Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Diabetes. Jul 10, 2016; 7(13): 260-270
Published online Jul 10, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i13.260
Published online Jul 10, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i13.260
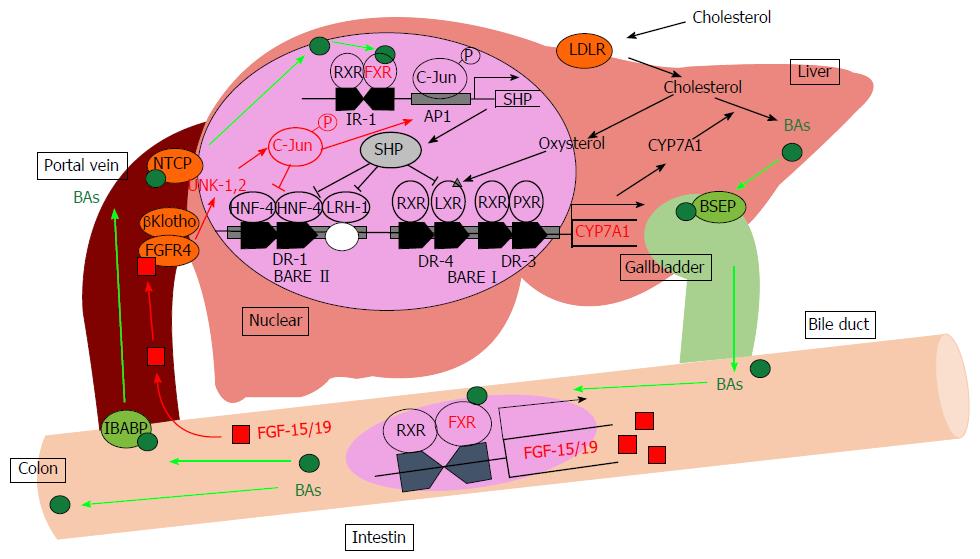
Figure 1 Bile acid metabolism in the liver.
BAs induce the FXR-SHP-mediated pathway and repress BA synthesis enzyme gene expression such as CYP7A1 and CYP8B1. Synthesized BAs increase the expression of FGF-15/19 in the small intestine. FGF-15/19 signaling induces JNK pathway activation resulting in the repression of CYP7A1 transcription. AP1: Activator protein 1; BAs: Bile acids; BARE: Bile acid response element; BSEP: Bile salt export pump; CYP7A1: Cholesterol-7α-hydroxylase; DR: Direct repeat element; FGF-15/19: Fibroblast growth factor-15/19; FGFR4: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4; FXR: Farnesoid X receptor; HNF-4: Hepatocyte nuclear factor; IBABP: Intestinal bile acid-binding protein; IR-1: Inverted repeat element-1; JNK: Jun-N-terminal kinase; LDLR: Low-density lipoprotein receptor; LRH-1: Liver receptor homolog-1; LXR: Liver X receptor; NTCP: Sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide; PXR: Pregnane X receptor; RXR: Retinoid X receptor; SHP: Small heterodimer partner.
- Citation: Taoka H, Yokoyama Y, Morimoto K, Kitamura N, Tanigaki T, Takashina Y, Tsubota K, Watanabe M. Role of bile acids in the regulation of the metabolic pathways. World J Diabetes 2016; 7(13): 260-270
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v7/i13/260.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v7.i13.260